11: Behavioral Ecology
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID
- 49583
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\dsum}{\displaystyle\sum\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dint}{\displaystyle\int\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dlim}{\displaystyle\lim\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\(\newcommand{\longvect}{\overrightarrow}\)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)Skills to Develop
- Compare innate and learned behavior
- Discuss how movement and migration behaviors are a result of natural selection
- Discuss the different ways members of a population communicate with each other
- Give examples of how species use energy for mating displays and other courtship behaviors
- Differentiate between various mating systems
- Describe different ways that species learn
Behavior is the change in activity of an organism in response to a stimulus. Behavioral biology is the study of the biological and evolutionary bases for such changes. The idea that behaviors evolved as a result of the pressures of natural selection is not new. Animal behavior has been studied for decades, by biologists in the science of ethology, by psychologists in the science of comparative psychology, and by scientists of many disciplines in the study of neurobiology. Although there is overlap between these disciplines, scientists in these behavioral fields take different approaches. Comparative psychology is an extension of work done in human and behavioral psychology. Ethology is an extension of genetics, evolution, anatomy, physiology, and other biological disciplines. Still, one cannot study behavioral biology without touching on both comparative psychology and ethology.
One goal of behavioral biology is to dissect out the innate behaviors, which have a strong genetic component and are largely independent of environmental influences, from the learned behaviors, which result from environmental conditioning. Innate behavior, or instinct, is important because there is no risk of an incorrect behavior being learned. They are “hard wired” into the system. On the other hand, learned behaviors, although riskier, are flexible, dynamic, and can be altered according to changes in the environment.
Innate Behaviors: Movement and Migration
Innate or instinctual behaviors rely on response to stimuli. The simplest example of this is a reflex action, an involuntary and rapid response to stimulus. To test the “knee-jerk” reflex, a doctor taps the patellar tendon below the kneecap with a rubber hammer. The stimulation of the nerves there leads to the reflex of extending the leg at the knee. This is similar to the reaction of someone who touches a hot stove and instinctually pulls his or her hand away. Even humans, with our great capacity to learn, still exhibit a variety of innate behaviors.
Kinesis and Taxis
Another activity or movement of innate behavior is kinesis, or the undirected movement in response to a stimulus. Orthokinesis is the increased or decreased speed of movement of an organism in response to a stimulus. Woodlice, for example, increase their speed of movement when exposed to high or low temperatures. This movement, although random, increases the probability that the insect spends less time in the unfavorable environment. Another example is klinokinesis, an increase in turning behaviors. It is exhibited by bacteria such as E. coli which, in association with orthokinesis, helps the organisms randomly find a more hospitable environment.
A similar, but more directed version of kinesis is taxis: the directed movement towards or away from a stimulus. This movement can be in response to light (phototaxis), chemical signals (chemotaxis), or gravity (geotaxis) and can be directed toward (positive) or away (negative) from the source of the stimulus. An example of a positive chemotaxis is exhibited by the unicellular protozoan Tetrahymena thermophila. This organism swims using its cilia, at times moving in a straight line, and at other times making turns. The attracting chemotactic agent alters the frequency of turning as the organism moves directly toward the source, following the increasing concentration gradient.
Fixed Action Patterns
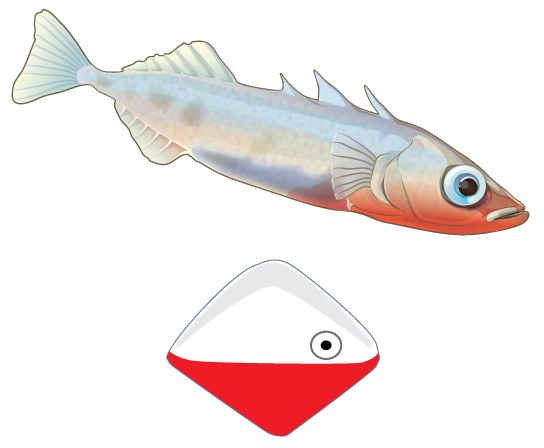
A fixed action pattern is a series of movements elicited by a stimulus such that even when the stimulus is removed, the pattern goes on to completion. An example of such a behavior occurs in the three-spined stickleback, a small freshwater fish (Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\)). Males of this species develop a red belly during breeding season and show instinctual aggressiveness to other males during this time. In laboratory experiments, researchers exposed such fish to objects that in no way resemble a fish in their shape, but which were painted red on their lower halves. The male sticklebacks responded aggressively to the objects just as if they were real male sticklebacks.
