The Endomembrane System*#
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
The Endomembrane System
The endomembrane system (endo = “within”) is a group of membranes and organelles in eukaryotic cells that works together to modify, package, and transport lipids and proteins. It includes the nuclear envelope, lysosomes, and vesicles, which we’ve already mentioned, and the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus, which we will cover shortly. Although not technically within the cell, the plasma membrane is included in the endomembrane system because, as you will see, it interacts with the other endomembranous organelles. The endomembrane system does not include the membranes of either mitochondria or chloroplasts.
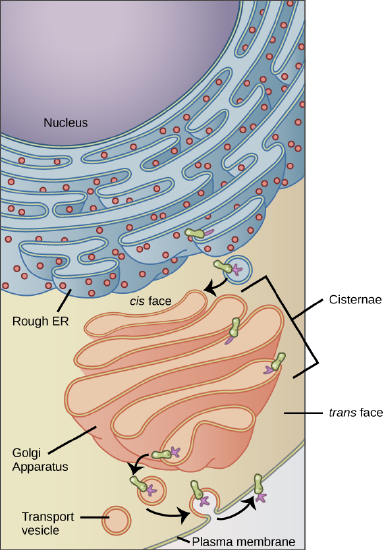
Membrane and secretory proteins are synthesized in the rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER). The RER also sometimes modifies proteins. In this illustration, a (green) integral membrane protein in the ER is modified by attachment of a (purple) carbohydrate. Vesicles with the integral protein bud from the ER and fuse with the cis face of the Golgi apparatus. As the protein passes along the Golgi’s cisternae, it is further modified by the addition of more carbohydrates. After its synthesis is complete, it exits as integral membrane protein of the vesicle that bud from the Golgi’s trans face and when the vesicle fuses with the cell membrane the protein becomes integral portion of that cell membrane. (credit: modification of work by Magnus Manske)
Possible discussion
If a peripheral membrane protein were synthesized in the lumen (inside) of the ER, would it end up on the inside or outside of the plasma membrane?
The Endoplasmic Reticulum
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) (see figure above) is a series of interconnected membranous sacs and tubules that collectively modifies proteins and synthesizes lipids. However, these two functions are performed in separate areas of the ER: the rough ER and the smooth ER, respectively.
The hollow portion of the ER tubules is called the lumen or cisternal space. The membrane of the ER, which is a phospholipid bilayer embedded with proteins, is continuous with the nuclear envelope.
Rough ER
The rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) is so named because the ribosomes attached to its cytoplasmic surface give it a studded appearance when viewed through an electron microscope (see figure below).
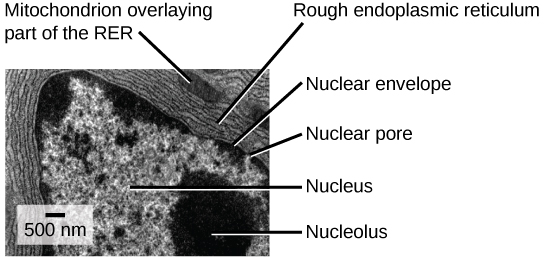
This transmission electron micrograph shows the rough endoplasmic reticulum and other organelles in a pancreatic cell. (credit: modification of work by Louisa Howard)
Ribosomes transfer their newly synthesized proteins into the lumen of the RER where they undergo structural modifications, such as folding or the acquisition of side chains. These modified proteins will be incorporated into cellular membranes—the membrane of the ER or those of other organelles—or secreted from the cell (such as protein hormones, enzymes). The RER also makes phospholipids for cellular membranes.
If the phospholipids or modified proteins are not destined to stay in the RER, they will reach their destinations via transport vesicles that bud from the RER’s membrane.
Since the RER is engaged in modifying proteins (such as enzymes, for example) that will be secreted from the cell, you would be correct in assuming that the RER is abundant in cells that secrete proteins. This is the case with cells of the liver, for example.
Smooth ER
The smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER) is continuous with the RER but has few or no ribosomes on its cytoplasmic surface. Functions of the SER include synthesis of carbohydrates, lipids, and steroid hormones; detoxification of medications and poisons; and storage of calcium ions.
In muscle cells, a specialized SER called the sarcoplasmic reticulum is responsible for storage of the calcium ions that are needed to trigger the coordinated contractions of the muscle cells.
The Golgi Apparatus
We have already mentioned that vesicles can bud from the ER and transport their contents elsewhere, but where do the vesicles go? Before reaching their final destination, the lipids or proteins within the transport vesicles still need to be sorted, packaged, and tagged so that they wind up in the right place. Sorting, tagging, packaging, and distribution of lipids and proteins takes place in the Golgi apparatus (also called the Golgi body), a series of flattened membranes (see figure below).
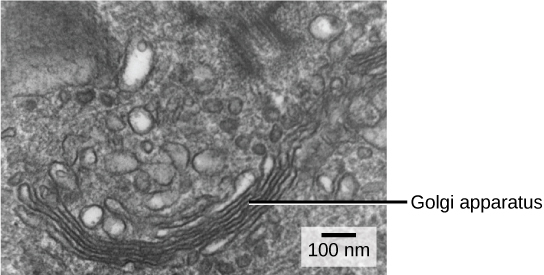
The Golgi apparatus in this white blood cell is visible as a stack of semicircular, flattened rings in the lower portion of the image. Several vesicles can be seen near the Golgi apparatus. (credit: modification of work by Louisa Howard)
The receiving side of the Golgi apparatus is called the cis face. The opposite side is called the trans face. The transport vesicles that formed from the ER travel to the cis face, fuse with it, and empty their contents into the lumen of the Golgi apparatus. As the proteins and lipids travel through the Golgi, they undergo further modifications that allow them to be sorted. The most frequent modification is the addition of short chains of sugar molecules. These newly modified proteins and lipids are then tagged with phosphate groups or other small molecules so that they can be routed to their proper destinations.
