2.1: The Properties of Light
- Page ID
- 5278
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)- Identify and define the characteristics of electromagnetic radiation (EMR) used in microscopy
- Explain how lenses are used in microscopy to manipulate visible and ultraviolet (UV) light
Cindy, a 17-year-old counselor at a summer sports camp, scraped her knee playing basketball 2 weeks ago. At the time, she thought it was only a minor abrasion that would heal, like many others before it. Instead, the wound began to look like an insect bite and has continued to become increasingly painful and swollen.
The camp nurse examines the lesion and observes a large amount of pus oozing from the surface. Concerned that Cindy may have developed a potentially aggressive infection, she swabs the wound to collect a sample from the infection site. Then she cleans out the pus and dresses the wound, instructing Cindy to keep the area clean and to come back the next day. When Cindy leaves, the nurse sends the sample to the closest medical lab to be analyzed under a microscope.
What are some things we can learn about these bacteria by looking at them under a microscope?
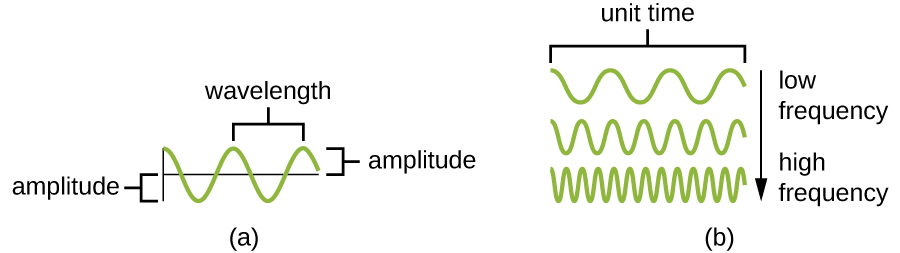
Visible light consists of electromagnetic waves that behave like other waves. Hence, many of the properties of light that are relevant to microscopy can be understood in terms of light’s behavior as a wave. An important property of light waves is the wavelength, or the distance between one peak of a wave and the next peak. The height of each peak (or depth of each trough) is called the amplitude. In contrast, the frequency of the wave is the rate of vibration of the wave, or the number of wavelengths within a specified time period (Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\)).
Interactions of Light
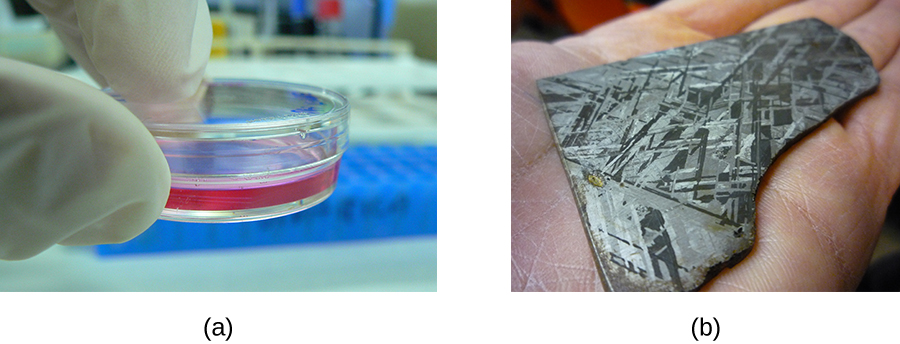
Light waves interact with materials by being reflected, absorbed, or transmitted. Reflection occurs when a wave bounces off of a material. For example, a red piece of cloth may reflect red light to our eyes while absorbing other colors of light. Absorbanceoccurs when a material captures the energy of a light wave. In the case of glow-in-the-dark plastics, the energy from light can be absorbed and then later re-emitted as another form of phosphorescence. Transmission occurs when a wave travels through a material, like light through glass (the process of transmission is called transmittance). When a material allows a large proportion of light to be transmitted, it may do so because it is thinner, or more transparent (having more transparency and less opacity). Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\) illustrates the difference between transparency and opacity.
Light waves can also interact with each other by interference, creating complex patterns of motion. Dropping two pebbles into a puddle causes the waves on the puddle’s surface to interact, creating complex interference patterns. Light waves can interact in the same way.
In addition to interfering with each other, light waves can also interact with small objects or openings by bending or scattering. This is called diffraction. Diffraction is larger when the object is smaller relative to the wavelength of the light (the distance between two consecutive peaks of a light wave). Often, when waves diffract in different directions around an obstacle or opening, they will interfere with each other.
- If a light wave has a long wavelength, is it likely to have a low or high frequency?
- If an object is transparent, does it reflect, absorb, or transmit light?