Migration
Migration is the long-range seasonal movement of animals. It is an evolved, adapted response to variation in resource availability, and it is a common phenomenon found in all major groups of animals. Birds fly south for the winter to get to warmer climates with sufficient food, and salmon migrate to their spawning grounds. The popular 2005 documentary March of the Penguins followed the 62-mile migration of emperor penguins through Antarctica to bring food back to their breeding site and to their young. Wildebeests (Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\)) migrate over 1800 miles each year in search of new grasslands.
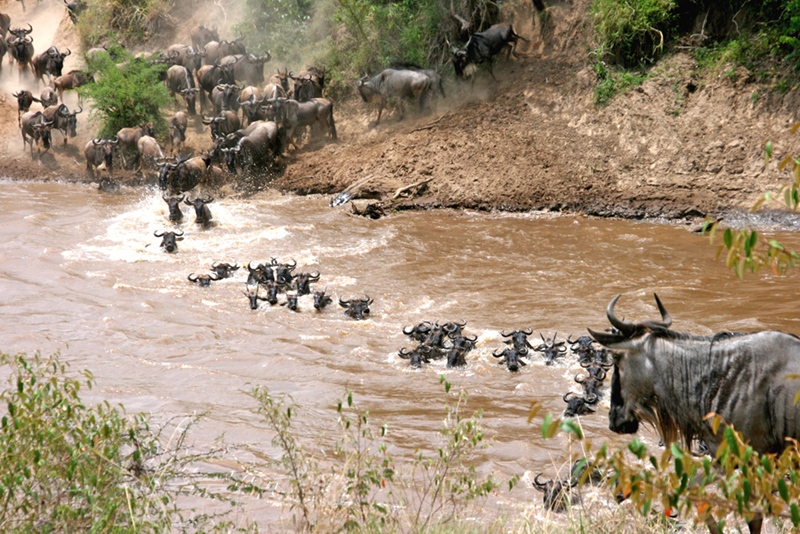

Although migration is thought of as innate behavior, only some migrating species always migrate (obligate migration). Animals that exhibit facultative migration can choose to migrate or not. Additionally, in some animals, only a portion of the population migrates, whereas the rest does not migrate (incomplete migration). For example, owls that live in the tundra may migrate in years when their food source, small rodents, is relatively scarce, but not migrate during the years when rodents are plentiful.
Foraging
Foraging is the act of searching for and exploiting food resources. Feeding behaviors that maximize energy gain and minimize energy expenditure are called optimal foraging behaviors, and these are favored by natural section. The painted stork, for example, uses its long beak to search the bottom of a freshwater marshland for crabs and other food (Figure \(\PageIndex{3}\)).
