4.6: Results
- Page ID
- 123043
A. Plate Count
1. Choose a plate that appears to have between 30 and 300 colonies.
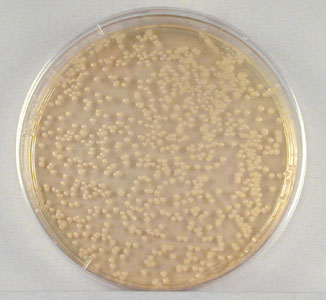
- Sample 1/100,000 dilution plate. (See Fig. \(\PageIndex{1A}\).)
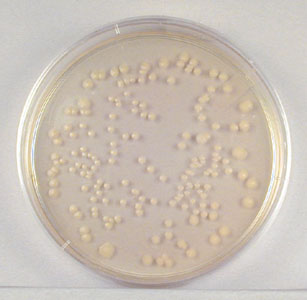
- Sample 1/1,000,000 dilution plate. (See Fig. \(\PageIndex{1B}\).)
- Sample 1/10,000,000 dilution plate. (See Fig.\(\PageIndex{1C}\).)
|
Fig. \(\PageIndex{1A}\): 1/100,000 Dilution of Bacterium (10- 5) |
Fig. Fig. \(\PageIndex{1B}\): 1/100,000 Dilution of Bacterium (10- 5) |
Fig. \(\PageIndex{1C}\): 1/10,000,000 Dilution of Bacterium (10- 7) |
|---|---|---|
 |
 |
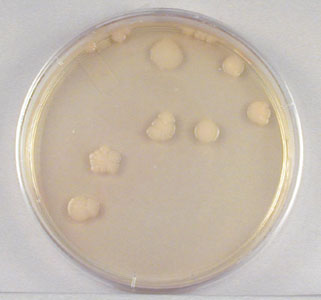 |
| This plate has over 300 colonies and cannot be used for counting. | This plate has between 30 and 300 colonies and is a suitable plate for counting. | This plate has less than 30 colonies and cannot be used for counting. |
| (Copyright; Gary E. Kaiser, Ph.D. The Community College of Baltimore County, Catonsville Campus CC-BY-3.0) | ||
2. Count the exact number of colonies on that plate using the colony counter (as demonstrated by your instructor).
3. Calculate the number of CFUs per ml of original sample as follows:
The number of CFUs per ml of sample =
The number of colonies (30-300 plate) X
The dilution factor of the plate counted
____________ = Number of colonies
____________ = Dilution factor of plate counted
____________ = Number of CFUs per ml
4. Record your results on the blackboard.
B. Direct Microscopic Method
Observe the demonstration of the Petroff-Hausser counting chamber.
C. Turbidity
Observe your instructor's demonstration of the spectrophotometer.
Contributors and Attributions
Dr. Gary Kaiser (COMMUNITY COLLEGE OF BALTIMORE COUNTY, CATONSVILLE CAMPUS)

