1.E: An Invisible World (Exercises)
- Page ID
- 77374
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
1.1: What Our Ancestors Knew
Microorganisms (or microbes) are living organisms that are generally too small to be seen without a microscope. Throughout history, humans have used microbes to make fermented foods such as beer, bread, cheese, and wine. Long before the invention of the microscope, some people theorized that infection and disease were spread by living things that were too small to be seen. They also correctly intuited certain principles regarding the spread of disease and immunity.
Multiple Choice
Which of the following foods is NOT made by fermentation?
- beer
- bread
- cheese
- orange juice
- Answer
-
D
Who is considered the “father of Western medicine”?
- Marcus Terentius Varro
- Thucydides
- Antonie van Leeuwenhoek
- Hippocrates
- Answer
-
D
Who was the first to observe “animalcules” under the microscope?
- Antonie van Leeuwenhoek
- Ötzi the Iceman
- Marcus Terentius Varro
- Robert Koch
- Answer
-
A
Who proposed that swamps might harbor tiny, disease-causing animals too small to see?
- Thucydides
- Marcus Terentius Varro
- Hippocrates
- Louis Pasteur
- Answer
-
B
Fill in the Blank
Thucydides is known as the father of _______________.
- Answer
-
scientific history
Researchers think that Ötzi the Iceman may have been infected with _____ disease.
- Answer
-
Lyme
The process by which microbes turn grape juice into wine is called _______________.
- Answer
-
fermentation
Short Answer
What did Thucydides learn by observing the Athenian plague?
Why was the invention of the microscope important for microbiology?
What are some ways people use microbes?
Critical Thinking
Explain how the discovery of fermented foods likely benefited our ancestors.
What evidence would you use to support this statement: Ancient people thought that disease was transmitted by things they could not see.
1.2: A Systematic Approach
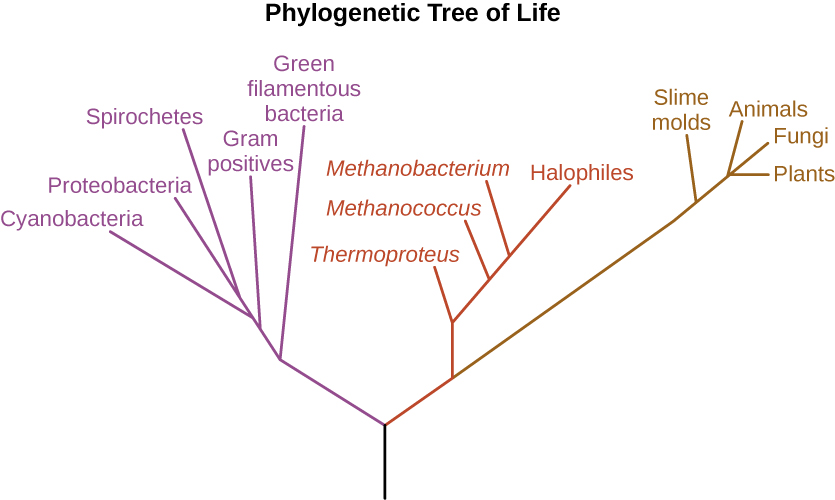
Carolus Linnaeus developed a taxonomic system for categorizing organisms into related groups. Binomial nomenclature assigns organisms Latinized scientific names with a genus and species designation. A phylogenetic tree is a way of showing how different organisms are thought to be related to one another from an evolutionary standpoint. The first phylogenetic tree contained kingdoms for plants and animals; Ernst Haeckel proposed adding a kingdom for protists.
Multiple Choice
Which of the following was NOT a kingdom in Linnaeus’s taxonomy?
- animal
- mineral
- protist
- plant
- Answer
-
C
Which of the following is a correct usage of binomial nomenclature?
- Homo Sapiens
- homo sapiens
- Homo sapiens
- Homo Sapiens
- Answer
-
C
Which scientist proposed adding a kingdom for protists?
- Carolus Linnaeus
- Carl Woese
- Robert Whittaker
- Ernst Haeckel
- Answer
-
D
Which of the following is NOT a domain in Woese and Fox’s phylogenetic tree?
- Plantae
- Bacteria
- Archaea
- Eukarya
- Answer
-
A
Which of the following is the standard resource for identifying bacteria?
- Systema Naturae
- Bergey’s Manual of Determinative Bacteriology
- Woese and Fox’s phylogenetic tree
- Haeckel’s General Morphology of Organisms
- Answer
-
B
Short Answer
What is a phylogenetic tree?
Which of the five kingdoms in Whittaker’s phylogenetic tree are prokaryotic, and which are eukaryotic?