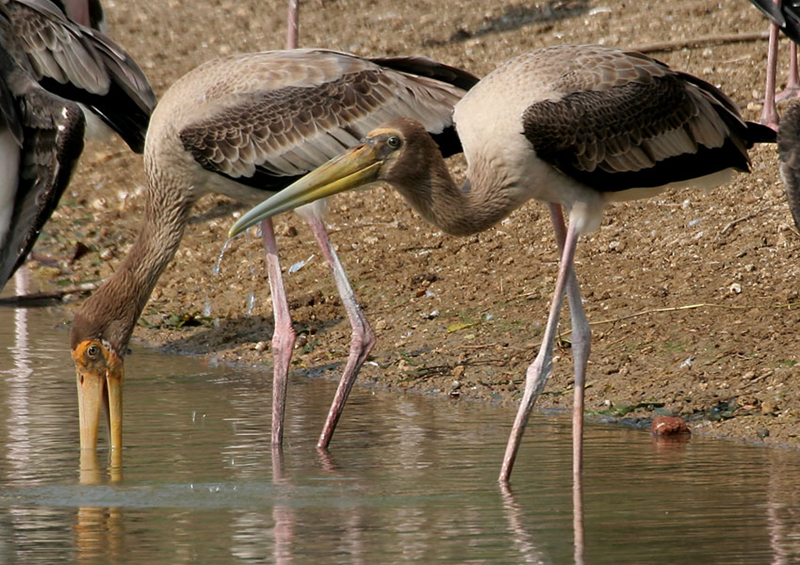

Innate Behaviors: Living in Groups
Not all animals live in groups, but even those that live relatively solitary lives, with the exception of those that can reproduce asexually, must mate. Mating usually involves one animal signaling another so as to communicate the desire to mate. There are several types of energy-intensive behaviors or displays associated with mating, called mating rituals. Other behaviors found in populations that live in groups are described in terms of which animal benefits from the behavior. In selfish behavior, only the animal in question benefits; in altruistic behavior, one animal’s actions benefit another animal; cooperative behavior describes when both animals benefit. All of these behaviors involve some sort of communication between population members.
Communication within a Species
Animals communicate with each other using stimuli known as signals. An example of this is seen in the three-spined stickleback, where the visual signal of a red region in the lower half of a fish signals males to become aggressive and signals females to mate. Other signals are chemical (pheromones), aural (sound), visual (courtship and aggressive displays), or tactile (touch). These types of communication may be instinctual or learned or a combination of both. These are not the same as the communication we associate with language, which has been observed only in humans and perhaps in some species of primates and cetaceans.
A pheromone is a secreted chemical signal used to obtain a response from another individual of the same species. The purpose of pheromones is to elicit a specific behavior from the receiving individual. Pheromones are especially common among social insects, but they are used by many species to attract the opposite sex, to sound alarms, to mark food trails, and to elicit other, more complex behaviors. Even humans are thought to respond to certain pheromones called axillary steroids. These chemicals influence human perception of other people, and in one study were responsible for a group of women synchronizing their menstrual cycles. The role of pheromones in human-to-human communication is still somewhat controversial and continues to be researched.
Songs are an example of an aural signal, one that needs to be heard by the recipient. Perhaps the best known of these are songs of birds, which identify the species and are used to attract mates. Other well-known songs are those of whales, which are of such low frequency that they can travel long distances underwater. Dolphins communicate with each other using a wide variety of vocalizations. Male crickets make chirping sounds using a specialized organ to attract a mate, repel other males, and to announce a successful mating.
Courtship displays are a series of ritualized visual behaviors (signals) designed to attract and convince a member of the opposite sex to mate. These displays are ubiquitous in the animal kingdom. Often these displays involve a series of steps, including an initial display by one member followed by a response from the other. If at any point, the display is performed incorrectly or a proper response is not given, the mating ritual is abandoned and the mating attempt will be unsuccessful. The mating display of the common stork is shown in Figure \(\PageIndex{4}\).
Aggressive displays are also common in the animal kingdom. An example is when a dog bares its teeth when it wants another dog to back down. Presumably, these displays communicate not only the willingness of the animal to fight, but also its fighting ability. Although these displays do signal aggression on the part of the sender, it is thought that these displays are actually a mechanism to reduce the amount of actual fighting that occurs between members of the same species: they allow individuals to assess the fighting ability of their opponent and thus decide whether it is “worth the fight.” The testing of certain hypotheses using game theory has led to the conclusion that some of these displays may overstate an animal’s actual fighting ability and are used to “bluff” the opponent. This type of interaction, even if “dishonest,” would be favored by natural selection if it is successful more times than not.

Distraction displays are seen in birds and some fish. They are designed to attract a predator away from the nest that contains their young. This is an example of an altruistic behavior: it benefits the young more than the individual performing the display, which is putting itself at risk by doing so.
Many animals, especially primates, communicate with other members in the group through touch. Activities such as grooming, touching the shoulder or root of the tail, embracing, lip contact, and greeting ceremonies have all been observed in the Indian langur, an Old World monkey. Similar behaviors are found in other primates, especially in the great apes.
