1.2: Chromosomes and chromatin
- Page ID
- 25721
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)Learning Objectives
- Understand that chromosomes contain genes, which are DNA sequences that encode products and describe how the positions of individual genes on a given chromosome are related to their positions on the homolog of that chromosome.
- Discuss how DNA is packaged in the chromosomes in terms of histones, nucleosomes, and chromatin (heterochromatin and euchromatin).
- Explain the meaning of ploidy (haploid, diploid) and how it relates to the number of homologues of each chromosome.
- Compare prokaryotic and eukaryotic chromosomes.
- Interpret a karyotype.
What is a chromosome?
Chromosomes are units of DNA stored within cells. In prokaryotes, these units are most often circular, whereas in eukaryotes the units are typically linear.
Genes are sequences within chromosomes that contain information in the sequence of nucleotide bases that encodes a product (RNA or a protein).
Features and Compaction of Circular Chromosomes
The bacterial chromosome is typically one molecule of double-stranded, helical DNA. In most bacteria, the two ends of the double-stranded DNA covalently bond together to form both a physical and genetic circle. The chromosome is generally around 1000 µm long and frequently contains as many as 3,500 genes. E. coli, a bacterium that is 2-3 µm in length, has a chromosome approximately 1400 µm long.
What does it mean to be haploid?
Prokaryotic cells usually have one only copy of their chromosome(s) and therefore one copy of each gene on the chromosome.
To enable a macromolecule this large to fit within the bacterium, proteins bind to the DNA, segregating the DNA molecule into around 50 chromosomal domains and making it more compact. Prokaryotes primarily compact chromosomes by supercoiling, the process of twisting a piece of DNA that causes it to "fold up" on itself. Think of an old-fashioned phone cord or piece of string that you keep twisting. Supercoiling is not random, but is controlled by enzymes (topoisomerases) that can add or remove "twists" in the double helix to loosen or tighten the chromosome compaction.
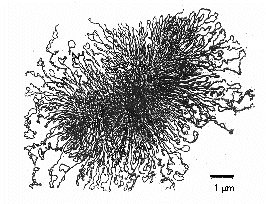
Video: Representing Bacterial DNA
Features of Linear Chromosomes
Linear chromosomes contain structural features such as centromeres and telomeres. In most cases, each chromosome contains one centromere. These sequences are bound by proteins that will link the centromere to microtubules that facilitate chromosome movement during cell division. Under the microscope, centromeres of metaphase chromosomes can sometimes appear as constrictions in the body of the chromosome. If a centromere is located near the middle of a chromosome, it is metacentric, whereas a telocentric centromere is at, or near, the very end of the chromosome. Some organisms also do not have a single centromere but are holocentric. Telomeres are repetitive sequences near the ends of linear chromosomes, and are important in maintaining the length of the chromosomes during replication, and protecting the ends of the chromosomes from alterations.
Homologous chromosomes are typically pairs of similar, but non-identical, chromosomes in which one member of the pair comes from the male parent, and the other comes from the female parent. Homologs contain the same gene loci in the same order. Non-homologous chromosomes contain different gene loci, and are usually distinguishable based on cytological features such as length, centromere position, and banding patterns produced by staining.
What does it mean to be diploid?
Most eukaryotic organisms are diploid, meaning they have two sets of chromosomes. The diploid number is represented by 2n.
Remember this means that each cell has:
- two homologs of each chromosome
- two copies of each gene
The number of non-homologous chromosomes varies by organism.
Levels of compaction in eukaryotes
If stretched to its full length, the DNA molecule of the largest human chromosome would be 85mm. Yet during mitosis and meiosis, this DNA molecule is compacted into a chromosome approximately 5µm long (17,000 times smaller!). Although this compaction makes it easier to transport DNA within a dividing cell, it also makes DNA less accessible for other cellular functions such as DNA synthesis and transcription. Thus, chromosomes vary in how tightly DNA is packaged, depending on the stage of the cell cycle and also on the level of gene activity required in any particular region of the chromosome.