What molecule did Woese and Fox use to construct their phylogenetic tree?
Name some techniques that can be used to identify and differentiate species of bacteria.
Critical Thinking
Why is using binomial nomenclature more useful than using common names?
Label the three Domains found on modern phylogenetic trees.
1.3: Types of Microorganisms
Microorganisms are very diverse and are found in all three domains of life: Archaea, Bacteria, and Eukarya. Archaea and bacteria are classified as prokaryotes because they lack a cellular nucleus. Archaea differ from bacteria in evolutionary history, genetics, metabolic pathways, and cell wall and membrane composition. Archaea inhabit nearly every environment on earth, but no archaea have been identified as human pathogens.
Multiple Choice
Which of the following types of microorganisms is photosynthetic?
- yeast
- virus
- helminth
- alga
- Answer
-
D
Which of the following is a prokaryotic microorganism?
- helminth
- protozoan
- cyanobacterium
- mold
- Answer
-
C
Which of the following is acellular?
- virus
- bacterium
- fungus
- protozoan
- Answer
-
A
Which of the following is a type of fungal microorganism?
- bacterium
- protozoan
- alga
- yeast
- Answer
-
D
Which of the following is not a subfield of microbiology?
- bacteriology
- botany
- clinical microbiology
- virology
- Answer
-
B
Fill in the Blank
A ________ is a disease-causing microorganism.
- Answer
-
pathogen
Multicellular parasitic worms studied by microbiologists are called ___________.
- Answer
-
helminths
The study of viruses is ___________.
- Answer
-
virology
The cells of prokaryotic organisms lack a _______.
- Answer
-
nucleus
Short Answer
Describe the differences between bacteria and archaea.
Name three structures that various protozoa use for locomotion.
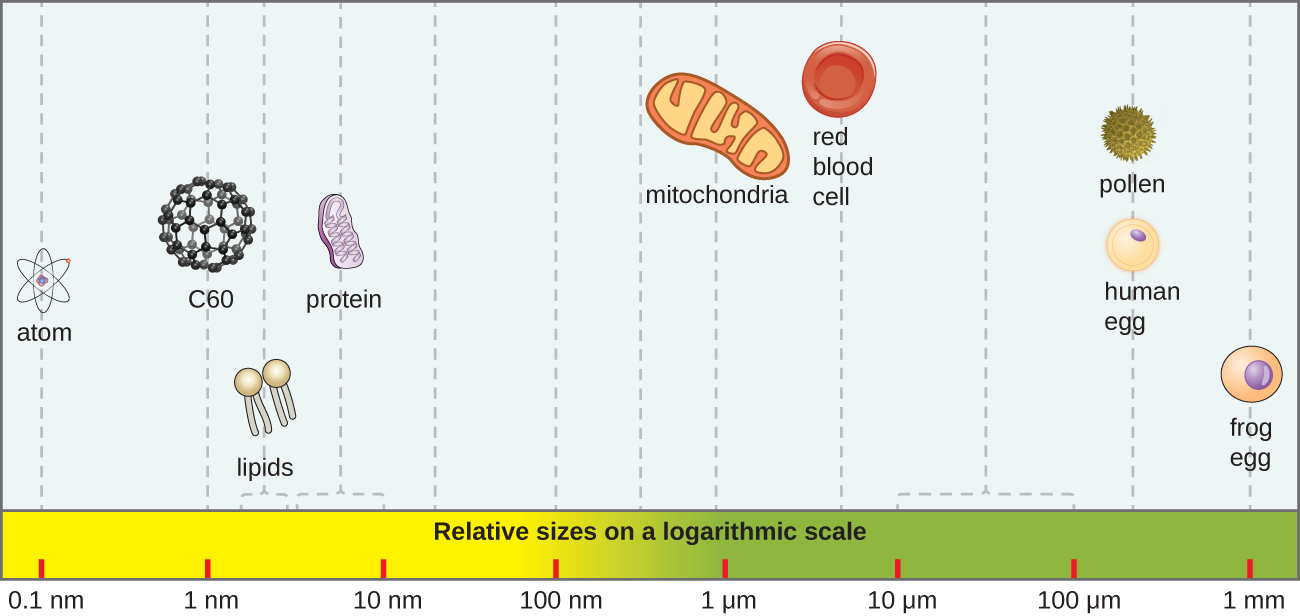
Describe the actual and relative sizes of a virus, a bacterium, and a plant or animal cell.
Critical Thinking
Contrast the behavior of a virus outside versus inside a cell.
Where would a virus, bacterium, animal cell, and a prion belong on this chart?