3.6: Mineral Resources and Mining
- Page ID
- 164496
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\dsum}{\displaystyle\sum\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dint}{\displaystyle\int\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dlim}{\displaystyle\lim\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\(\newcommand{\longvect}{\overrightarrow}\)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)![By James St. John [<a data-cke-saved-href="http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0" href="http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0">CC BY 2.0</a>], <a data-cke-saved-href="https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File%3AMother_Lode_Gold_OreHarvard_mine_quartz-gold_vein.jpg" href="https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File%3AMother_Lode_Gold_OreHarvard_mine_quartz-gold_vein.jpg">via Wikimedia Commons</a> The yellow gold is inside white quartz.](https://bio.libretexts.org/@api/deki/files/57537/Mother_Lode_Gold_OreHarvard_mine_quartz-gold_vein-300x209.jpg?revision=1&size=bestfit&width=338&height=235)
Mineral resources, while principally nonrenewable, are generally placed in two main categories: metallic (containing metals) or nonmetallic (containing other useful materials). Metallic minerals are those from which valuable metals (e.g. iron, copper) can be extracted for commercial use. Metals that are considered geochemically abundant occur at crustal abundances of 0.1 percent or more (e.g. iron, aluminum, manganese, magnesium, titanium). Metals that are considered geochemically scarce occur at crustal abundances of less than 0.1 percent (e.g. nickel, copper, zinc, platinum metals). Some important metallic minerals are: hematite (a source of iron), bauxite (a source of aluminum), sphalerite (a source of zinc) and galena (a source of lead). Metallic minerals occasionally but rarely occur as a single element (e.g. native gold or copper). Most mining is focused on metallic minerals. A significant part of the advancement of human society has been developing the knowledge and technologies that yielded metal from the Earth and allowed the machines, buildings, and monetary systems that dominate our world today. The location and recovery of these metals have been a key facet of the study of geology since its inception.
While receiving much less attention, nonmetallic mineral resources (also known as industrial minerals) are just as vital to ancient and modern society as metallic minerals. Nonmetallic minerals are valuable, not for the metals they contain, but for their properties as chemical compounds. Because they are commonly used in industry, they are also often referred to as industrial minerals. They are classified according to their use. The most basic of these is building stone. Limestone, travertine, granite, slate, and marble are common building stones and have been quarried for centuries (Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\)). Some industrial minerals are also used for building materials (e.g. gypsum for plaster and kaolin for bricks). Some industrial minerals are used as sources of important chemicals (e.g. halite for sodium chloride and borax for borates). For everything made out of concrete or asphalt, we need sand and gravel. To make the cement that holds concrete together, we also need limestone. Others are used for making fertilizers (e.g. apatite for phosphate and sylvite for potassium). Still others are used as abrasives (e.g. diamond and corrundum). For the glass in our computer screens and for glass-sided buildings, we need silica sand plus sodium oxide (Na2O), sodium carbonate (Na2CO3), and calcium oxide (CaO). For a wide range of applications (e.g., ceramics and many industrial processes), we also need various types of clay. Some nonmetallic mineral resources are not mineral specific; nearly any rock or mineral can be used. This is generally called aggregate and is used in concrete, roads, and foundations. Gravel is one of the more common aggregates. Quarried rock is also used in some applications where rounded gravel isn’t suitable, such as the ballast (road bed) for railways, where crushed angular rock is needed.
![By Michele Buzzi, Studio Cicero. [<a data-cke-saved-href="http://www.gnu.org/copyleft/fdl.html" href="http://www.gnu.org/copyleft/fdl.html">GFDL</a>, <a data-cke-saved-href="http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/" href="http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/">CC-BY-SA-3.0</a> or <a data-cke-saved-href="http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.5" href="http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.5">CC BY 2.5</a>], <a data-cke-saved-href="https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File%3AMarblequarry.JPG" href="https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File%3AMarblequarry.JPG">via Wikimedia Commons</a> The image shows a hillside with blocks of marble removed.](https://bio.libretexts.org/@api/deki/files/57539/CarraraMarblequarry-225x300.jpg?revision=1)
Mineral Deposits
Minerals are everywhere around us. For example, the ocean is estimated to contain more than 70 million tons of gold. Yet, it would be much too expensive to recover that gold because of its very low concentration in the water. Minerals must be concentrated into deposits to make their collection economically feasible. A mineral deposit containing one or more minerals that can be extracted profitably is called an ore. Many minerals are commonly found together (e.g. quartz and gold; molybdenum, tin and tungsten; copper, lead and zinc; platinum and palladium). Because various geologic processes can create local enrichments of minerals, mineral deposits can be classified according to the concentration process that formed them. The five basic types of mineral deposits are: hydrothermal, magmatic, sedimentary, placer and residual.
If the material can be mined at a profit, the body constitutes an ore deposit. Typically, the term ore is used for only metal-bearing minerals, though the concept of ore as a non-renewable resource can be applied to valuable concentrations of fossil fuels, building stones, and other non-metal deposits, even groundwater. Mineral ores are found in just a relatively few areas, because it takes a special set of circumstances to create them. Therefore, the signs of a mineral deposit are often small and difficult to recognize. Locating deposits requires experience and knowledge. Geologists can search for years before finding an economic mineral deposit. Deposit size, its mineral content, extracting efficiency, processing costs and market value of the processed minerals are all factors that determine if a mineral deposit can be profitably developed. For example, when the market price of copper increased significantly in the 1970s, some marginal or low-grade copper deposits suddenly became profitable ore bodies.
Magmatic Deposits
Magmatic mineral deposits are formed when processes such as partial melting and fractional crystallization occur during the melting and cooling of rocks. Layered intrusion (typically ultramafic to mafic) can be host to deposits that contain copper, nickel, platinum-palladium-rhodium, and chromium. The Stillwater Complex in Montana is an example of an economic layered mafic intrusion [30]. Associated deposit types can contain chromium or titanium-vanadium. The largest magmatic deposits in the world are the chromite deposits in the Bushveld Igneous Complex in South Africa [31] (Figure \(\PageIndex{3}\)). Rocks of the Bushveld Igneous Complex have an areal extent larger than the state of Utah. The chromite occurs in layers, which resemble sedimentary layers, except this occurred within a crystallizing magma chamber.
![By kevinzim / Kevin Walsh [<a data-cke-saved-href="http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0" href="http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0">CC BY 2.0</a>], <a data-cke-saved-href="https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File%3AChromitite_Bushveld_South_Africa.jpg" href="https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File%3AChromitite_Bushveld_South_Africa.jpg">via Wikimedia Commons</a> The rock has several layers, with the dark layers being the ones with value.](https://bio.libretexts.org/@api/deki/files/57543/LayeredIntrusionChromitite_Bushveld_South_Africa-300x211.jpg?revision=1)
Water and other volatiles that are not incorporated into mineral crystals while a magma crystallizes become concentrated around the margins of these crystallizing magmas. Ions in these hot fluids are very mobile and can form exceptionally large crystals. Once crystallized, masses of these large crystals are called pegmatites that form from the concentration of magma fluids near the end of crystallization when nearly the entire magma body has crystallized (Figure \(\PageIndex{4}\)). In addition to minerals that are predominant in the main igneous mass, such as quartz, feldspar, and mica, pegmatite bodies may also contain very large crystals of unusual minerals that contain rare elements like beryllium, lithium, tantalum, niobium, and tin, as well as native elements like gold [32]. Such pegmatites are ores of these metals.