Lenses and Refraction
In the context of microscopy, refraction is perhaps the most important behavior exhibited by light waves. Refraction occurs when light waves change direction as they enter a new medium (Figure \(\PageIndex{3}\)). Different transparent materials transmit light at different speeds; thus, light can change speed when passing from one material to another. This change in speed usually also causes a change in direction (refraction), with the degree of change dependent on the angle of the incoming light.
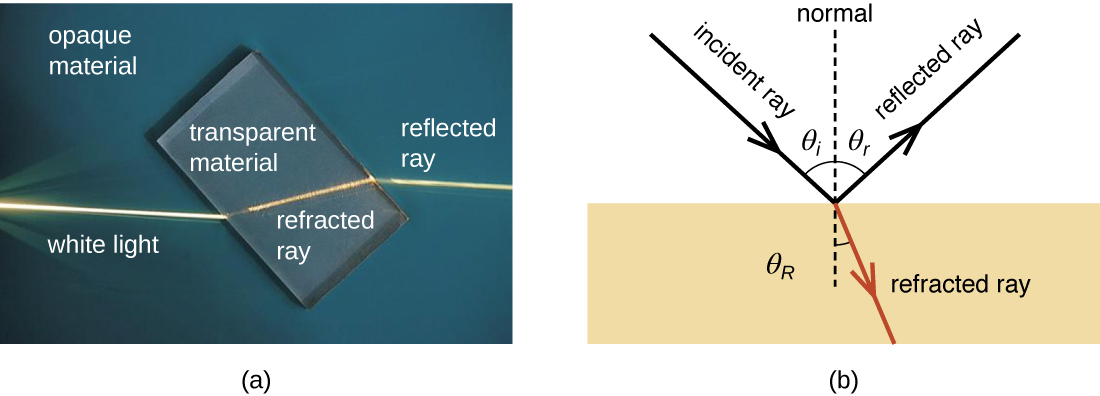
The extent to which a material slows transmission speed relative to empty space is called the refractive index of that material. Large differences between the refractive indices of two materials will result in a large amount of refraction when light passes from one material to the other. For example, light moves much more slowly through water than through air, so light entering water from air can change direction greatly. We say that the water has a higher refractive index than air (Figure \(\PageIndex{4}\)).

When light crosses a boundary into a material with a higher refractive index, its direction turns to be closer to perpendicular to the boundary (i.e., more toward a normal to that boundary; Figure \(\PageIndex{5}\)). This is the principle behind lenses. We can think of a lens as an object with a curved boundary (or a collection of prisms) that collects all of the light that strikes it and refracts it so that it all meets at a single point called the image point (focus). A convex lens can be used to magnify because it can focus at closer range than the human eye, producing a larger image. Concave lenses and mirrors can also be used in microscopes to redirect the light path. Figure \(\PageIndex{5}\) shows the focal point (the image point when light entering the lens is parallel) and the focal length (the distance to the focal point) for convex and concave lenses.
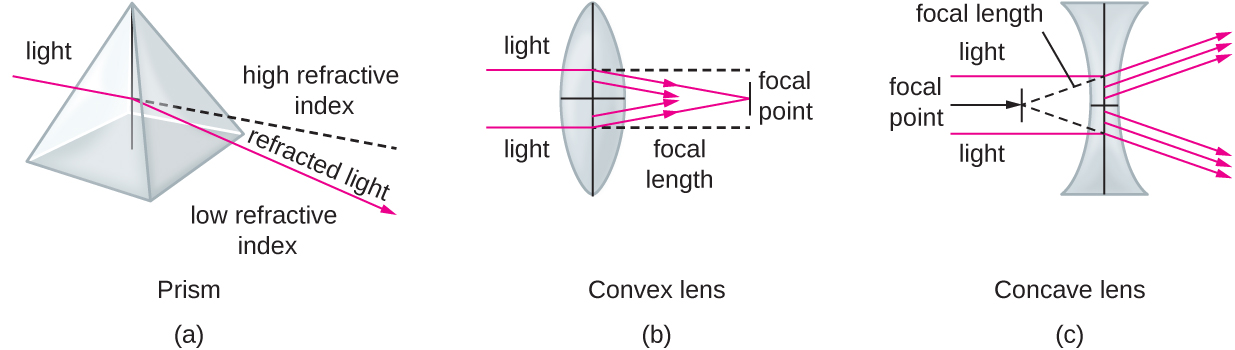
The human eye contains a lens that enables us to see images. This lens focuses the light reflecting off of objects in front of the eye onto the surface of the retina, which is like a screen in the back of the eye. Artificial lenses placed in front of the eye (contact lenses, glasses, or microscopic lenses) focus light before it is focused (again) by the lens of the eye, manipulating the image that ends up on the retina (e.g., by making it appear larger).
