2.6: Practice - Non-Mendelian inheritance
- Page ID
- 73735
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\dsum}{\displaystyle\sum\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dint}{\displaystyle\int\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dlim}{\displaystyle\lim\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\(\newcommand{\longvect}{\overrightarrow}\)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)Query \(\PageIndex{1}\)
- Step-by-step solution
-
- In incomplete dominance, heterozygotes show an intermediate phenotype, such as blue-tipped feathers.
The blue-tipped parent's genotype is Bb and the white parent's genotype is bb, so the cross for these parents is Bb x bb.
We can complete a Punnett square to find the possible offspring combinations.
If we complete the cross, we find that the possible offspring can be either Bb or bb.
-
Bb offspring will have blue-tipped feathers, and bb offspring will have white feathers.
In order to have blue feathers, the offspring's genotype must be BB. Because this is not a possible genotype of this cross, 0/4 or 0% of the offspring can be blue. -
The correct answer is
0%
- In incomplete dominance, heterozygotes show an intermediate phenotype, such as blue-tipped feathers.
Query \(\PageIndex{2}\)
- Step-by-step solution
-
- The lethal yellow allele is a spontaneous mutation in mice that makes their coats yellow. Mice that have a homozygous (\(A^YA^Y\)) genotype die early in development.
- Some genes have alleles that prevent survival when homozygous or heterozygous. These are known as lethal alleles.
- The correct answer is
Lethal allele
Query \(\PageIndex{3}\)
- Step-by-step solution
-
- In codominance, both traits are dominant and will be expressed equally if present.
The cross for these parents is WR x WR.
We can complete a Punnett square to find the possible offspring combinations.
If we complete the cross, we find that the possible offspring can be WW, WR, or RR.
- 1/4 of the offspring will be white (WW), 1/4 of the offspring will be red (RR), and 2/4 of the offspring will be roan (WR).
2/4 WR = 1/2 = 50% - The correct answer is
50%
- In codominance, both traits are dominant and will be expressed equally if present.
Query \(\PageIndex{4}\)
- Step-by-step solution
-
- Lethal alleles result in the death of affected individuals.
Multiple alleles refers to a gene that is controlled by more than two alleles. - Codominance refers to traits that are both expressed at the same time in heterozygotes.
If this was an example of codominance, the offspring would have both black and white hairs. - Incomplete dominance is the blending of alleles, resulting in a phenotype that is in between the two extremes.
In this example, the gray color is an intermediate between the black and the white coats. - The correct answer is
Incomplete dominance
- Lethal alleles result in the death of affected individuals.
Query \(\PageIndex{5}\)
- Step-by-step solution
-
- Many characteristics, such as height, skin color, eye color, and risk of diseases, are controlled by many factors. These factors may be genetic, environmental, or both.
- Some characteristics are polygenic, meaning that they’re controlled by a number of different genes. In polygenic inheritance, traits often form a phenotypic spectrum rather than falling into clear-cut categories.
- The correct answer is
Polygenic inheritance; it involves multiples genes coding for a trait that falls within a wide spectrum
Query \(\PageIndex{6}\)
- Step-by-step solution
-
- The cross for these parents is AB x AO.
We can complete a Punnett square to find the possible offspring combinations.
If we complete the cross, we find that the possible offspring can be AA, AB, AO or BO.
- The offspring that are AA or AO will have A type blood and the offspring that are BO will have B type blood.
In order to have AB type blood, offspring must be AB because of codominance. Therefore, 1/4 or 25% of the offspring will have AB type blood. - The correct answer is
25%
- The cross for these parents is AB x AO.
Query \(\PageIndex{7}\)
- Step-by-step solution
-
- In incomplete dominance, heterozygotes show an intermediate phenotype, such as wavy hair.
The cross for these parents is Hh x Hh.
We can complete a Punnett square to find the possible offspring combinations.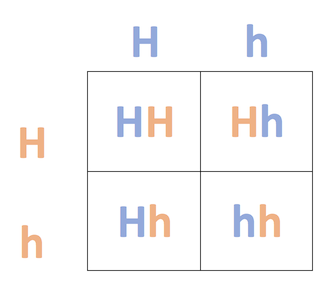
If we complete the cross, we find that the possible offspring can be HH, Hh, or hh.
- HH offspring will have curly hair, hh offspring will have straight hair, and heterozygous offspring (Hh) will have the intermediate phenotype, wavy hair.
Based on the Punnett square, the overall chance of having wavy haired (Hh) children is:
2/4 Hh = 1/2 wavy hair - The correct answer is
1/2
- In incomplete dominance, heterozygotes show an intermediate phenotype, such as wavy hair.
Query \(\PageIndex{8}\)
- Step-by-step solution
-
-