Link to Learning
The killdeer bird distracts predators from its eggs by faking a broken wing display in this video taken in Boise, Idaho.
Altruistic Behaviors
Behaviors that lower the fitness of the individual but increase the fitness of another individual are termed altruistic. Examples of such behaviors are seen widely across the animal kingdom. Social insects such as worker bees have no ability to reproduce, yet they maintain the queen so she can populate the hive with her offspring. Meerkats keep a sentry standing guard to warn the rest of the colony about intruders, even though the sentry is putting itself at risk. Wolves and wild dogs bring meat to pack members not present during a hunt. Lemurs take care of infants unrelated to them. Although on the surface, these behaviors appear to be altruistic, it may not be so simple.
There has been much discussion over why altruistic behaviors exist. Do these behaviors lead to overall evolutionary advantages for their species? Do they help the altruistic individual pass on its own genes? And what about such activities between unrelated individuals? One explanation for altruistic-type behaviors is found in the genetics of natural selection. In the 1976 book, The Selfish Gene, scientist Richard Dawkins attempted to explain many seemingly altruistic behaviors from the viewpoint of the gene itself. Although a gene obviously cannot be selfish in the human sense, it may appear that way if the sacrifice of an individual benefits related individuals that share genes that are identical by descent (present in relatives because of common lineage). Mammal parents make this sacrifice to take care of their offspring. Emperor penguins migrate miles in harsh conditions to bring food back for their young. Selfish gene theory has been controversial over the years and is still discussed among scientists in related fields.
Even less-related individuals, those with less genetic identity than that shared by parent and offspring, benefit from seemingly altruistic behavior. The activities of social insects such as bees, wasps, ants, and termites are good examples. Sterile workers in these societies take care of the queen because they are closely related to it, and as the queen has offspring, she is passing on genes from the workers indirectly. Thus, it is of fitness benefit for the worker to maintain the queen without having any direct chance of passing on its genes due to its sterility. The lowering of individual fitness to enhance the reproductive fitness of a relative and thus one’s inclusive fitness evolves through kin selection. This phenomenon can explain many superficially altruistic behaviors seen in animals. However, these behaviors may not be truly defined as altruism in these cases because the actor is actually increasing its own fitness either directly (through its own offspring) or indirectly (through the inclusive fitness it gains through relatives that share genes with it).
Unrelated individuals may also act altruistically to each other, and this seems to defy the “selfish gene” explanation. An example of this observed in many monkey species where a monkey will present its back to an unrelated monkey to have that individual pick the parasites from its fur. After a certain amount of time, the roles are reversed and the first monkey now grooms the second monkey. Thus, there is reciprocity in the behavior. Both benefit from the interaction and their fitness is raised more than if neither cooperated nor if one cooperated and the other did not cooperate. This behavior is still not necessarily altruism, as the “giving” behavior of the actor is based on the expectation that it will be the “receiver” of the behavior in the future, termed reciprocal altruism. Reciprocal altruism requires that individuals repeatedly encounter each other, often the result of living in the same social group, and that cheaters (those that never “give back”) are punished.
Evolutionary game theory, a modification of classical game theory in mathematics, has shown that many of these so-called “altruistic behaviors” are not altruistic at all. The definition of “pure” altruism, based on human behavior, is an action that benefits another without any direct benefit to oneself. Most of the behaviors previously described do not seem to satisfy this definition, and game theorists are good at finding “selfish” components in them. Others have argued that the terms “selfish” and “altruistic” should be dropped completely when discussing animal behavior, as they describe human behavior and may not be directly applicable to instinctual animal activity. What is clear, though, is that heritable behaviors that improve the chances of passing on one’s genes or a portion of one’s genes are favored by natural selection and will be retained in future generations as long as those behaviors convey a fitness advantage. These instinctual behaviors may then be applied, in special circumstances, to other species, as long as it doesn’t lower the animal’s fitness.