![By Parent Géry (Own work) [<a data-cke-saved-href="http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0" href="http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0">CC BY-SA 3.0</a> or <a data-cke-saved-href="http://www.gnu.org/copyleft/fdl.html" href="http://www.gnu.org/copyleft/fdl.html">GFDL</a>], <a data-cke-saved-href="https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File%3AElba%C3%AFte_et_mica_(Br%C3%A9sil)_1.JPG" href="https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File%3AElba%C3%AFte_et_mica_(Br%C3%A9sil)_1.JPG">via Wikimedia Commons</a> The rock is mostly green and purple](https://bio.libretexts.org/@api/deki/files/57540/Elbai%25CC%2588te_et_mica_Bre%25CC%2581sil_1-300x199.jpg?revision=1)
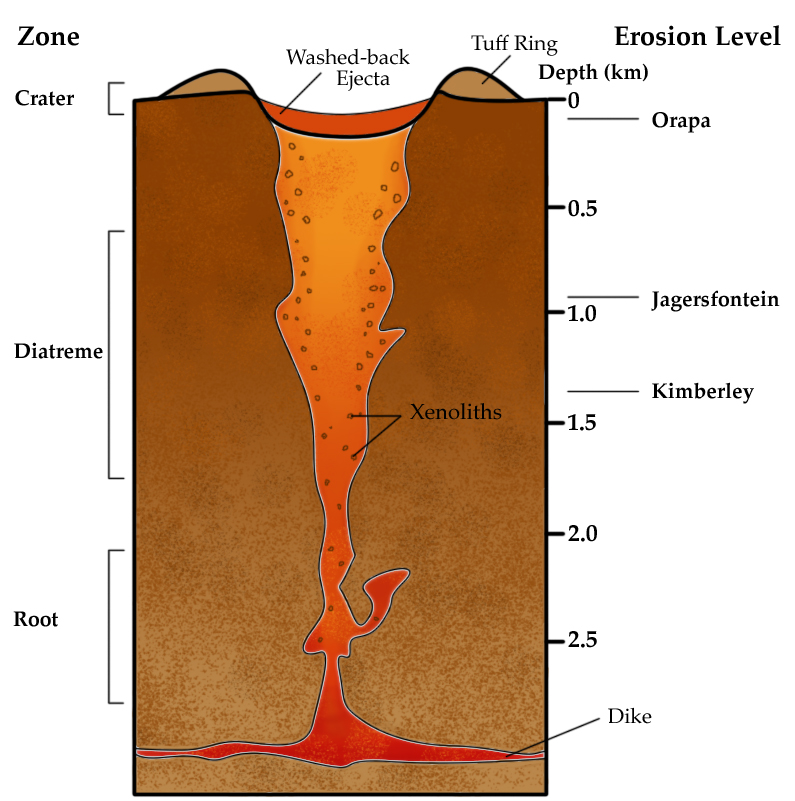
An unusual magmatic process is a kimberlite pipe, which is a volcanic conduit that transports ultramafic magma from depths in the mantle to the surface (Figure \(\PageIndex{5}\)). Diamonds, which are formed at great temperature and depth, are transported this way to locations where they can be mined. The process that emplaced these kimberlite (ultramafic) rocks is no longer common on Earth, and most of the known deposits are Archean [33].
Hydrothermal Deposits
Hydrothermal mineral deposits are formed when minerals are deposited by hot, aqueous solutions flowing through fractures and pore spaces of crustal rock (Figure \(\PageIndex{6}\)). Many famous ore bodies have resulted from hydrothermal deposition, including the tin mines in Cornwall, England and the copper mines in Arizona and Utah.
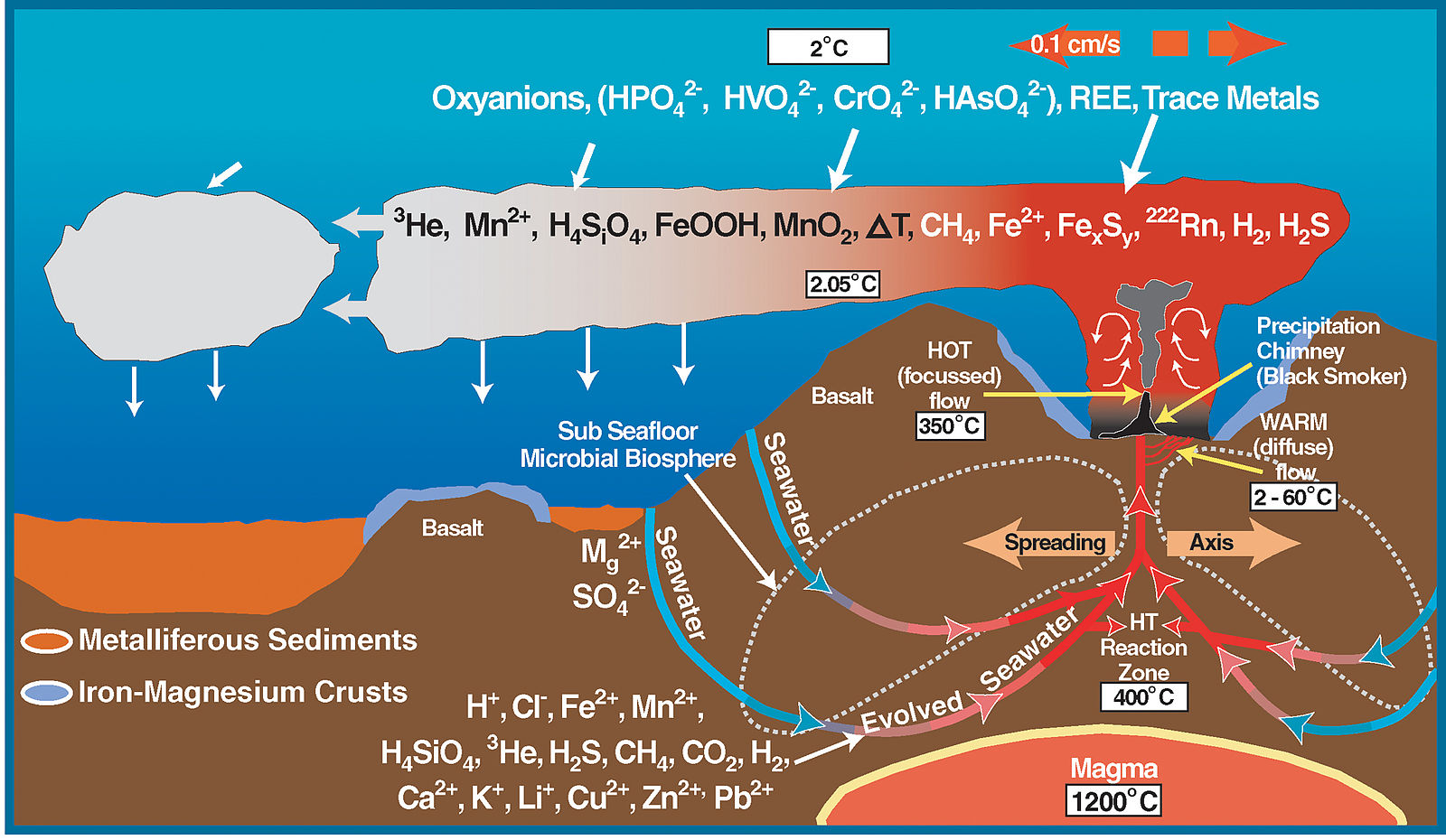
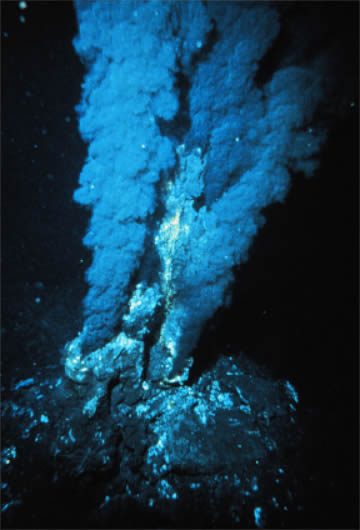
Figure \(\PageIndex{7}\): Black Smoker A billowing discharge of superheated mineral-rich water at an oceanic ridge, in the Atlantic Ocean. Black “smoke” is actually from metallic sulfide minerals that form modern ore deposits. Source: P. Rona of U.S. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration via Wikimedia Commons
The most active hydrothermal process today produces volcanogenic massive sulfide (VMS) deposits, which form from black smoker activity (Figure \(\PageIndex{7}\)) near mid-ocean ridges all over the world, and commonly contain copper, zinc, lead, gold, and silver when found on the surface [34]. The largest of these deposits occur in Precambrian age rocks. The Jerome deposit in central Arizona is a good example.
