3.E: Biochemistry of the Genome (Exercises)
- Page ID
- 80819
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
3.1: Structure and Function of DNA
Nucleic acids are composed of nucleotides, each of which contains a pentose sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base. Deoxyribonucleotides within DNA contain deoxyribose as the pentose sugar. DNA contains the pyrimidines cytosine and thymine, and the purines adenine and guanine. Nucleotides are linked together by phosphodiester bonds between the 5ʹ phosphate group of one nucleotide and the 3ʹ hydroxyl group of another.
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not found within DNA?
- thymine
- phosphodiester bonds
- complementary base pairing
- amino acids
- Answer
-
D
If 30% of the bases within a DNA molecule are adenine, what is the percentage of thymine?
- 20%
- 25%
- 30%
- 35%
- Answer
-
C
Which of the following statements about base pairing in DNA is incorrect?
- Purines always base pairs with pyrimidines.
- Adenine binds to guanine.
- Base pairs are stabilized by hydrogen bonds.
- Base pairing occurs at the interior of the double helix.
- Answer
-
B
If a DNA strand contains the sequence 5ʹ-ATTCCGGATCGA-3ʹ, which of the following is the sequence of the complementary strand of DNA?
- 5ʹ-TAAGGCCTAGCT-3ʹ
- 5ʹ-ATTCCGGATCGA-3ʹ
- 3ʹ-TAACCGGTACGT-5ʹ
- 5ʹ-TCGATCCGGAAT-3ʹ
- Answer
-
D
During denaturation of DNA, which of the following happens?
- Hydrogen bonds between complementary bases break.
- Phosphodiester bonds break within the sugar-phosphate backbone.
- Hydrogen bonds within the sugar-phosphate backbone break.
- Phosphodiester bonds between complementary bases break.
- Answer
-
A.
Fill in the Blank
The end of a nucleic acid strand with a free phosphate group is called the ________.
- Answer
-
5ʹ end
True/False
The work of Rosalind Franklin and R.G. Gosling was important in demonstrating the helical nature of DNA.
- Answer
-
True
The A-T base pair has more hydrogen bonding than the C-G base pair.
- Answer
-
False
Short Answer
What is the role of phosphodiester bonds within the sugar-phosphate backbone of DNA?
What is meant by the term “antiparallel?”
Why is DNA with a high GC content more difficult to denature than that with a low GC content?
Critical Thinking
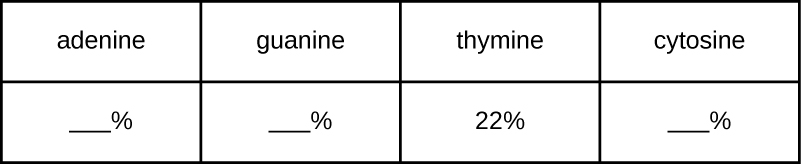
A certain DNA sample is found to have a makeup consisting of 22% thymine. Use Chargaff’s rules to fill in the percentages for the other three nitrogenous bases.
In considering the structure of the DNA double helix, how would you expect the structure to differ if there was base pairing between two purines? Between two pyrimidines?
3.2: Structure and Function of RNA
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is typically single stranded and contains ribose as its pentose sugar and the pyrimidine uracil instead of thymine. An RNA strand can undergo significant intramolecular base pairing to take on a three-dimensional structure. There are three main types of RNA, all involved in protein synthesis. Messenger RNA (mRNA) serves as the intermediary between DNA and the synthesis of protein products during translation.
Multiple Choice
Which of the following types of RNA codes for a protein?
- dsRNA
- mRNA
- rRNA
- tRNA
- Answer
-
B
A nucleic acid is purified from a mixture. The molecules are relatively small, contain uracil, and most are covalently bound to an amino acid. Which of the following was purified?
- DNA
- mRNA
- rRNA
- tRNA
- Answer
-
D
Which of the following types of RNA is known for its catalytic abilities?
- dsRNA
- mRNA
- rRNA
- tRNA
- Answer
-
C
Ribosomes are composed of rRNA and what other component?
- protein
- polypeptides
- DNA
- mRNA
- Answer
-
A
Which of the following may use RNA as its genome?
- a bacterium
- an archaeon
- a virus
- a eukaryote
- Answer
-
C
Matching
Match the correct molecule with its description:
|
___tRNA ___rRNA ___mRNA |
A. is a major component of ribosome B. is a copy of the information in a gene C. carries an amino acid to the ribosome |
- Answer
-
C, A, B
True/False
Ribosomes are composed mostly of RNA.
- Answer
-
True
Double-stranded RNA is commonly found inside cells.
- Answer
-
False
Short Answer
What are the differences between DNA nucleotides and RNA nucleotides?
How is the information stored within the base sequence of DNA used to determine a cell’s properties?
How do complementary base pairs contribute to intramolecular base pairing within an RNA molecule?
If an antisense RNA has the sequence 5ʹAUUCGAAUGC3ʹ, what is the sequence of the mRNA to which it will bind? Be sure to label the 5ʹ and 3ʹ ends of the molecule you draw.
Why does double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) stimulate RNA interference?
Critical Thinking
Identify the location of mRNA, rRNA, and tRNA in the figure.
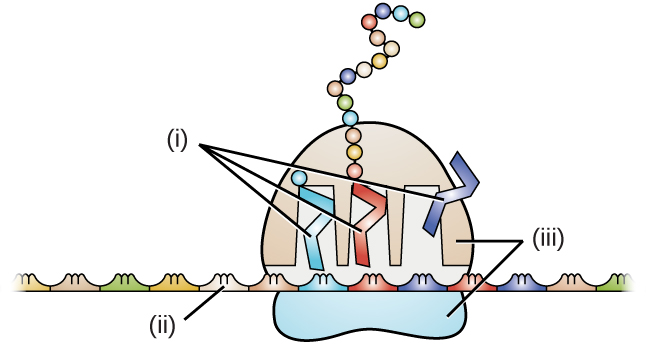
Why does it make sense that tRNA and rRNA molecules are more stable than mRNA molecules?