Finding Sex Partners
Not all animals reproduce sexually, but many that do have the same challenge: they need to find a suitable mate and often have to compete with other individuals to obtain one. Significant energy is spent in the process of locating, attracting, and mating with the sex partner. Two types of selection occur during this process and can lead to traits that are important to reproduction called secondary sexual characteristics: intersexual selection, the choosing of a mate where individuals of one sex choose mates of the other sex, and intrasexual selection, the competition for mates between species members of the same sex. Intersexual selection is often complex because choosing a mate may be based on a variety of visual, aural, tactile, and chemical cues. An example of intersexual selection is when female peacocks choose to mate with the male with the brightest plumage. This type of selection often leads to traits in the chosen sex that do not enhance survival, but are those traits most attractive to the opposite sex (often at the expense of survival). Intrasexual selection involves mating displays and aggressive mating rituals such as rams butting heads—the winner of these battles is the one that is able to mate. Many of these rituals use up considerable energy but result in the selection of the healthiest, strongest, and/or most dominant individuals for mating. Three general mating systems, all involving innate as opposed to learned behaviors, are seen in animal populations: monogamous, polygynous, and polyandrous.
In monogamous systems, one male and one female are paired for at least one breeding season. In some animals, such as the gray wolf, these associations can last much longer, even a lifetime. Several explanations have been proposed for this type of mating system. The “mate-guarding hypothesis” states that males stay with the female to prevent other males from mating with her. This behavior is advantageous in such situations where mates are scarce and difficult to find. Another explanation is the “male-assistance hypothesis,” where males that remain with a female to help guard and rear their young will have more and healthier offspring. Monogamy is observed in many bird populations where, in addition to the parental care from the female, the male is also a major provider of parental care for the chicks. A third explanation for the evolutionary advantages of monogamy is the “female-enforcement hypothesis.” In this scenario, the female ensures that the male does not have other offspring that might compete with her own, so she actively interferes with the male’s signaling to attract other mates.
Polygynous mating refers to one male mating with multiple females. In these situations, the female must be responsible for most of the parental care as the single male is not capable of providing care to that many offspring. In resourced-based polygyny, males compete for territories with the best resources, and then mate with females that enter the territory, drawn to its resource richness. The female benefits by mating with a dominant, genetically fit male; however, it is at the cost of having no male help in caring for the offspring. An example is seen in the yellow-rumped honeyguide, a bird whose males defend beehives because the females feed on their wax. As the females approach, the male defending the nest will mate with them. Harem mating structures are a type of polygynous system where certain males dominate mating while controlling a territory with resources. Elephant seals, where the alpha male dominates the mating within the group are an example. A third type of polygyny is a lek system. Here there is a communal courting area where several males perform elaborate displays for females, and the females choose their mate from this group. This behavior is observed in several bird species including the sage grouse and the prairie chicken.
In polyandrous mating systems, one female mates with many males. These types of systems are much rarer than monogamous and polygynous mating systems. In pipefishes and seahorses, males receive the eggs from the female, fertilize them, protect them within a pouch, and give birth to the offspring (Figure \(\PageIndex{5}\)). Therefore, the female is able to provide eggs to several males without the burden of carrying the fertilized eggs.


Simple Learned Behaviors
The majority of the behaviors previously discussed were innate or at least have an innate component (variations on the innate behaviors may be learned). They are inherited and the behaviors do not change in response to signals from the environment. Conversely, learned behaviors, even though they may have instinctive components, allow an organism to adapt to changes in the environment and are modified by previous experiences. Simple learned behaviors include habituation and imprinting—both are important to the maturation process of young animals.
Habituation
Habituation is a simple form of learning in which an animal stops responding to a stimulus after a period of repeated exposure. This is a form of non-associative learning, as the stimulus is not associated with any punishment or reward. Prairie dogs typically sound an alarm call when threatened by a predator, but they become habituated to the sound of human footsteps when no harm is associated with this sound, therefore, they no longer respond to them with an alarm call. In this example, habituation is specific to the sound of human footsteps, as the animals still respond to the sounds of potential predators.
