The Anatomy of the Kidney and Nephron
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
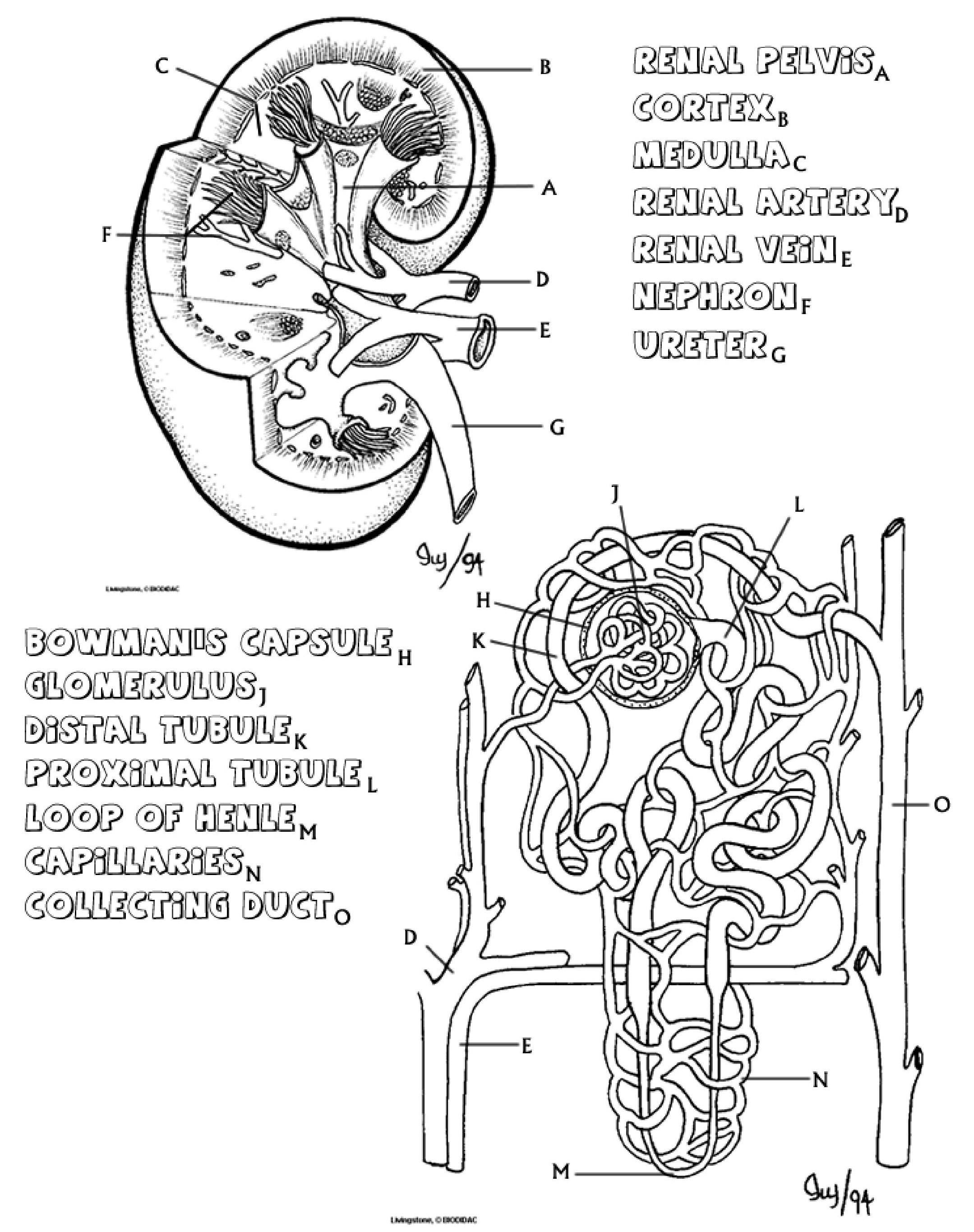.jpg?revision=2&size=bestfit&width=900&height=1138)
The kidney is a bean shaped organ that has an outer area called the cortex. The inner area, the renal medulla is composed of seven cone shaped renal pyramids (only 3 of them are shown in the image) with the tubes visible from them making up a collection of nephrons. The renal pyramids merge to form the renal pelvis at the center of the kidney, urine collects here before draining into the ureter and traveling to the bladder for storage.
- Color the medulla area light green. Color the cortex pink, and the renal pelvis and ureter yellow. The nephrons pictured on the kidney should be colored orange .
- Note the two vessels attached to the kidney, color the artery red and the vein blue .