Another type of deposit which draws on heated water from magma is a porphyry deposit (Figure \(\PageIndex{8}\)). This is not to be confused with the igneous texture porphyritic, although the name is derived from the porphyritic texture that is nearly always present in the igneous rocks in a porphyry deposit. Several types of porphyry deposits exist: porphyry copper, porphyry molybdenum, and porphyry tin. They are characterized by the presence of low-grade disseminated ore minerals closely associated with intermediate and felsic intrusive rocks over a very large area [35]. Porphyry deposits are typically the largest mines on Earth. One of the largest, richest, and possibly best-studied mines in the world is Utah’s Bingham Canyon open-pit mine, which has had over 100 years of high production of several elements including copper, gold, molybdenum, and silver. Associated underground carbonate replacement deposits have produced lead, zinc, gold, silver, and copper [36]. Past open pit production at this mine was dominated by copper and gold from chalcopyrite and bornite. Gold occurs in minor quantities in the copper-bearing mineral, but the large scale of production makes Bingham Canyon one of the largest gold mines in the U.S. Future production may be more copper and molybdenum (molybdenite) from deeper underground mines.
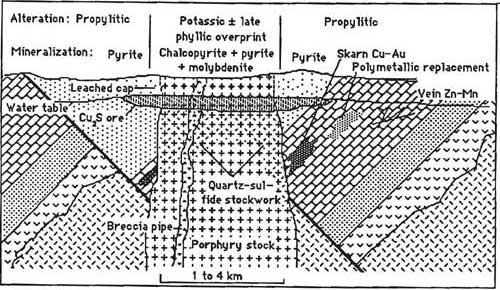
The majority of porphyry copper deposits owe their economic value to concentration by weathering processes occurring millions of years after the hosting intrusion called supergene enrichment (Figure \(\PageIndex{9}\)). These occur once the hydrothermal event has ceased and the ore body has been uplifted, eroded, and exposed to oxidation [37]. When the upper pyrite-rich portion of the deposit is exposed to rain, pyrite in the oxidizing zone creates an extremely acid condition which dissolves copper out of copper minerals such as chalcopyrite, converting the chalcopyrite to iron oxides like hematite or goethite. The copper is carried downward in the solution until it arrives at the groundwater table and a reducing environment where the copper precipitates, converting primary copper minerals into secondary higher-copper content minerals. Chalcopyrite (35% Cu) is converted to bornite (63% Cu) and ultimately chalcocite (80% Cu). Without this enriched zone (2 to 5 times higher in copper content than the main deposit) most porphyry copper deposits would not be economic.
![By Stephanie Salisbury (IMG_4218) [<a data-cke-saved-href="http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0" href="http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0">CC BY 2.0</a>], <a data-cke-saved-href="https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File%3AMorenci_Mine_2012.jpg" href="https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File%3AMorenci_Mine_2012.jpg">via Wikimedia Commons</a> The mine contains grey rocks, which are not enriched, and red rocks, which is where the enrichment occurs.](https://bio.libretexts.org/@api/deki/files/57541/Morenci_Mine_2012-300x200.jpg?revision=1&size=bestfit&width=365&height=243)
If limestone or other calcareous sedimentary rocks are present adjacent to the magmatic body, then another type of ore deposit called a skarn deposit can form (Figure \(\PageIndex{10}\)). These metamorphic rocks form as magma-derived, highly saline metalliferous fluids react with carbonate rocks, creating calcium-magnesium-silicate minerals like pyroxene, amphibole, and garnet, as well as high-grade zones of iron, copper, and zinc minerals and gold [38]. Intrusions that are genetically related to the intrusion that made the Bingham Canyon deposit have also produced copper-gold skarns that were mined by the early European settlers in Utah [39; 40]. Metamorphism of iron and/or sulfide deposits commonly results in an increase in grain size that makes separation of gangue from the desired sulfide or oxide minerals much easier.
![By Siim Sepp (Sandatlas) (Own work) [<a data-cke-saved-href="http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0" href="http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0">CC BY-SA 3.0</a>], <a data-cke-saved-href="https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File%3A00031_6_cm_grossular_calcite_augite_skarn.jpg" href="https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File%3A00031_6_cm_grossular_calcite_augite_skarn.jpg">via Wikimedia Commons</a> Calcite is blue, augite green, and garnet brown/orange in this rock.](https://bio.libretexts.org/@api/deki/files/57547/16.3_6_cm_grossular_calcite_augite_skarn-300x255.jpg?revision=1)
Sediment-hosted disseminated gold deposits consist of low concentrations of microscopic gold as inclusions and disseminated atoms in pyrite crystals (Figure \(\PageIndex{11}\)). These are formed via low-level hydrothermal reactions (generally in the realm of diagenesis) that occur in certain rock types, namely muddy carbonates and limey mudstones. This hydrothermal alteration is generally far-removed from a magma source but can be found in extended rocks with a high geothermal gradient. The earliest locally mined deposit of this type was the Mercur deposit in the Oquirrh Mountains of Utah where almost one million ounces of gold were recovered between 1890 and 1917. In the 1960s a metallurgical process using cyanide was developed for these types of low-grade ores. These deposits are also called Carlin-type deposits because the disseminated deposit near Carlin, Nevada is where the new technology was first applied and because the first definitive scientific studies were conducted there [41]. Gold was introduced by hydrothermal fluids which reacted with silty calcareous rocks, removing carbonate, creating additional permeability, and adding silica and gold-bearing pyrite in the pore space between grains. The Betze-Post mine and the Gold Quarry mine on the “Carlin Trend” are two of the largest of the disseminated gold deposits in Nevada. Similar deposits, but not as large, have been found in China, Iran, and Macedonia [42].