Imprinting
Imprinting is a type of learning that occurs at a particular age or a life stage that is rapid and independent of the species involved. Hatchling ducks recognize the first adult they see, their mother, and make a bond with her. A familiar sight is ducklings walking or swimming after their mothers (Figure \(\PageIndex{6}\)). This is another type of non-associative learning, but is very important in the maturation process of these animals as it encourages them to stay near their mother so they will be protected, greatly increasing their chances of survival. However, if newborn ducks see a human before they see their mother, they will imprint on the human and follow it in just the same manner as they would follow their real mother.

Link to Learning
The International Crane Foundation has helped raise the world’s population of whooping cranes from 21 individuals to about 600. Imprinting hatchlings has been a key to success: biologists wear full crane costumes so the birds never “see” humans. Watch this video to learn more.
Conditioned Behavior
Conditioned behaviors are types of associative learning, where a stimulus becomes associated with a consequence. During operant conditioning, the behavioral response is modified by its consequences, with regards to its form, strength, or frequency.
Classical Conditioning
In classical conditioning, a response called the conditioned response is associated with a stimulus that it had previously not been associated with, the conditioned stimulus. The response to the original, unconditioned stimulus is called the unconditioned response. The most cited example of classical conditioning is Ivan Pavlov’s experiments with dogs (Figure \(\PageIndex{7}\)). In Pavlov’s experiments, the unconditioned response was the salivation of dogs in response to the unconditioned stimulus of seeing or smelling their food. The conditioning stimulus that researchers associated with the unconditioned response was the ringing of a bell. During conditioning, every time the animal was given food, the bell was rung. This was repeated during several trials. After some time, the dog learned to associate the ringing of the bell with food and to respond by salivating. After the conditioning period was finished, the dog would respond by salivating when the bell was rung, even when the unconditioned stimulus, the food, was absent. Thus, the ringing of the bell became the conditioned stimulus and the salivation became the conditioned response. Although it is thought by some scientists that the unconditioned and conditioned responses are identical, even Pavlov discovered that the saliva in the conditioned dogs had characteristic differences when compared to the unconditioned dog.
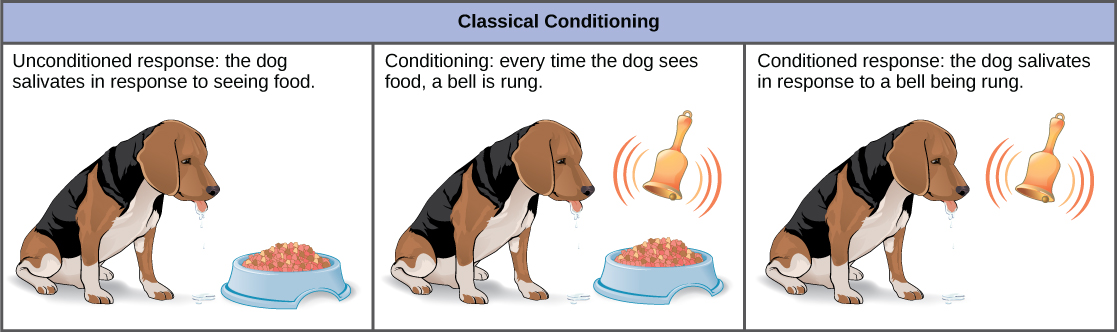
It had been thought by some scientists that this type of conditioning required multiple exposures to the paired stimulus and response, but it is now known that this is not necessary in all cases, and that some conditioning can be learned in a single pairing experiment. Classical conditioning is a major tenet of behaviorism, a branch of psychological philosophy that proposes that all actions, thoughts, and emotions of living things are behaviors that can be treated by behavior modification and changes in the environment.
Operant Conditioning
In operant conditioning, the conditioned behavior is gradually modified by its consequences as the animal responds to the stimulus. A major proponent of such conditioning was psychologist B.F. Skinner, the inventor of the Skinner box. Skinner put rats in his boxes that contained a lever that would dispense food to the rat when depressed. While initially the rat would push the lever a few times by accident, it eventually associated pushing the lever with getting the food. This type of learning is an example of operant conditioning. Operant learning is the basis of most animal training. The conditioned behavior is continually modified by positive or negative reinforcement, often a reward such as food or some type of punishment, respectively. In this way, the animal is conditioned to associate a type of behavior with the punishment or reward, and, over time, can be induced to perform behaviors that they would not have done in the wild, such as the “tricks” dolphins perform at marine amusement park shows (Figure \(\PageIndex{8}\)).