Images are commonly manipulated by controlling the distances between the object, the lens, and the screen, as well as the curvature of the lens. For example, for a given amount of curvature, when an object is closer to the lens, the focal points are farther from the lens. As a result, it is often necessary to manipulate these distances to create a focused image on a screen. Similarly, more curvature creates image points closer to the lens and a larger image when the image is in focus. This property is often described in terms of the focal distance, or distance to the focal point.
- Explain how a lens focuses light at the image point.
- Name some factors that affect the focal length of a lens.
Electromagnetic Spectrum and Color
Visible light is just one form of electromagnetic radiation (EMR), a type of energy that is all around us. Other forms of EMR include microwaves, X-rays, and radio waves, among others. The different types of EMR fall on the electromagnetic spectrum, which is defined in terms of wavelength and frequency. The spectrum of visible light occupies a relatively small range of frequencies between infrared and ultraviolet light (Figure \(\PageIndex{6}\)).
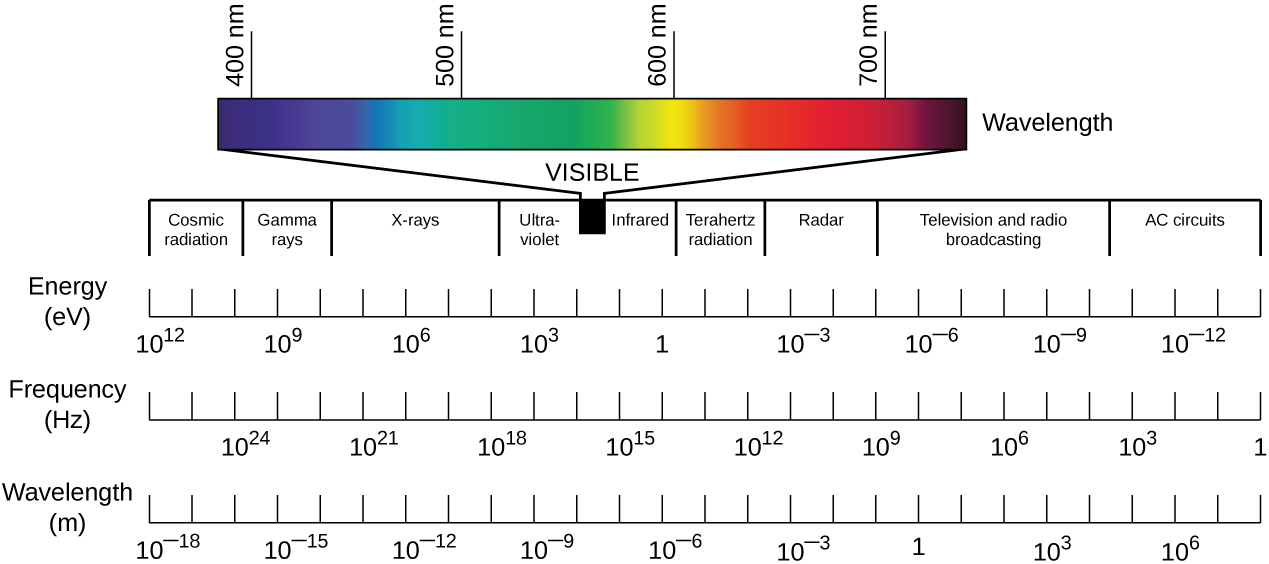
Whereas wavelength represents the distance between adjacent peaks of a light wave, frequency, in a simplified definition, represents the rate of oscillation. Waves with higher frequencies have shorter wavelengths and, therefore, have more oscillations per unit time than lower-frequency waves. Higher-frequency waves also contain more energy than lower-frequency waves. This energy is delivered as elementary particles called photons. Higher-frequency waves deliver more energetic photons than lower-frequency waves.
Photons with different energies interact differently with the retina. In the spectrum of visible light, each color corresponds to a particular frequency and wavelength (Figure \(\PageIndex{6}\)).The lowest frequency of visible light appears as the color red, whereas the highest appears as the color violet. When the retina receives visible light of many different frequencies, we perceive this as white light. However, white light can be separated into its component colors using refraction. If we pass white light through a prism, different colors will be refracted in different directions, creating a rainbow-like spectrum on a screen behind the prism. This separation of colors is called dispersion, and it occurs because, for a given material, the refractive index is different for different frequencies of light.
Certain materials can refract nonvisible forms of EMR and, in effect, transform them into visible light. Certain fluorescent dyes, for instance, absorb ultraviolet or blue light and then use the energy to emit photons of a different color, giving off light rather than simply vibrating. This occurs because the energy absorption causes electrons to jump to higher energy states, after which they then almost immediately fall back down to their ground states, emitting specific amounts of energy as photons. Not all of the energy is emitted in a given photon, so the emitted photons will be of lower energy and, thus, of lower frequency than the absorbed ones. Thus, a dye such as Texas red may be excited by blue light, but emit red light; or a dye such as fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) may absorb (invisible) high-energy ultraviolet light and emit green light (Figure \(\PageIndex{7}\)). In some materials, the photons may be emitted following a delay after absorption; in this case, the process is called phosphorescence. Glow-in-the-dark plastic works by using phosphorescent material.