![<a data-cke-saved-href="https://en.Wikipedia.org/wiki/User:Qfl247" href="https://en.Wikipedia.org/wiki/User:Qfl247" class="extiw" title="en:User:Qfl247">Matt Affolter</a> at <a class="external text" data-cke-saved-href="http://en.Wikipedia.org" href="http://en.Wikipedia.org">en.Wikipedia</a> [<a data-cke-saved-href="http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0" href="http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0">CC BY-SA 3.0</a> or <a data-cke-saved-href="http://www.gnu.org/copyleft/fdl.html" href="http://www.gnu.org/copyleft/fdl.html">GFDL</a>], <a data-cke-saved-href="https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File%3AGoldinPyriteDrainage_acide.JPG" href="https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File%3AGoldinPyriteDrainage_acide.JPG">from Wikimedia Commons</a> The rock is red.](https://bio.libretexts.org/@api/deki/files/57538/GoldinPyrite-300x240.jpg?revision=1&size=bestfit&width=320&height=256)
Deposits from Sedimentary and Weathering Processes
![<a data-cke-saved-href="https://en.Wikipedia.org/wiki/User:Qfl247" href="https://en.Wikipedia.org/wiki/User:Qfl247" class="extiw" title="Wikipedia:User:Qfl247">Matt Affolter</a> at <a data-cke-saved-href="https://en.Wikipedia.org/wiki/" href="https://en.Wikipedia.org/wiki/" class="extiw" title="Wikipedia:">English Wikipedia</a> [<a data-cke-saved-href="http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0" href="http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0">CC BY-SA 3.0</a> or <a data-cke-saved-href="http://www.gnu.org/copyleft/fdl.html" href="http://www.gnu.org/copyleft/fdl.html">GFDL</a>], <a data-cke-saved-href="https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File%3AUraniumMineUtah.JPG" href="https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File%3AUraniumMineUtah.JPG">via Wikimedia Commons</a> A dark shaft runs into the mountain.](https://bio.libretexts.org/@api/deki/files/57535/16.1_UraniumMineUtah-300x225.jpg?revision=1&size=bestfit&width=325&height=244)
Geochemical processes that occur at or near the surface without the aid of magma also concentrate metals, but to a lesser degree than hydrothermal processes. One of the main reactions is redox (short for reduction/oxidation) chemistry, which has to do with the amount of available oxygen in a system. Places where oxygen is plentiful, as in the atmosphere today, are considered oxidizing environments, while oxygen-poor environments are considered reducing. Uranium deposition is an example of redox mobilization. Uranium is soluble in oxidizing groundwater environments and precipitates as uraninite when reducing conditions are encountered. Many of the deposits across the Colorado Plateau (e.g. Moab, Utah) were formed by this method [43].
Redox reactions were also responsible for the creation of banded iron formations (BIFs), which are interbedded layers of iron oxide (hematite and magnetite), chert, and shale beds (Figure \(\PageIndex{13}\)). These deposits formed early in the Earth’s history as the atmosphere was becoming oxygenated. Cyclic oxygenation of iron-rich waters initiated the precipitation of the iron beds. Because BIFs are generally Precambrian in age, they are only found in some of the older exposed rocks in the United States, in the upper peninsula of Michigan and northeastern Minnesota [44].
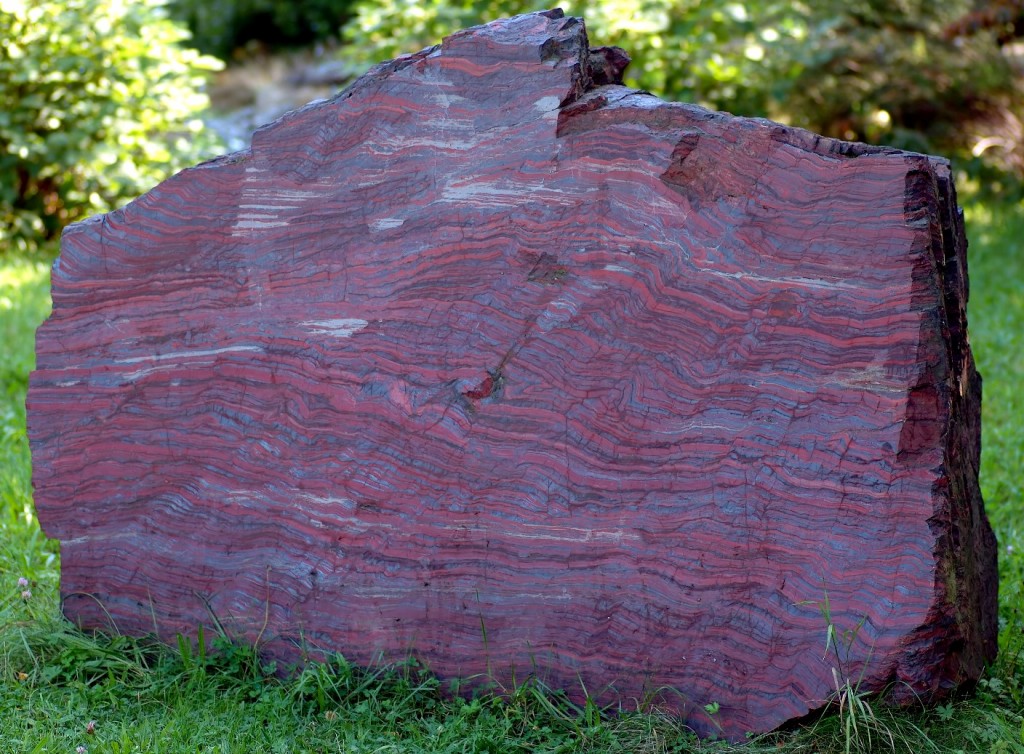

Figure \(\PageIndex{13}\): Banded iron formation from an unknown location in North America on display at a museum in Germany. The rock is about 2 m across. The dark grey layers are magnetite and the red layers are hematite. Chert is also present. [https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikiped...%28aka%29.jpg]
Deep, saline, connate fluids (trapped in the pore spaces), within sedimentary basins may be highly metalliferous. When expelled outward and upward during basin compaction, these fluids may form lead and zinc deposits in limestone by replacement or by filling open spaces (caves, faults) and in sandstone by filling pore spaces. The most famous of these are called Mississippi Valley-type deposits [44] (Figure \(\PageIndex{14}\)). Also known as carbonate-hosted replacement deposits, they are large deposits of galena and sphalerite (lead and zinc ores) which form from fluids in the temperature range of 100 to 200°C. Although they are named for occurrences along the Mississippi River Valley in the United States, they are found worldwide.
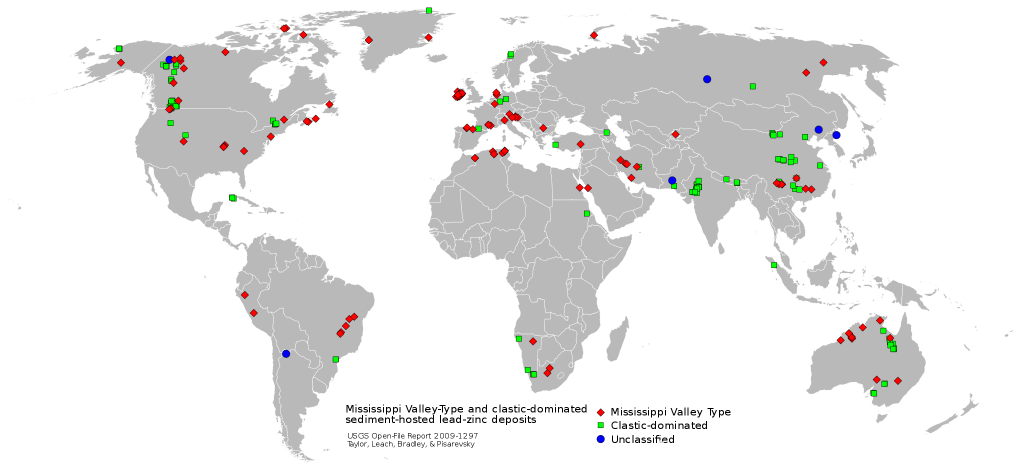
Sediment-hosted copper deposits occurring in sandstones, shales, and marls are enormous in size and their contained resources are comparable to porphyry copper deposits. These were most-likely formed diagenetically by groundwater fluids in highly-permeable rocks [45]. Well-known examples are the Kupferschiefer in Europe, which has an areal coverage of >500,000 Km2, and the Zambian Copper Belt in Africa.