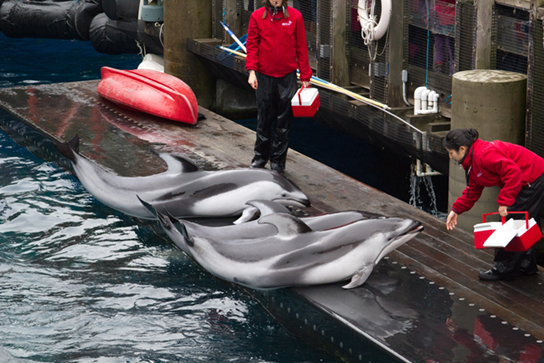
Cognitive Learning
Classical and operant conditioning are inefficient ways for humans and other intelligent animals to learn. Some primates, including humans, are able to learn by imitating the behavior of others and by taking instructions. The development of complex language by humans has made cognitive learning, the manipulation of information using the mind, the most prominent method of human learning. In fact, that is how students are learning right now by reading this book. As students read, they can make mental images of objects or organisms and imagine changes to them, or behaviors by them, and anticipate the consequences. In addition to visual processing, cognitive learning is also enhanced by remembering past experiences, touching physical objects, hearing sounds, tasting food, and a variety of other sensory-based inputs. Cognitive learning is so powerful that it can be used to understand conditioning in detail. In the reverse scenario, conditioning cannot help someone learn about cognition.
Classic work on cognitive learning was done by Wolfgang Köhler with chimpanzees. He demonstrated that these animals were capable of abstract thought by showing that they could learn how to solve a puzzle. When a banana was hung in their cage too high for them to reach, and several boxes were placed randomly on the floor, some of the chimps were able to stack the boxes one on top of the other, climb on top of them, and get the banana. This implies that they could visualize the result of stacking the boxes even before they had performed the action. This type of learning is much more powerful and versatile than conditioning.
Cognitive learning is not limited to primates, although they are the most efficient in using it. Maze running experiments done with rats by H.C. Blodgett in the 1920s were the first to show cognitive skills in a simple mammal. The motivation for the animals to work their way through the maze was a piece of food at its end. In these studies, the animals in Group I were run in one trial per day and had food available to them each day on completion of the run (Figure \(\PageIndex{9}\)). Group II rats were not fed in the maze for the first six days and then subsequent runs were done with food for several days after. Group III rats had food available on the third day and every day thereafter. The results were that the control rats, Group I, learned quickly, and figured out how to run the maze in seven days. Group III did not learn much during the three days without food, but rapidly caught up to the control group when given the food reward. Group II learned very slowly for the six days with no reward to motivate them, and they did not begin to catch up to the control group until the day food was given, and then it took two days longer to learn the maze.
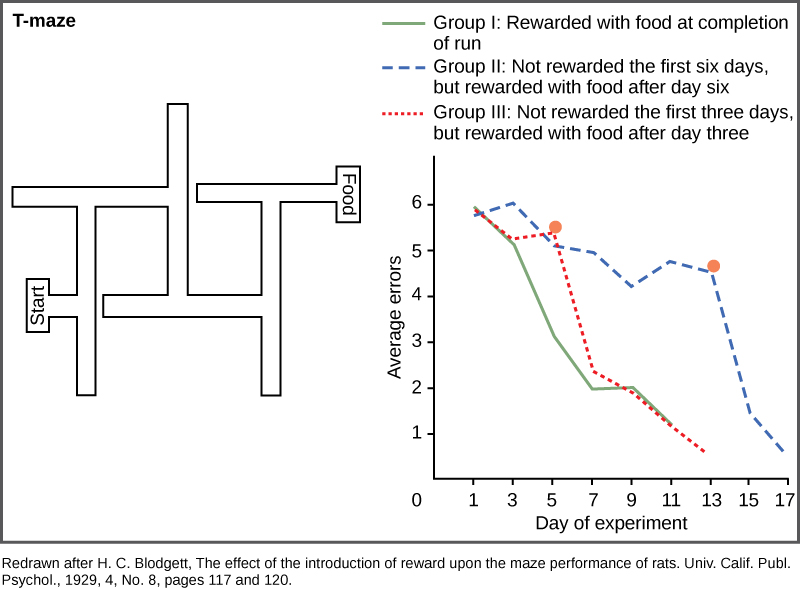
It may not be immediately obvious that this type of learning is different than conditioning. Although one might be tempted to believe that the rats simply learned how to find their way through a conditioned series of right and left turns, E.C. Tolman proved a decade later that the rats were making a representation of the maze in their minds, which he called a “cognitive map.” This was an early demonstration of the power of cognitive learning and how these abilities were not just limited to humans.