- Which has a higher frequency: red light or green light?
- Explain why dispersion occurs when white light passes through a prism.
- Why do fluorescent dyes emit a different color of light than they absorb?
Magnification, Resolution, and Contrast
Microscopes magnify images and use the properties of light to create useful images of small objects. Magnification is defined as the ability of a lens to enlarge the image of an object when compared to the real object. For example, a magnification of 10⨯ means that the image appears 10 times the size of the object as viewed with the naked eye.
Greater magnification typically improves our ability to see details of small objects, but magnification alone is not sufficient to make the most useful images. It is often useful to enhance the resolution of objects: the ability to tell that two separate points or objects are separate. A low-resolution image appears fuzzy, whereas a high-resolution image appears sharp. Two factors affect resolution. The first is wavelength. Shorter wavelengths are able to resolve smaller objects; thus, an electron microscope has a much higher resolution than a light microscope, since it uses an electron beam with a very short wavelength, as opposed to the long-wavelength visible light used by a light microscope. The second factor that affects resolution is numerical aperture, which is a measure of a lens’s ability to gather light. The higher the numerical aperture, the better the resolution.
Even when a microscope has high resolution, it can be difficult to distinguish small structures in many specimens because microorganisms are relatively transparent. It is often necessary to increase contrast to detect different structures in a specimen. Various types of microscopes use different features of light or electrons to increase contrast—visible differences between the parts of a specimen (see Instruments of Microscopy). Additionally, dyes that bind to some structures but not others can be used to improve the contrast between images of relatively transparent objects (see Staining Microscopic Specimens).
- Explain the difference between magnification and resolution.
- Explain the difference between resolution and contrast.
- Name two factors that affect resolution.
Key Concepts and Summary
- Light waves interacting with materials may be reflected, absorbed, or transmitted, depending on the properties of the material.
- Light waves can interact with each other (interference) or be distorted by interactions with small objects or openings (diffraction).
- Refraction occurs when light waves change speed and direction as they pass from one medium to another. Differences in the refraction indices of two materials determine the magnitude of directional changes when light passes from one to the other.
- A lens is a medium with a curved surface that refracts and focuses light to produce an image.
- Visible light is part of the electromagnetic spectrum; light waves of different frequencies and wavelengths are distinguished as colors by the human eye.
- A prism can separate the colors of white light (dispersion) because different frequencies of light have different refractive indices for a given material.
- Fluorescent dyes and phosphorescent materials can effectively transform nonvisible electromagnetic radiation into visible light.
- The power of a microscope can be described in terms of its magnification and resolution.
- Resolution can be increased by shortening wavelength, increasing the numerical aperture of the lens, or using stains that enhance contrast.
Glossary
- absorbance
- when a molecule captures energy from a photon and vibrates or stretches, using the energy
- amplitude
- the height of a wave
- contrast
- visible differences between parts of a microscopic specimen
- diffraction
- the changing of direction (bending or spreading) that occurs when a light wave interacts with an opening or barrier
- dispersion
- the separation of light of different frequencies due to different degrees of refraction
- fluorescent
- the ability of certain materials to absorb energy and then immediately release that energy in the form of light
- focal length
- the distance from the lens to the image point when the object is at a definite distance from the lens (this is also the distance to the focal point)
- focal point
- a property of the lens; the image point when light entering the lens is parallel (i.e., the object is an infinite distance from the lens)
- frequency
- the rate of vibration for a light wave or other electromagnetic wave
- image point (focus)
- a property of the lens and the distance of the object to the lens; the point at which an image is in focus (the image point is often called the focus)
- interference
- distortion of a light wave due to interaction with another wave
- magnification
- the power of a microscope (or lens) to produce an image that appears larger than the actual specimen, expressed as a factor of the actual size
- numerical aperture
- a measure of a lens’s ability to gather light
- opacity
- the property of absorbing or blocking light
- phosphorescence
- the ability of certain materials to absorb energy and then release that energy as light after a delay
- reflection
- when light bounces back from a surface
- refraction
- bending of light waves, which occurs when a light wave passes from one medium to another
- refractive index
- a measure of the magnitude of slowing of light waves by a particular medium
- resolution
- the ability to distinguish between two points in an image
- transmittance
- the amount of light that passes through a medium
- transparency
- the property of allowing light to pass through
- wavelength
- the distance between one peak of a wave and the next peak