![Rob Lavinsky, <a rel="nofollow" class="external text" data-cke-saved-href="http://www.irocks.com/" href="http://www.irocks.com/">iRocks.com</a> – CC-BY-SA-3.0 [<a data-cke-saved-href="http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0" href="http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0">CC BY-SA 3.0</a>], <a data-cke-saved-href="https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File%3AApatite-(CaF)-280343.jpg" href="https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File%3AApatite-(CaF)-280343.jpg">via Wikimedia Commons</a> The crystal is hexagonal and light green.](https://bio.libretexts.org/@api/deki/files/57545/Apatite-CaF-280343-300x267.jpg?revision=1)
Phosphorus is an essential element that occurs in the mineral apatite, which is found in trace amounts in common igneous rocks (Figure \(\PageIndex{15}\)). Phosphorite rock, which is formed in sedimentary environments in the ocean [50], contains abundant apatite and is mined to make fertilizer. Without phosphorus, life as we know it is not possible. Phosphorous is a major component of bone and a key component of DNA. Bone ash and guano are natural sources of phosphorus.
![By Werner Schellmann (Own work) [<a data-cke-saved-href="http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/2.5" href="http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/2.5">CC BY-SA 2.5</a>], <a data-cke-saved-href="https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File%3ABauxite_with_unweathered_rock_core._C_021.jpg" href="https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File%3ABauxite_with_unweathered_rock_core._C_021.jpg">via Wikimedia Commons</a> The outside of the rock is tan and weathered, the inside is grey.](https://bio.libretexts.org/@api/deki/files/57548/Bauxite_with_unweathered_rock_core._C_021-300x195.jpg?revision=1&size=bestfit&width=338&height=220)
Residual mineral deposits can form when weathering processes remove water soluble minerals from an area, leaving a concentration of less soluble minerals. The aluminum ore, bauxite, was originally formed in this manner under tropical weathering conditions [46] (Figure \(\PageIndex{16}\)). The best known bauxite deposit in the United States occurs in Arkansas. Aluminum concentrates in soils as feldspar and ferromagnesian minerals in igneous and metamorphic rocks undergo chemical weathering processes. Weathering of ultramafic rocks results in the formation of nickel-rich soils and weathering of magnetite and hematite in banded iron formation results in the formation of goethite, a friable mineral that is easily mined for its iron content.
At the earth’s surface, the physical process of mass wasting or fluid movement concentrates high-density minerals by hydraulic sorting. When these minerals are concentrated in streams, rivers, and beaches, they are called placer deposits, whether in modern sands or ancient lithified rocks [47] (Figure \(\PageIndex{17}\)). Native gold, native platinum, zircon, ilmenite, rutile, magnetite, diamonds, and other gemstones can be found in placers. Humans have mimicked this natural process to recover gold manually by gold panning and by mechanized means such as dredging.
![By Photograph taken by Mark A. Wilson (Department of Geology, The College of Wooster). [1] (Original photograph) [Public domain], <a data-cke-saved-href="https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File%3AHeavyMineralsBeachSand.jpg" href="https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File%3AHeavyMineralsBeachSand.jpg">via Wikimedia Commons</a> The tan rock has dark streaks of minerals.](https://bio.libretexts.org/@api/deki/files/57546/HeavyMineralsBeachSand-300x205.jpg?revision=1&size=bestfit&width=337&height=230)
The best types of aggregate (sand and gravel) resources are those that have been sorted by streams, and in Canada the most abundant and accessible fluvial deposits are associated with glaciation (Figure \(\PageIndex{18}\)). That doesn’t include till of course, because it has too much silt and clay, but it does include glaciofluvial outwash, which is present in thick deposits in many parts of the country, similar to the one shown in Figure 20.15. In a typical gravel pit, these materials are graded on-site according to size and then used in a wide range of applications from constructing huge concrete dams to filling children’s sandboxes. Sand is also used to make glass, but for most types of glass, it has to be at least 95% quartz (which the sandy layers shown in Figure 20.15 are definitely not), and for high-purity glass and the silicon wafers used for electronics, the source sand has to be over 98% quartz.
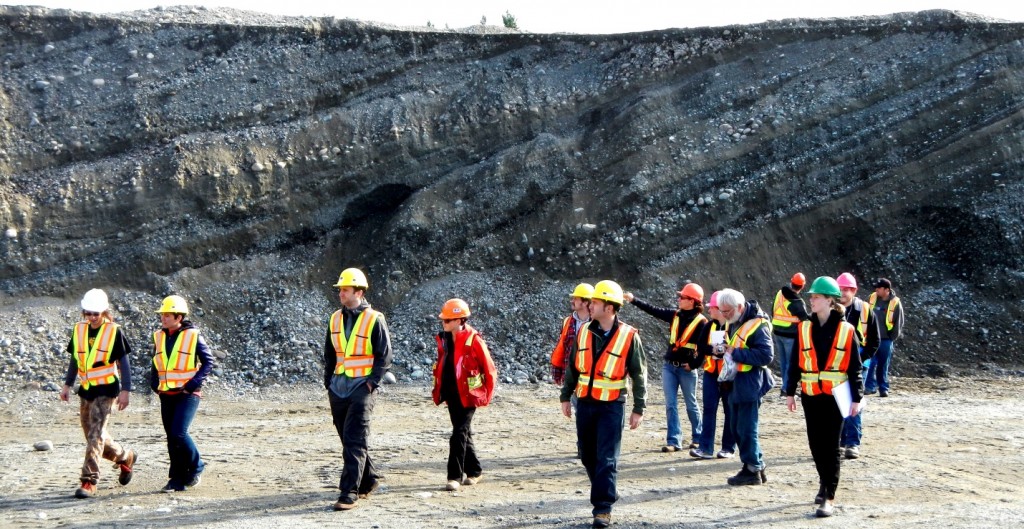

Figure \(\PageIndex{18}\): Sand and gravel in an aggregate pit near Nanaimo, BC. [SE]
Evaporite deposits form in restricted basins, such as the Great Salt Lake or the Dead Sea, where evaporation of water exceeds the recharge of water into the basin [49] (Figure \(\PageIndex{19}\)). As the waters evaporate, soluble minerals are concentrated and become supersaturated, at which point they precipitate from the now highly-saline waters. If these conditions persist for long stretches of time, thick deposits of rock salt and rock gypsum and other minerals can accumulate.
![By Hermann Luyken (Own work) [<a data-cke-saved-href="http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/deed.en" href="http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/deed.en">CC0</a>], <a data-cke-saved-href="https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File%3A2012.10.02.111543_Bonneville_Salt_Flats_Utah.jpg" href="https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File%3A2012.10.02.111543_Bonneville_Salt_Flats_Utah.jpg">via Wikimedia Commons</a> The ground is white and flat for a long distance.](https://bio.libretexts.org/@api/deki/files/57536/Bonneville_Salt_Flats_Utah-300x200.jpg?revision=1&size=bestfit&width=342&height=228)
Evaporite minerals like halite are used in our food as common table salt. Salt was a vitally important economic resource prior to refrigeration as a food preservative. While still used in food, now it is mainly mined as a chemical agent, water softener, or a de-icer for roads. The largest salt mine in the world is at Goderich, Ontario, where salt is recovered from the 100 m thick Silurian Salina Formation. Gypsum (CaSO4.2H20) is a common nonmetallic mineral used as a building material, being the main component of drywall. It is also used as a fertilizer. Other evaporites include sylvite (potassium chloride) and bischofite (magnesium chloride), both of which are used in agriculture, medicine, food processing, and other applications. Potash, a group of highly soluble potassium-bearing evaporite minerals, is used as a fertilizer. In hyperarid locations, even rarer and more complex evaporites, like borax, trona, ulexite, and hanksite, are found and mined. They can be found in such localities as Searles Dry Lake and Death Valley, California, and in ancient evaporite deposits of the Green River Formation of Utah and Wyoming.