Sociobiology
Sociobiology is an interdisciplinary science originally popularized by social insect researcher E.O. Wilson in the 1970s. Wilson defined the science as “the extension of population biology and evolutionary theory to social organization.”1 The main thrust of sociobiology is that animal and human behavior, including aggressiveness and other social interactions, can be explained almost solely in terms of genetics and natural selection. This science is controversial; noted scientist such as the late Stephen Jay Gould criticized the approach for ignoring the environmental effects on behavior. This is another example of the “nature versus nurture” debate of the role of genetics versus the role of environment in determining an organism’s characteristics.
Sociobiology also links genes with behaviors and has been associated with “biological determinism,” the belief that all behaviors are hardwired into our genes. No one disputes that certain behaviors can be inherited and that natural selection plays a role retaining them. It is the application of such principles to human behavior that sparks this controversy, which remains active today.
Summary
Behaviors are responses to stimuli. They can either be instinctual/innate behaviors, which are not influenced by the environment, or learned behaviors, which are influenced by environmental changes. Instinctual behaviors include mating systems and methods of communication. Learned behaviors include imprinting and habituation, conditioning, and, most powerfully, cognitive learning. Although the connection between behavior, genetics, and evolution is well established, the explanation of human behavior as entirely genetic is controversial.
Footnotes
- 1 Edward O. Wilson. On Human Nature (1978; repr., Cambridge: Harvard University Press, 2004), xx.
Glossary
- aggressive display
- visual display by a species member to discourage other members of the same species or different species
- behavior
- change in an organism’s activities in response to a stimulus
- behavioral biology
- study of the biology and evolution of behavior
- classical conditioning
- association of a specific stimulus and response through conditioning
- cognitive learning
- knowledge and skills acquired by the manipulation of information in the mind
- conditioned behavior
- behavior that becomes associated with a specific stimulus through conditioning
- courtship display
- visual display used to attract a mate
- distraction display
- visual display used to distract predators away from a nesting site
- ethology
- biological study of animal behavior
- fixed action pattern
- series of instinctual behaviors that, once initiated, always goes to completion regardless of changes in the environment
- foraging
- behaviors species use to find food
- habituation
- ability of a species to ignore repeated stimuli that have no consequence
- imprinting
- identification of parents by newborns as the first organism they see after birth
- innate behavior
- instinctual behavior that is not altered by changes in the environment
- intersexual selection
- selection of a desirable mate of the opposite sex
- intrasexual selection
- competition between members of the same sex for a mate
- kin selection
- sacrificing one’s own life so that one’s genes will be passed on to future generations by relatives
- kinesis
- undirected movement of an organism in response to a stimulus
- learned behavior
- behavior that responds to changes in the environment
- migration
- long-range seasonal movement of animal species
- monogamy
- mating system whereby one male and one female remain coupled for at least one mating season
- operant conditioning
- learned behaviors in response to positive and/or negative reinforcement
- polyandry
- mating system where one female mates with many males
- polygyny
- mating system where one male mates with many females
- reflex action
- action in response to direct physical stimulation of a nerve
- signal
- method of communication between animals including those obtained by the senses of smell, hearing, sight, or touch
- taxis
- directed movement in response to a stimulus