If you view a nephron close up, as shown in the second picture, you can see that it is a complex structure composed of many tubes, and each kidney has about 1 million nephrons. The nephron's primary function is to filter waste from the blood. The nephron has three major parts: the glomerulus, the Bowman's Capsule, and the tubules, which consist of the promimal and distal tubule and the Loop of Henle.
Blood enters the kidney from the renal artery and moves into the glomerulus, where filtration occurs. Filtration is the process by which water and dissolved particles are pulled out of the blood. The resulting liquid, called filtrate contains many of the toxic substances that might have accumulated in the blood (like ammonia). The glomerulus is enclosed by the Bowman's capsule, small molecules and water can pass through this area, but larger molecules do not. The filtrate is then collected in the Bowman's capsule for transport through the nephron.
- Color the renal artery red on both images. On the second image the artery enters the glomerulus and then exits to twist around the larger tubules. Color the renal vein blue , it is also twisted around the tubules. These two vessels, the artery and the veins meet near the loop of henle, color this area purple .
- Color the Bowman's capsule brown , leave the glomerulus white, you should have already colored the arteries inside it red.
The nephron itself will restore vital nutrients and water back into the blood, while retaining the waste products the body needs to eliminate. Two processes accomplish this task: tubular reabsorption and tubular secretion. During tubular reabsorption, cells in the proximal tubule remove water and nutrients from the filtrate and pass them back into the blood, wastes such as urea are retained in the tubule. During tubular secretion, wastes that were not initially filtered out in the Bowman's capsule are removed from the blood in the distal tubule. Ammonia and many drugs are removed from the blood during tubular secretion.
- Color the proximal tubule dark green , until it reaches the loop of henle. The loop of henle should be colored pink , and then when it changes into the distal tubule, color the distal tubule light green .
Notice the vessels that wrap around the tubules. At the points of contact with the tubule and the capillaries, water and nutrients are reabsorbed into the blood. In addition, wastes remaining in the blood after filtration are passed to the tubule. The filtrate flows from the proximal tubule and into the Loop of Henle. The loop of Henle concentrates the filtrate, by removing more water from it, and passes it to the distal tubule. From the distal tubule it travels to the collecting duct - now called urine. The collecting duct prepares the urine for transport out of the body, it is collected in the renal pelvis where it eventually enters the ureter. From there it goes to the bladder.
- Color both the collecting duct and the ureter yellow .
Questions
- What is the function of the glomerulus and the bowman's capsule?
- What is the function of the loop of henle?
- Compare the processes of the distal tubule to the proximal tubule.
- Describe the path the blood takes as it flows through the nephron.
- Describe the path the filtrate takes as it flows through the nephron (beginning at the glomerulus).
- Diffusion is a process where molecules move from areas of high concentration to low concentration. Toxins diffuse from the blood and into the tubules of the nephron. How might this process be altered if there were fewer blood vessels intertwined with the tubules?
- Dialysis is a process where a person with nonfunctioning kidneys can have their blood filtered by a machine. The image below outlines this process.
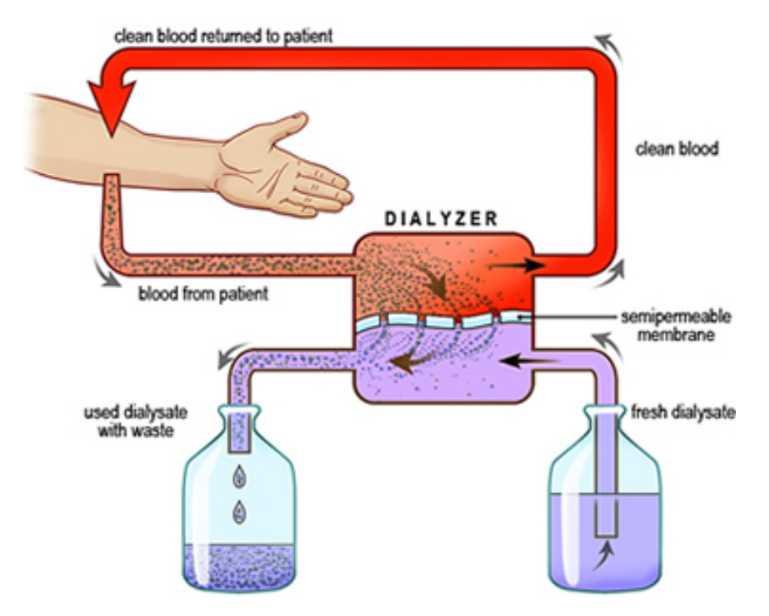
Re-label the image to indicate which parts would match the anatomy of the kidney:
- renal artery
- renal vein
- ureter
- nephron
- bladder