Mining

Mining is defined as the extraction, from the Earth, of valuable material for societal use. Usually, this includes solid materials (e.g. gold, iron, coal, diamond, sand, and gravel), but can also include fluid resources such as oil and natural gas. Modern mining has a long relationship with modern society. The oldest evidence of mining, with a concentrated area of digging into the Earth for materials, has a history that may go back 40,000 years to the hematite (used as red dye) of the Lion Cave in Swaziland [4]. Resources extracted by mining are generally considered to be nonrenewable. After a potentially profitable mineral deposit is located, it is mined by one of several techniques. Which technique is used depends upon the type of deposit and whether the deposit is shallow and thus suitable for surface mining or deep and thus requiring sub-surface mining. The style of mining is a function of technology, social license, and economics. It is in the best interest of the company extracting the resources to do so in a cost-effective way.
It is implicit that the technology to mine is available, economic conditions are suitable, and political, social and environmental considerations are satisfied in order to classify a natural resource deposit as ore. Depending on the substance, it can be concentrated in a narrow vein or distributed over a large area as a low-concentration ore. Some materials are mined directly from bodies of water (e.g. sylvite for potassium; water through desalination) and the atmosphere (e.g. nitrogen for fertilizers). These differences lead to various methods of mining, and differences in terminology depending on the certainty. Ore mineral resource is used for an indication of ore that is potentially extractable, and the term ore mineral reserve is used for a well defined (proven), profitable amount of extractable ore.
Surface Mining Techniques
Surface mining techniques include: open-pit mining, area strip mining, contour strip mining and hydraulic mining. Open-pit mining involves digging a large, terraced hole in the ground in order to remove a near-surface ore body (Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\)). This technique is used in copper ore mines in Arizona and Utah and iron ore mines in Minnesota. Typically, the pit progressively deepens through additional mining cuts to extract the ore, and the walls of the pit are as steep as can safely be managed. A steep wall means there is less waste (non-valuable) rock or overburden to remove and is an engineering balance between efficient mining and mass wasting. Occasionally landslides do occur, including a very large landslide that occurred in the Bingham Canyon mine in 2013. These events are costly and dangerous, though careful monitoring gave the Bingham Canyon mine ample warning time.
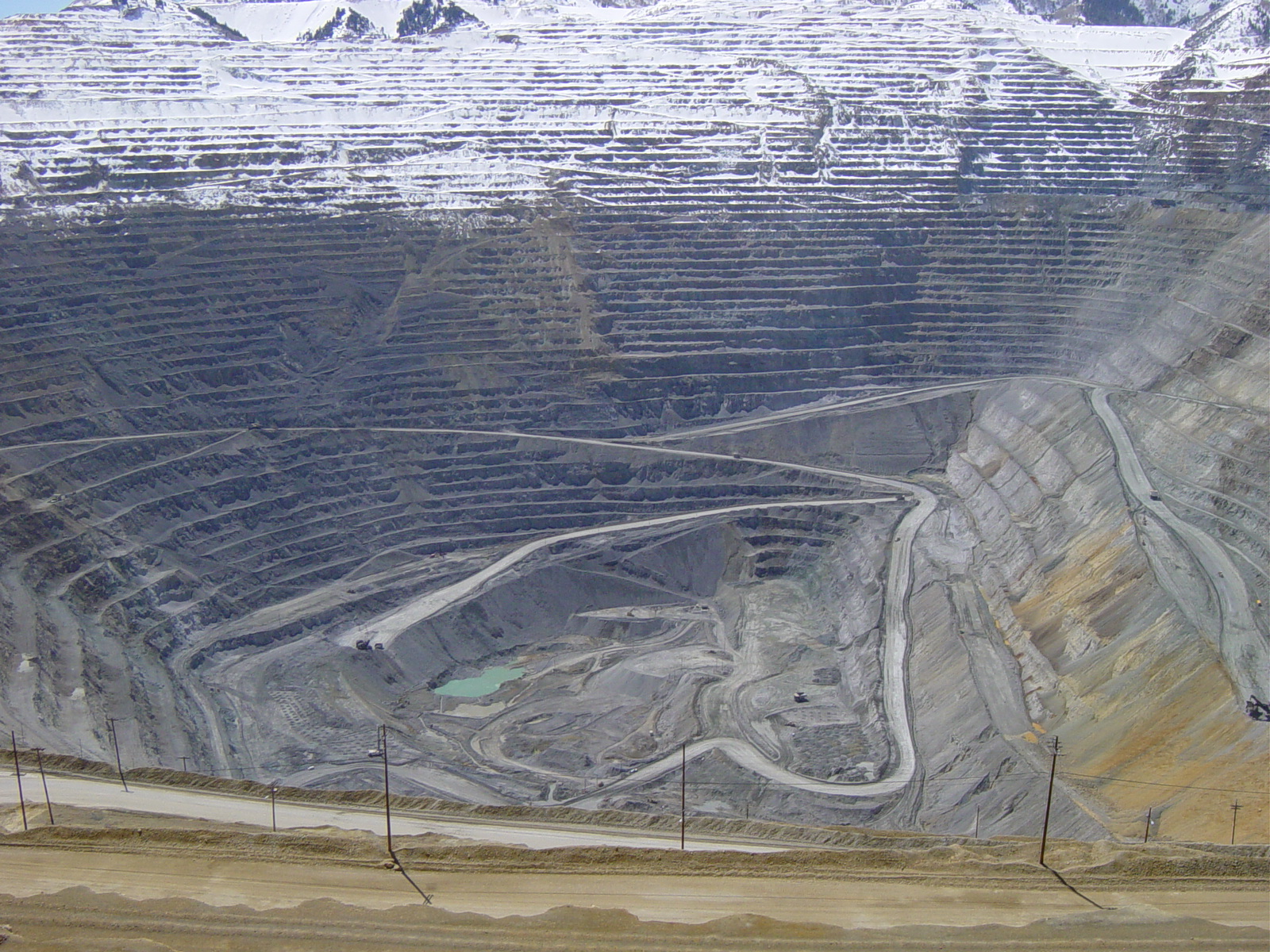

Area strip mining is used in relatively flat areas. The overburden of soil and rock is removed from a large trench in order to expose the ore body. After the minerals are removed, the old trench is filled and a new trench is dug. This process is repeated until the available ore is exhausted. Contour strip mining is a similar technique except that it is used on hilly or mountainous terrains. A series of terraces are cut into the side of a slope, with the overburden from each new terrace being dumped into the old one below. In mountaintop removal mining, a specific type of strip mining, an entire mountaintop or rock layer is removed to gain access to the ore below. The environmental impacts of surface mining are usually greater due to the larger surface disturbance footprint [7].
![BLM [Public domain], <a data-cke-saved-href="https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File%3ACoal_mine_Wyoming.jpg" href="https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File%3ACoal_mine_Wyoming.jpg">via Wikimedia Commons</a> A large machine is removing coal.](https://bio.libretexts.org/@api/deki/files/57554/Coal_mine_Wyoming-300x200.jpg?revision=1&size=bestfit&width=378&height=252)
Hydraulic mining is used in places such as the Amazon in order to extract gold from hillsides. Powerful, high-pressure streams of water are used to blast away soil and rock containing gold, which is then separated from the runoff. This process is very damaging to the environment, as entire hills are eroded away and streams become clogged with sediment. If land subjected to any of these surface mining techniques is not properly restored after its use, then it leaves an unsightly scar on the land and is highly susceptible to erosion.
