4.3: Pedigrees review
- Page ID
- 65145
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\dsum}{\displaystyle\sum\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dint}{\displaystyle\int\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dlim}{\displaystyle\lim\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\(\newcommand{\longvect}{\overrightarrow}\)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)Key terms
| Term | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Pedigree | Chart that shows the presence or absence of a trait within a family across generations |
| Genotype | The genetic makeup of an organism (ex: TT) |
| Phenotype | The physical characteristics of an organism (ex: tall) |
| Dominant allele | Allele that is phenotypically expressed over another allele |
| Recessive allele | Allele that is only expressed in absence of a dominant allele |
| Autosomal trait | Trait that is located on an autosome (non-sex chromosome) |
| Sex-linked trait | Trait that is located on one of the two sex chromosomes |
| Homozygous | Having two identical alleles for a particular gene |
| Heterozygous | Having two different alleles for a particular gene |
Pedigrees
Pedigrees are used to analyze the pattern of inheritance of a particular trait throughout a family. Pedigrees show the presence or absence of a trait as it relates to the relationship among parents, offspring, and siblings.
Reading a pedigree
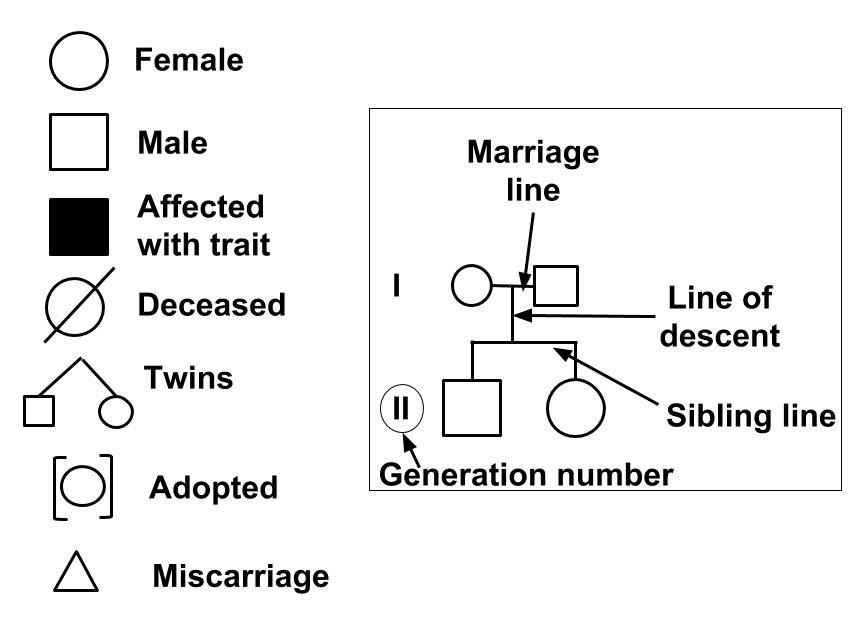
Pedigrees represent family members and relationships using standardized symbols.
By analyzing a pedigree, we can determine genotypes, identify phenotypes, and predict how a trait will be passed on in the future. The information from a pedigree makes it possible to determine how certain alleles are inherited: whether they are dominant, recessive, autosomal, or sex-linked.
To start reading a pedigree:
-
Determine whether the trait is dominant or recessive. If the trait is dominant, one of the parents must have the trait. Dominant traits will not skip a generation. If the trait is recessive, neither parent is required to have the trait since they can be heterozygous.
-
Determine if the chart shows an autosomal or sex-linked (usually X-linked) trait. For example, in X-linked recessive traits, males are much more commonly affected than females. In autosomal traits, both males and females are equally likely to be affected (usually in equal proportions).
Example: Autosomal dominant trait

The diagram shows the inheritance of freckles in a family. The allele for freckles (F) is dominant to the allele for no freckles (f).
At the top of the pedigree is a grandmother (individual I-2) who has freckles. Two of her three children have the trait (individuals II-3 and II-5) and three of her grandchildren have the trait (individuals III-3, III-4, and III-5).
- [What is the genotype of individual I-2?]
-
Since freckles are dominant to no freckles, an affected individual such as I-2 must at least have one F allele.
The trait shows up in all generations and affects both males and females equally. This suggests that it is an autosomal dominant trait.
Unaffected individuals must have two recessive alleles (ff) in order to not have freckles. If we notice, I-2 has some children who do not have freckles. In order to produce children with a genotype of ff, I-2 must be able to donate a f allele.
We can therefore conclude that her genotype is Ff.
Example: X-linked recessive trait
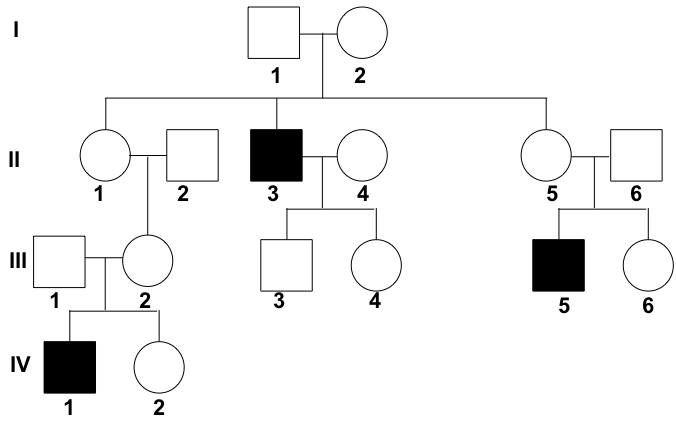
The diagram shows the inheritance of colorblindness in a family. Colorblindness is a recessive and X-linked trait \((\text{X}^b)\). The allele for normal vision is dominant and is represented by \(\text{X}^B\).
In generation I, neither parent has the trait, but one of their children (II-3) is colorblind. Because there are unaffected parents that have affected offspring, it can be assumed that the trait is recessive. In addition, the trait appears to affect males more than females (in this case, exclusively males are affected), suggesting that the trait may be X-linked.
- [What is the genotype of individual III-2?]
-
We can determine the genotype of III-2 by looking at her children. Since she is an unaffected female, she must have at least one normal vision allele \((\text{X}^B)\). Her two genotype options are then \(\text{X}^{B}\text{X}^{B}\) or \(\text{X}^{B}\text{X}^{b}\).
However, her son (IV-1) is colorblind, meaning that he has a genotype of \(\text{X}^{b}\text{Y}\). Because males always get their \(\text{X}\) chromosome from their mothers (and their \(\text{Y}\) from their fathers), his colorblind allele must come from III-2.
We can then determine that III-2's genotype is \(\text{X}^{B}\text{X}^{b}\), so she can pass the \(\text{X}^{b}\) on to her son.
Common mistakes and misconceptions
-
The presence of many affected individuals in a family does not always mean that the trait is dominant. The terms dominant and recessive refer to the way that a trait is expressed, not by how often it shows up in a family. In fact, although it is uncommon, a trait may be recessive but still show up in all generations of a pedigree.
-
You may not always be able to determine the genotype of an individual based on a pedigree. Sometimes an individual can either be homozygous dominant or heterozygous for a trait. Often, we can use the relationships between an individual and their parents, siblings, and offspring to determine genotypes. However, not all carriers are always explicitly indicated in a pedigree, and it may not be possible to determine based on the information provided.
Contributors and Attributions
Khan Academy (CC BY-NC-SA 3.0; All Khan Academy content is available for free at www.khanacademy.org)

