Mitosis - Internet Exploration
This page is a draft and is under active development.
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
Site 1: Bioman: Mitosis Mover
https://biomanbio.com/HTML5GamesandLabs/Genegames/mito sismoverpage.html
sismoverpage.html
Click on “start a new game” and spacebar to continue.
1. What are the three main parts of the cell cycle: ___________________________________________
(press spacebar to continue).
Proceed through the game by answering questions and clicking “OK.”
2. What is uncoiled stringy DNA called? ______________________________
3. During interphase, DNA do what before mitosis can occur? _______________________________
4. List one reason why the body needs to make more cells? ________________________________
5. Mitosis ultimately results in the formation of what? _______________________________________
6. What is the correct order for the phases of mitosis? _______________________________________
7. What happens during prophase to the chromatin? ___________________________________________
8. Each half of a chromosome is called a what? _____________________________________
9. What happens to the nucleus during prophase? ________________________________
10. What happens during metaphase? ____________________________________
11. What happens in anaphase? ______________________________
12. What happens to the chromosomes during telophase?__________________________________
13. What happens during cytokinesis? _________________________________
Mitosis Tutorial
Go to the “Interactive Eukaryote Cell Cycle” and click on MITOSIS. Click on “Start the Animation”. Use the right side links to click through the phases of the cell cycle.
1. Which stage does the following occur:
|
Chromatin condenses into chromosomes. |
|
|
Chromosomes align in center of cell. |
|
|
Longest part of the cell cycle. |
|
|
Nuclear envelope breaks down. |
|
|
Cell is cleaved into two new daughter cells. |
|
|
Daughter chromosomes arrive at the poles. |
|
|
Chromatids are pulled apart |
2. Watch the video carefully. The colored chromosomes represent chromatids. There are two of each color because one is an exact duplicate of the other.
- How many chromosomes are visible at the beginning of mitosis? ________________
- How many are in each daughter cell at the end of mitosis? __________________
- The little green T shaped things on the cell are: ____________________________
- What happens to the centrioles during mitosis? _____________________________
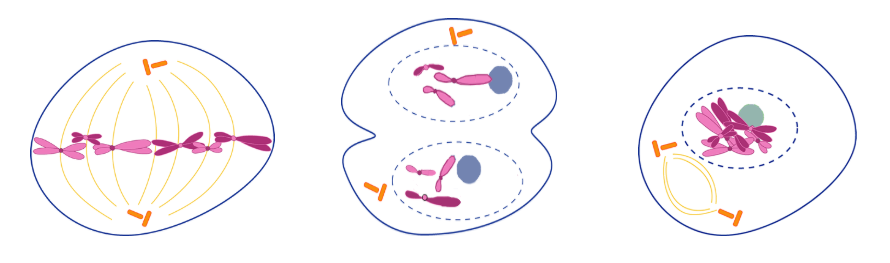
3. Identify the stages of these cells and label the structures shown.
Onion Root Tip
http://www.biology.arizona.edu/cell_bio/activities/cell_cycle/cell_cycle.html
Read the introduction, then click the “next” button.
You will have 36 cells to classify. When finished, record data in the chart below. Round to whole numbers.
|
|
Interphase |
Prophase |
Metaphase |
Anaphase |
Telophase |
Total |
|
Number of Cells |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Percent of Cells (calculate: number of cells divided by total cells x 100) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Based on your data, cells spend most of their time in which phase? _________________________________
Mitosis in Whitefish & Onion Roots
http://www.biologycorner.com/projects/mitosis.html
Click on the Whitefish embryo and the onion root tip. For each view, identify the stage of mitosis.
|
|
View 1 |
View 2 |
View 3 |
View 4 |
View 5 |
|
Whitefish |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Onion |
|
|
|
|
|
What are the similarities between the two types of cells (onion and whitefish)?
What are the differences?
You Draw It!
Use the space below to draw the four stages of mitosis your own way, be sure to represent the major events of each phase and label structures. You may also use an online program, like sketchtoy.com to draw and share your image.