Sub-Surface Mining Techniques
Some mineral deposits are too deep to be surface mined and therefore require a sub-surface mining method. Underground mining is often used for higher-grade, more localized, or very concentrated resources. In the traditional sub surface method a deep vertical shaft is dug and tunnels are dug horizontally outward from the shaft into the ore body. The ore is removed and transported to the surface. The deepest such subsurface mines (deeper than 3500 m) in the world are located in the Witwatersrand basin of South Africa, where gold is mined. This type of mining is less disturbing to the land surface than surface mining. It also usually produces fewer waste materials. However, it is more expensive and more dangerous than surface mining methods.
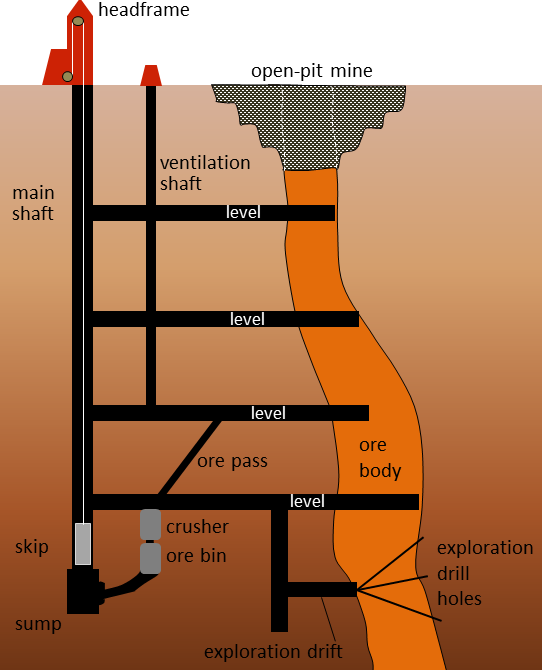
Figure \(\PageIndex{4}\): Schematic cross-section of a typical underground mine. © Steven Earle. CC BY

A newer form of subsurface mining known as in-situ mining is designed to co-exist with other land uses, such as agriculture. An in-situ mine typically consists of a series of injection wells and recovery wells built with acid-resistant concrete and polyvinyl chloride casing. A weak acid solution is pumped into the ore body in order to dissolve the minerals. Then, the metal-rich solution is drawn up through the recovery wells for processing at a surface refining facility where the mineral of interest is precipitated. This method is used for the in-situ mining of copper ore.
Ore Processing
Once an ore has been mined, it must be processed to extract pure metal. All ore minerals are mixed with less desirable components called gangue. The process of physically separating gangue minerals from ore-bearing minerals is called concentrating. When ore is processed (typically very close to the mine), it is ground to a fine powder and the ore minerals are physically separated from the rest of the rock to make a concentrate. At a molybdenum mine, for example, this concentrate may be almost pure molybdenite (MoS2). The rest of the rock is known as tailings. It comes out of the concentrator as a wet slurry and must be stored near the mine, in most cases, in a tailings pond. The tailings pond at the Myra Falls Mine on Vancouver Island is shown in Figure \(\PageIndex{6}\), and the settling ponds for waste water from the concentrator are shown in Figure \(\PageIndex{7}\). The tailings are contained by an embankment. Also visible in the foreground of Figure \(\PageIndex{6}\) is a pile of waste rock, which is non-ore rock that was mined in order to access the ore. Although this waste rock contains little or no ore minerals, at many mines it contains up to a few percent pyrite.

Figure \(\PageIndex{6}\): The tailings pond at the Myra Falls Mine on Vancouver Island. The dry rock in the middle of the image is waste rock. The structure on the right is the headframe for the mine shaft. Myra Creek flows between the tailings pond and the headframe. © Steven Earle. CC BY

Figure \(\PageIndex{7}\): The tailings pond (lower left) at Myra Falls Mine with settling ponds (right) for processing water from the concentrator. © Steven Earle. CC BY
Processes for extracting metal include smelting, electrowinning and heap leaching. In preparation for the smelting process, the ore is crushed and concentrated by a flotation method. The concentrated ore is melted in a smelting furnace where impurities are either burned-off as gas or separated as molten slag (Figure \(\PageIndex{8}\)). Slag is the glassy unwanted by-product of smelting ore and is sometimes mistaken for metorites. The smelting step is usually repeated several times to increase the purity of the metal.
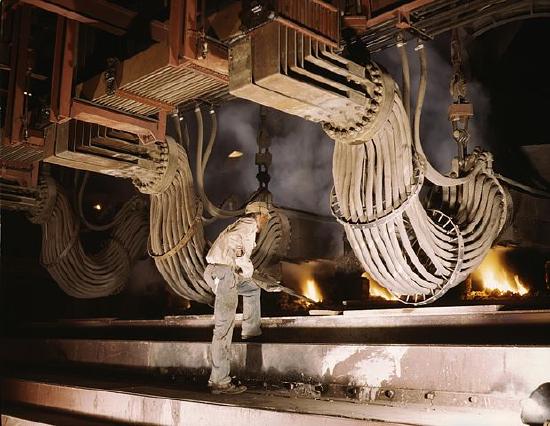

For the electrowinning method ore or mine tailings are first leached with a weak acid solution to remove the desired metal. An electric current is passed through the solution and pure metal is electroplated onto a starter cathode made of the same metal. Copper can be refined from oxide ore by this method. In addition, copper metal initially produced by the smelting method can be purified further by using a similar electrolytic procedure.
Gold is sometimes extracted from ore by the heap leaching process. A large pile of crushed ore is sprayed with a cyanide solution. As the solution percolates through the ore it dissolves the gold. The solution is then collected and the gold extracted from it. All of the refining methods can damage the environment. Smelters produce large amounts of air pollution in the form of sulfur dioxide which leads to acid rain. Leaching methods can pollute streams with toxic chemicals that kill wildlife.
Environmental Impacts of Metallic Mineral Mining
The primary impact of metallic mineral mining comes from the mining itself, including disturbance of the land surface, covering of landscapes by tailings impoundments, and increased mass wasting by accelerated erosion [48]. Surface mines can create enormous pits (Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\)) in the ground as well as large piles of overburden and tailings that need to be reclaimed, i.e., restored to a useful landscape. Since 1977 surface mines in U.S. are required to be reclaimed, and commonly reclamation is relatively well done in this country. Unfortunately, surface mine reclamation is not done everywhere, especially in underdeveloped countries, due to lack of regulations or lax enforcement of regulations. Unreclaimed surface mines and active surface mines can be major sources of water and sediment pollution.
In addition, many metal deposits contain pyrite, an uneconomic sulfide mineral placed on waste dumps, which may generate acid rock drainage (ARD) during weathering (Figure \(\PageIndex{9}\)). In the presence of oxygenated water, sulfides such as pyrite react undergo complex reactions to release metal ions and hydrogen ions, lowering pH to highly acidic levels. Mining and processing of mined materials typically increase the surface area to volume ratio in the material, causing reactions to occur even faster than what would occur naturally. If not managed properly, these reactions may lead to acidification of streams and groundwater plumes that can carry dissolved toxic metals. In mines where limestone is a waste rock of carbonate minerals like calcite or dolomite are present, their acid-neutralizing potential helps reduce the likelihood of generating ARD. Although this is a natural process too, it is very important to isolate mine dumps and tailings from oxygenated water, both to prevent the dissolution of sulfides and subsequent percolation of the sulfate-rich water into waterways. Industry has taken great strides in preventing contamination in recent decades, but earlier mining projects are still causing problems with local ecosystems.