There are several different levels of structural organization in eukaryotic chromosomes, with each successive level contributing to the further compaction of DNA. The compaction of DNA requires proteins and the combination of proteins and DNA is chromatin. For more loosely compacted DNA, only the first few levels of organization may apply. Each level involves a specific set of proteins that associate with the DNA to compact it. First, proteins called the core histones act as spool around which DNA is coiled twice to form a structure called the nucleosome, which is composed of eight polypeptides, two copies of histone proteins H2A, H2B, H3, and H4. Nucleosomes are formed at regular intervals along the DNA strand, giving the molecule the appearance of “beads on a string”.
At the next level of organization, histone H1 helps to compact the DNA strand and its nucleosomes into a 30nm fiber. Subsequent levels of organization involve the addition of scaffold proteins that wind the 30nm fiber into coils, which are in turn wound around other scaffold proteins.
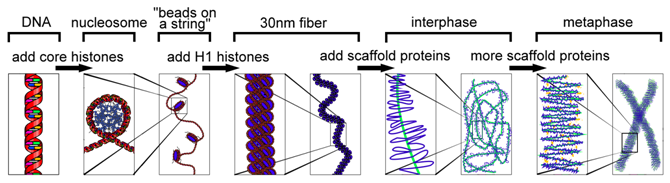
Chromatin Packaging Varies Within a Chromosome: Euchromatin & Heterochromatin
Classically, there are two major types of chromatin, but these are more the ends of a continuous and varied spectrum. Euchromatin is more loosely packed, and tends to contain genes that are being transcribed (or actively being utilized by the cell). For example, there might be widely-spaced nucleosomes within a euchromatin region, leaving more of the DNA accessible for proteins that interact with that region. In contrast, heterochromatin usually contains densely-packed nucleosomes, is often rich in repetitive sequences, and tends not to contain genes that are actively being transcribed. Within these regions, nucleosomes might be close together, restricting protein access to DNA. Both the centromeres and telomeres are usually heterochromatin, whereas other regions of chromosomes can be switched from heterochromatin to euchromatin or vice versa, often by proteins that modify histones and nucleosomes.
Keeping chromosomes organized in nuclei
During interphase, the decondensed chromosomes often have specific locations within the nucleus and relative to one another, which has been studied using a technique called FISH, fluorescent in situ hybridization. In FISH, fluorescently-tagged probes (pieces of single-stranded DNA) recognize complementary sequences specific to each chromosome and allow visualization of specific chromosome locations within a nucleus full of DNA.
Breaking down terms to understand FISH:
F = fluorescent because a small molecule that is excited by a certain wavelength of light is attached to the probe
IS = in situ is a Latin term that means "in the original place" because the experiment examines something within a cell
H = hybridization because the probe and the cellular DNA are complementary and therefore bind each other (or hybridize)
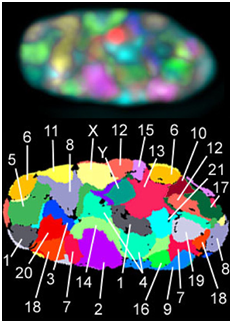
Exercise \(\PageIndex{1}\)
How do DNA probes recognize sequences of DNA in cells in this experiment?
- Answer
-
The rules of base pairing A-T and G-C and anti-parallel orientation! The probes are complementary to sequences of DNA specific to each chromosome.
Karyotypes
Chromosomes stain with some types of dyes, which is how they got their name (chromosome means “colored body”). Certain dyes stain some regions along a chromosome more intensely than others, giving some chromosomes a banded appearance when stained. A karyotype is a representation of a complete set of chromosomes. Karyotypes are usually determined by isolating mitotic chromosomes to view them as a karyogram. Chemicals that arrest the cells in metaphase of mitosis are used and then the chromosomes are released from nuclei, usually onto a slide. Chromosomes at this stage are at the most compact state. The images of these chromosomes can be captured digitally and arranged into pairs based on size, centromere position, and banding pattern to examine the complete set of chromosomes in the cell.