Finally, the modified and tagged proteins are packaged into secretory vesicles that bud from the trans face of the Golgi. While some of these vesicles deposit their contents into other parts of the cell where they will be used, other secretory vesicles fuse with the plasma membrane and release their contents outside the cell.
In another example of form following function, cells that engage in a great deal of secretory activity (such as cells of the salivary glands that secrete digestive enzymes or cells of the immune system that secrete antibodies) have an abundance of Golgi.
In plant cells, the Golgi apparatus has the additional role of synthesizing polysaccharides, some of which are incorporated into the cell wall and some of which are used in other parts of the cell.
Lysosomes
In addition to their role as the digestive component and organelle-recycling facility of animal cells, lysosomes are considered to be parts of the endomembrane system. Lysosomes also use their hydrolytic enzymes to destroy pathogens (disease-causing organisms) that might enter the cell. A good example of this occurs in a group of white blood cells called macrophages, which are part of your body’s immune system. In a process known as phagocytosis or endocytosis, a section of the plasma membrane of the macrophage invaginates (folds in) and engulfs a pathogen. The invaginated section, with the pathogen inside, then pinches itself off from the plasma membrane and becomes a vesicle. The vesicle fuses with a lysosome. The lysosome’s hydrolytic enzymes then destroy the pathogen (figure below).
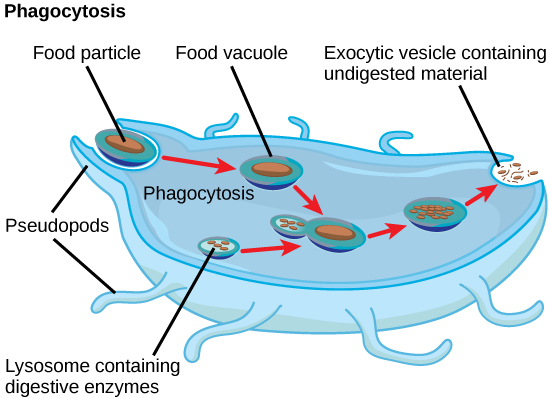
A macrophage has engulfed (phagocytized) a potentially pathogenic bacterium and then fuses with a lysosomes within the cell to destroy the pathogen. Other organelles are present in the cell but for simplicity are not shown.
Summary of Endomembranes
The endomembrane system includes the nuclear envelope, lysosomes, vesicles, the ER, and Golgi apparatus, as well as the plasma membrane. These cellular components work together to modify, package, tag, and transport proteins and lipids that form the membranes.
The RER modifies proteins and synthesizes phospholipids used in cell membranes. The SER synthesizes carbohydrates, lipids, and steroid hormones; engages in the detoxification of medications and poisons; and stores calcium ions. Sorting, tagging, packaging, and distribution of lipids and proteins take place in the Golgi apparatus. Lysosomes are created by the budding of the membranes of the RER and Golgi. Lysosomes digest macromolecules, recycle worn-out organelles, and destroy pathogens.
Review Questions
Exercise 1
Which of the following is not a component of the endomembrane system?
- mitochondrion
- Golgi apparatus
- endoplasmic reticulum
- lysosome
Answer: A
Exercise 2
The process by which a cell engulfs a foreign particle is known as:
- endosymbiosis
- phagocytosis
- hydrolysis
- membrane synthesis
Answer: B
Exercise 3
Which of the following is most likely to have the greatest concentration of smooth endoplasmic reticulum?
- a cell that secretes enzymes
- a cell that destroys pathogens
- a cell that makes steroid hormones
- a cell that engages in photosynthesis
Answer: C
Exercise 4
Which of the following sequences correctly lists in order the steps involved in the incorporation of a proteinaceous molecule within a cell?
- synthesis of the protein on the ribosome; modification in the Golgi apparatus; packaging in the endoplasmic reticulum; tagging in the vesicle
- synthesis of the protein on the lysosome; tagging in the Golgi; packaging in the vesicle; distribution in the endoplasmic reticulum
- synthesis of the protein on the ribosome; modification in the endoplasmic reticulum; tagging in the Golgi; distribution via the vesicle
- synthesis of the protein on the lysosome; packaging in the vesicle; distribution via the Golgi; tagging in the endoplasmic reticulum
Answer: C
Free Response
Exercise 5
In the context of cell biology, what do we mean by form follows function? What are at least two examples of this concept?
“Form follows function” refers to the idea that the function of a body part dictates the form of that body part. As an example, compare your arm to a bat’s wing. While the bones of the two correspond, the parts serve different functions in each organism and their forms have adapted to follow that function.
Exercise 6
In your opinion, is the nuclear membrane part of the endomembrane system? Why or why not? Defend your answer.
Since the external surface of the nuclear membrane is continuous with the rough endoplasmic reticulum, which is part of the endomembrane system, then it is correct to say that it is part of the system.