![By Carol Stoker, NASA [Public domain], <a data-cke-saved-href="https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File%3ARio_tinto_river_CarolStoker_NASA_Ames_Research_Center.jpg" href="https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File%3ARio_tinto_river_CarolStoker_NASA_Ames_Research_Center.jpg">via Wikimedia Commons</a> The water in the river is bright orange.](https://bio.libretexts.org/@api/deki/files/57542/Rio_tinto_river_CarolStoker_NASA_Ames_Research_Center-300x225.jpg?revision=1&size=bestfit&width=365&height=274)
Tailings ponds and waste-rock storage piles must be carefully maintained to ensure their integrity and monitored to ensure that acidic and metal-rich water is not leaking out. In August 2014, the tailings pond at the Mt. Polley Mine in central B.C. failed and 10 million cubic metres of waste water along with 4.5 million cubic metres of tailings slurry was released into Polley Lake, Hazeltine Creek, and Quesnel Lake (Figure \(\PageIndex{10-11}\)). As of July 2015, the environmental implications of this event are still not fully understood.
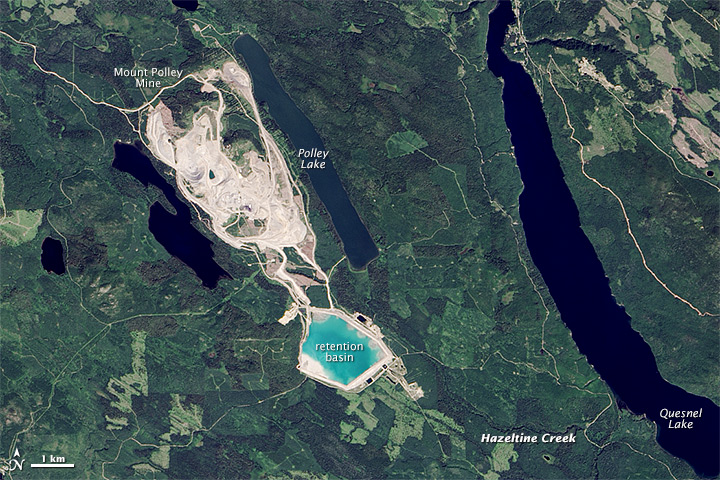
Figure \(\PageIndex{10}\): The Mt. Polley Mine area prior to the dam breach of August 2014. The tailings were stored in the area labelled “retention basin.” [https://en.Wikipedia.org/wiki/Mount_...mine_disaster]
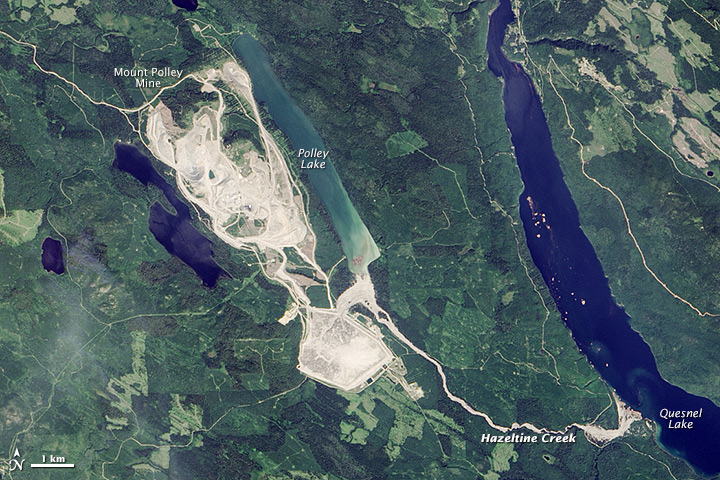

Figure \(\PageIndex{11}\): The Mt. Polley Mine area after the tailings dam breach of August 2014. The water and tailings released flowed into Hazeltine Creek, and Polley and Quesnel Lakes. [https://en.Wikipedia.org/wiki/Mount_...mine_disaster]
MINERAL SUFFICIENCY AND THE FUTURE
Mineral resources are essential to life as we know it. A nation cannot be prosperous without a reliable source of minerals, and no country has all the mineral resources it requires. The United States has about 5 percent of the world's population and 7 percent of the world's land area, but uses about 30 percent of the world's mineral resources. It imports a large percentage of its minerals; in some cases sufficient quantities are unavailable in the U.S., and in others they are cheaper to buy from other countries. Certain minerals, particularly those that are primarily imported and considered of vital importance, are stockpiled by the United States in order to protect against embargoes or other political crises. These strategic minerals include: bauxite, chromium, cobalt, manganese and platinum.
Because minerals are produced slowly over geologic time scales, they are considered non-renewable resources. The estimated mineral deposits that are economically feasible to mine are known as mineral reserves. The growing use of mineral resources throughout the world raises the question of how long these reserves will last. Most minerals are in sufficient supply to last for many years, but a few (e.g. gold, silver, lead, tungsten and zinc) are expected to fall short of demand in the near future. Currently, reserves for a particular mineral usually increase as the price for that mineral increases. This is because the higher price makes it economically feasible to mine some previously unprofitable deposits, which then shifts these deposits to the reserves. However, in the long term this will not be the case because mineral deposits are ultimately finite.
There are ways to help prolong the life of known mineral reserves. Conservation is an obvious method for stretching reserves. If you use less, you need less. Recycling helps increase the amount of time a mineral or metal remains in use, which decreases the demand for new production. It also saves considerable energy, because manufacturing products from recycled metals (e.g. aluminum, copper) uses less energy than manufacturing them from raw materials. Government legislation that encourages conservation and recycling is also helpful. The current "General Mining Act of 1872," however, does just the opposite. It allows mining companies to purchase government land very inexpensively and not pay any royalties for minerals extracted from that land. As a result, mineral prices are kept artificially low which discourages conservation and recycling.
References
4. Vogel, J. C. Groningen radiocarbon dates IX. Radiocarbon 12, 444–471 (1970).
Clugston, C. (2010) Increasing Global Nonrenewable Natural Resource Scarcity - An Analysis, The Oil Drum. Retrieved from http://www.theoildrum.com/node/6345
Craig J, Vaughan D, and Skinner B (2011) Earth Resources and the Environment (4th ed.). Pearson Prentice Hall, p. 92
43. Lehmann, I. P’, Publ. Bur. Centr. Seism. Internat. Serie A 14, 87–115 (1936).
46. Bárdossy, G. & Aleva, G. J. J. Lateritic bauxites. 27, (Elsevier Science Ltd, 1990).
Contributors and Attributions
Modified by Kyle Whittinghill from the following sources
- Metal Deposits and Industrial Minerals from Physical Geology by Steven Earle (licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License)
- Minerals from AP Environmental Science by University of California College Prep
- Non-Renewable Resources from Environmental Science: A Canadian Perspective by Bill Freedman (Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial)
- Mineral Resources and Mining from An Introduction to Geology by Chris Johnson, Matthew D. Affolter, Paul Inkenbrandt, & Cam Mosher (Geology Faculty at Salt Lake Community College), download free from OpenGeology
- Mineral Resources: Formation, Mining, Environmental Impact from Sustainability: A Comprehensive Foundation by Tom Theis and Jonathan Tomkin