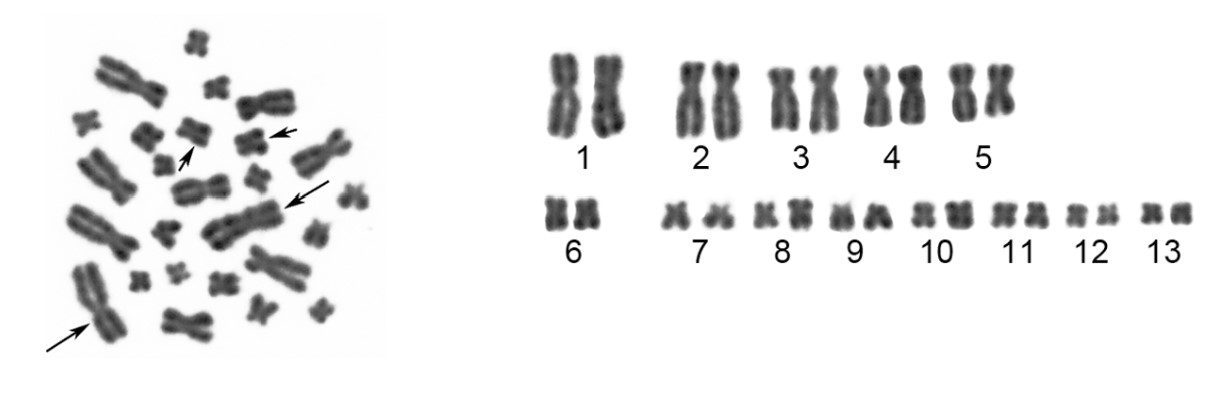
Exercise \(\PageIndex{1}\)
Based on the above karyotype from the spiny frog, what is the diploid (2n) number of this species?
- Answer
-
2n = 26
Thinking ahead \(\PageIndex{2}\)
A karyotype is a representation of a complete set of chromosomes. These chromosomes are typically extracted from a cell arrested in metaphase of mitosis. Why do you think the chromosomes are extracted during the mitotic phase instead of interphase?
- Answer
-
During interphase, chromosomes are in a decondensed configuration. However, during mitosis, chromosomes become highly condensed (17,000 times smaller than during interphase). It is much easier to extract chromosomes from a cell when they are tightly packaged as opposed to being in a loose configuration.
Video: Performing Cytogenetic Test for Chromosomal Study
Additional resources
For additional information about karyotyping: https://www.nature.com/scitable/topicpage/karyotyping-for-chromosomal-abnormalities-298/
References
Bolzer A, Kreth G, Solovei I, Koehler D, Saracoglu K, Fauth C, et al. (2005) Three-Dimensional Maps of All Chromosomes in Human Male Fibroblast Nuclei and Prometaphase Rosettes. PLoS Biol 3(5): e157. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.0030157
Duan J, Jiang W, Cheng Z, Heikkila JJ, Glick BR (2013) The Complete Genome Sequence of the Plant Growth-Promoting Bacterium Pseudomonas sp. UW4. PLoS ONE 8(3): e58640. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0058640
Qing L, Xia Y, Zheng Y, Zeng X (2012) A De Novo Case of Floating Chromosomal Polymorphisms by Translocation in Quasipaa boulengeri (Anura, Dicroglossidae). PLoS ONE 7(10): e46163. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0046163
Contributors and Attributions
Dr. Todd Nickle and Isabelle Barrette-Ng (Mount Royal University) The content on this page is licensed under CC SA 3.0 licensing guidelines.
- Chromsome-DNA-gene image By Thomas Splettstoesser - This file has been altered from the original under a creative commons license. Original can be found at https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/F...e-DNA-gene.png, CC BY-SA 4.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/inde...curid=76810117