This diagram shows how the human ABO blood type system works.
- Codominance is a pattern of heredity in which both alleles are simultaneously expressed in the heterozygote (e.g. AB blood type).
Multiple allele inheritance is when a gene that is controlled by more than two alleles (e.g. A, B, and O alleles). - The correct answers are
- The A and B alleles are codominant because both alleles are simultaneously expressed in the heterozygote.
- Human blood type is an example of multiple allele inheritance.
-
Query \(\PageIndex{9}\)
- Step-by-step solution
-
- In codominance, both traits are dominant and will be expressed equally if present.
The cross for these parents is RR x RW.
We can complete a Punnett square to find the possible offspring combinations.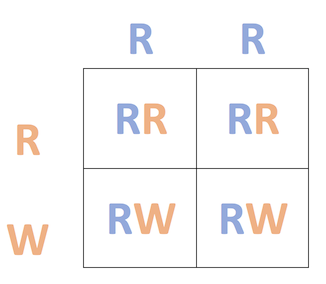
If we complete the cross, we find that the possible offspring can be either RR or RW.
- 2/4, or 50%, of the offspring will be red (RR) and 2/4, or 50%, of the offspring will be red-and-white (RW).
- The correct answer is
50% of the offspring will be red and 50% of the offspring will be red-and-white.
- In codominance, both traits are dominant and will be expressed equally if present.
Query \(\PageIndex{10}\)
- Step-by-step solution
-
-

This diagram describes how pleiotropy works.
-

These human skin color charts exemplify polygenic inheritance.
- The major difference between the two is that pleiotropy is when one gene affects multiple characteristics (e.g. Marfan syndrome) and polygenic inheritance is when one trait is controlled by multiple genes (e.g. skin pigmentation).
-
The correct answer is
Pleiotropy is when one gene affects multiple characteristics (e.g. Marfan syndrome).
-
Query \(\PageIndex{11}\)
- Step-by-step solution
-
- Pleiotropy occurs when one gene is controlled by multiple alleles and polygenic inheritance occurs when one trait is controlled by multiple genes.
-
Incomplete dominance is the blending of alleles, resulting in a phenotype that is in between the two extremes.
If this was an example of incomplete dominance, we would see corn with an intermediate color (such as light yellow) rather than corn that has mixed kernels.
-
Codominance refers to traits that are both expressed at the same time in heterozygotes.
In this example, both the yellow kernels and the white kernels are expressed in the phenotype.
-
The correct answer is
Codominance
Query \(\PageIndex{12}\)
- Step-by-step solution
-
-
The cross for these parents is cbc x Ccb.
We can complete a Punnett square to find the possible offspring combinations.

If we complete the cross, we find that the possible offspring can be Ccb, Cc, cbcb, or cbc.
-
Because C (agouti) is dominant to both other alleles, it will be displayed if present. This means the offspring that are Ccb or Cc will have agouti coats (2/4 = 50%).
cb (black) is recessive to C but dominant to c, so the cbcb and cbc will have black fur (2/4 = 50%).
-
The correct answer is
50% of the offspring will have agouti coats and 50% will have black coats.
-
Contributors and Attributions
Khan Academy (CC BY-NC-SA 3.0; All Khan Academy content is available for free at www.khanacademy.org)

