Mb, Hb, Allostery, and Motors
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
QUATERNARY STRUCTURES AND COMPLEX ENZYMES
- shows advantage of quaternary structure
- shows examples of flexibility: low ΔG of shape change
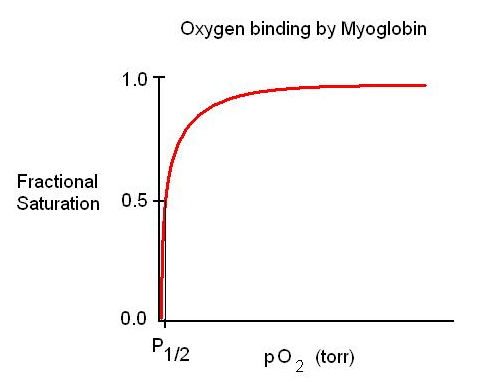
Why is this an O2 buffer? High slope below the P50 means that considerable Mb is charged (or uncharged) for a small change in pO2 (as pO2 drops, MbO2 replenishes O2)
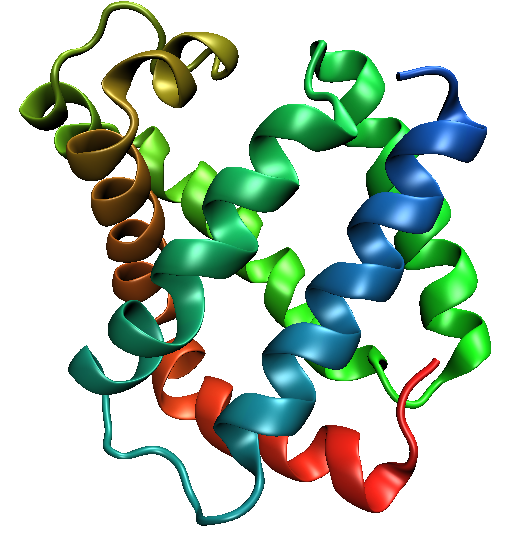
Hemoglobin
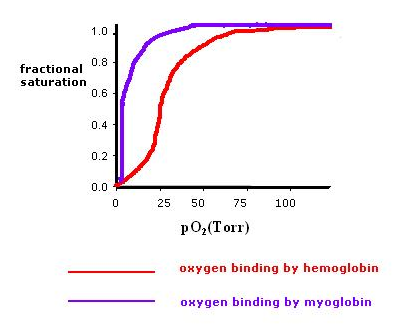
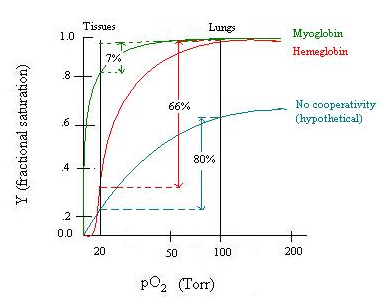
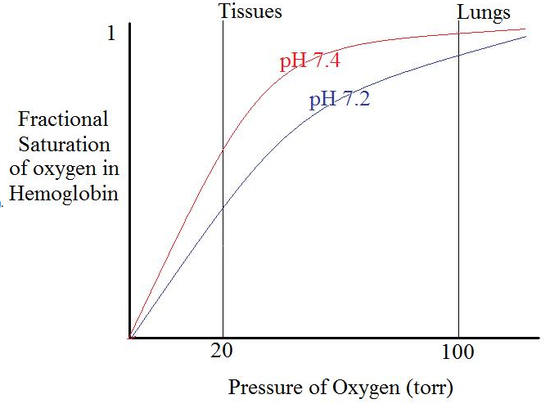
Bohr effect: H+, CO2 promote dissociation of O2 from Hb-O2: "negative, heterotropic, allosteric effector." The Bohr effect in hemoglobin can also be depicted as an oxygen-binding curve. There is a proportional relationship between the affinity of pxygen and pH level. As the pH level decreases, the affinity of oxygen in hemoglobin also decreases. As hemoglobin approaches low pH, more oxygen is released.
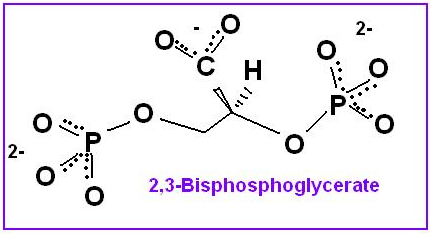
2,3-bisphosphoglycerate also promotes dissociation of O2. Purified hemoglobin binds much more tightly to the oxygen, making it less useful in oxygen transport. The difference in characteristics is due to the presence of 2,3-Bisphosphoglycerate(2,3-BPG) in human blood, which acts as an allosteric effector. An allosteric effector binds in one site and affects binding in another. 2,3-BPG binds to a pocket in the T-state (taut) of hemoglobin and is released as it forms the R-state (relaxed). The presence of 2,3-BPG means that more oxygen must be bound to the hemoglobin before the transition to the R-form is possible.
Lung conditions (Low H+, CO2) promotes O2 saturation; tissue conditions (high H+, CO2) promote O2 release; 2,4-BPG magnifies the allosteric effects. Allosteric effects match the saturation curve to the conditions in lung and tissue.
Motor Proteins
Microtubule--kinesin
Microtubule: right handed hallow helix of tubulin α/β dimers

kinesin: left-handed helix with two globular heads
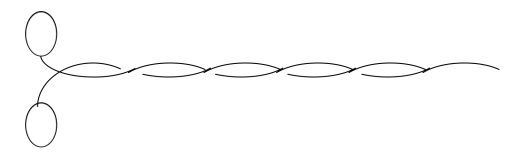
Actin-Myosin
Microfilaments: right-handed double helix of actin monomers
myosin: left-handed coil- (alpha-helix) coil
Actomyosin in Muscles
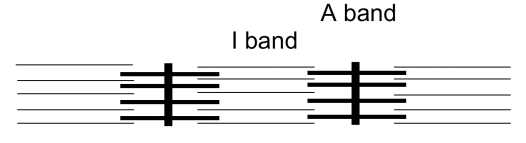
Contraction: sliding in the A band from myosin-actin connections
Why rigor mortis? When there is a loss of ATP, the muscles cannot relax because it cannot be broken down into ADP
Conclusion
- Reversible O2 and CO2 binding
- Reversible protein-protein (kinesin-MT) binding