5.1: Introduction
- Page ID
- 105810
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
Introduction
As you’ve learned, biological macromolecules are large molecules, necessary for life, that are built from smaller organic molecules. There are four major classes of biological macromolecules (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids); each is an important cell component and performs a wide array of functions. Combined, these molecules make up the majority of a cell’s dry mass (recall that water makes up the majority of its complete mass). Biological macromolecules are organic, meaning they contain carbon. In addition, they may contain hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and additional minor elements.
In today’s lab, we will learn to identify three of the four types of macromolecules: carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. The fourth type, nucleotides, will be studied in detail in future labs.
A. Carbohydrates
Most people are familiar with carbohydrates, one type of macromolecule, especially when it comes to what we eat. To lose weight, some individuals adhere to “low-carb” diets. Athletes, in contrast, often “carb-load” before important competitions to ensure that they have enough energy to compete at a high level. Carbohydrates are, in fact, an essential part of our diet; grains, fruits, and vegetables are all natural sources of carbohydrates. Carbohydrates provide energy to the body, particularly through glucose, a simple sugar that is a component of starch and an ingredient in many staple foods. Carbohydrates also have other important functions in humans, animals, and plants.
Molecular Structures
Carbohydrates can be represented by the stoichiometric formula (CH2O)n, where n is the number of carbons in the molecule. In other words, the ratio of carbon to hydrogen to oxygen is 1:2:1 in carbohydrate molecules. This formula also explains the origin of the term “carbohydrate”: the components are carbon (“carbo”) and the components of water (hence, “hydrate”). Carbohydrates are classified into three subtypes: monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides.
Monosaccharides
Monosaccharides (mono- = “one”; sacchar- = “sweet”) are simple sugars, the most common of which is glucose. In monosaccharides, the number of carbons usually ranges from three to seven. Most monosaccharide names end with the suffix -ose. If the sugar has an aldehyde group (the functional group with the structure R-CHO), it is known as an aldose, and if it has a ketone group (the functional group with the structure RC(=O)R'), it is known as a ketose. Depending on the number of carbons in the sugar, they also may be known as trioses (three carbons), pentoses (five carbons), and or hexoses (six carbons). See Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\) for an illustration of the monosaccharides.
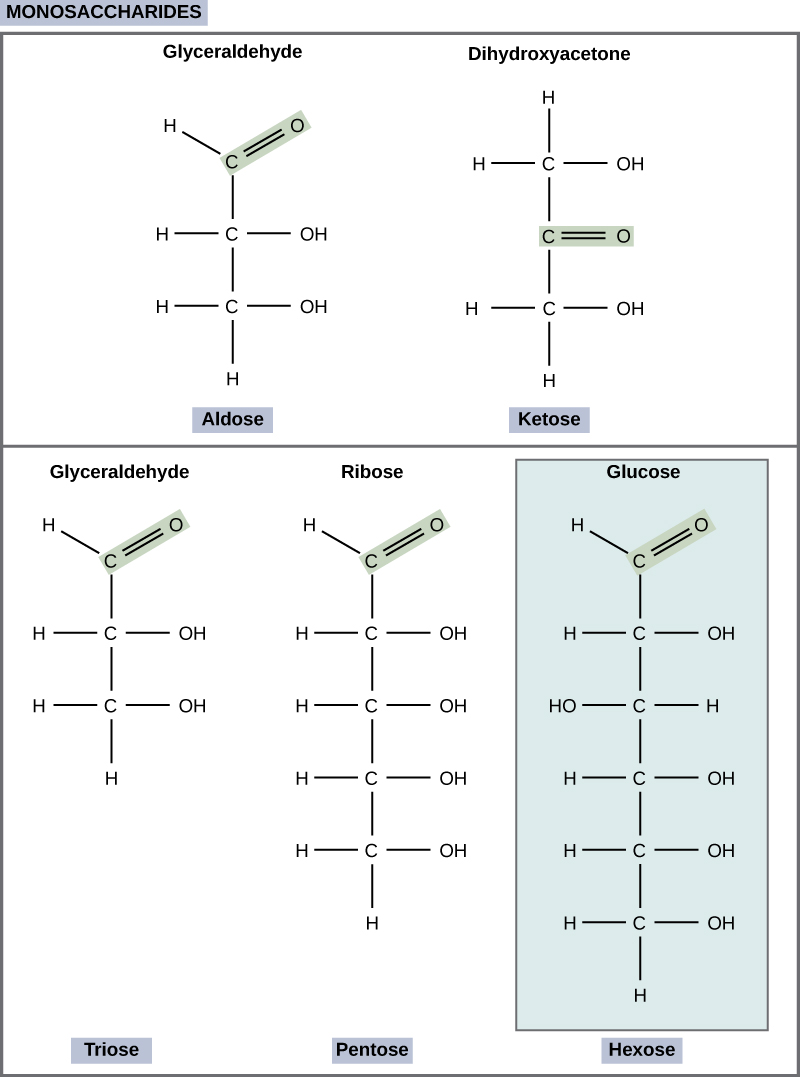
The chemical formula for glucose is C6H12O6. In humans, glucose is an important source of energy. During cellular respiration, energy is released from glucose, and that energy is used to help make adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Plants synthesize glucose using carbon dioxide and water, and glucose in turn is used for energy requirements for the plant. Excess glucose is often stored as starch that is catabolized (the breakdown of larger molecules by cells) by humans and other animals that feed on plants.
Galactose (part of lactose, or milk sugar) and fructose (found in sucrose, in fruit) are other common monosaccharides. Although glucose, galactose, and fructose all have the same chemical formula (C6H12O6), they differ structurally and chemically (and are known as isomers) because of the different arrangement of functional groups around the asymmetric carbon; all of these monosaccharides have more than one asymmetric carbon (Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\)).
Art Connection
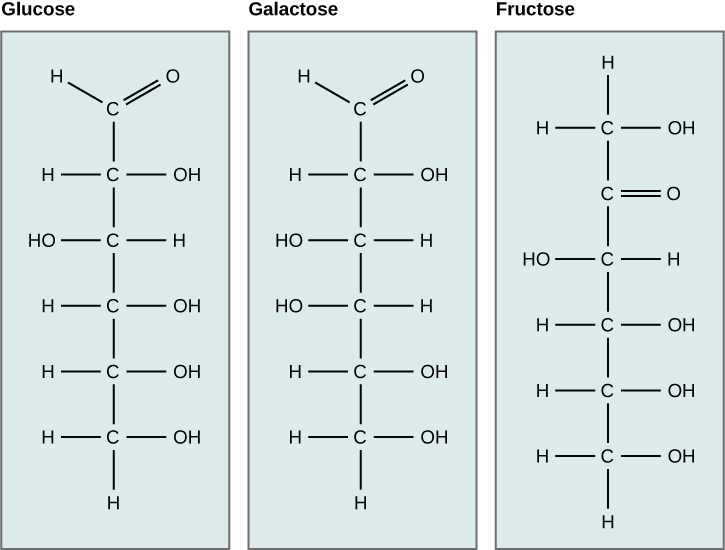
What kind of sugars are these, aldose or ketose?
Glucose, galactose, and fructose are isomeric monosaccharides (hexoses), meaning they have the same chemical formula but have slightly different structures. Glucose and galactose are aldoses, and fructose is a ketose.
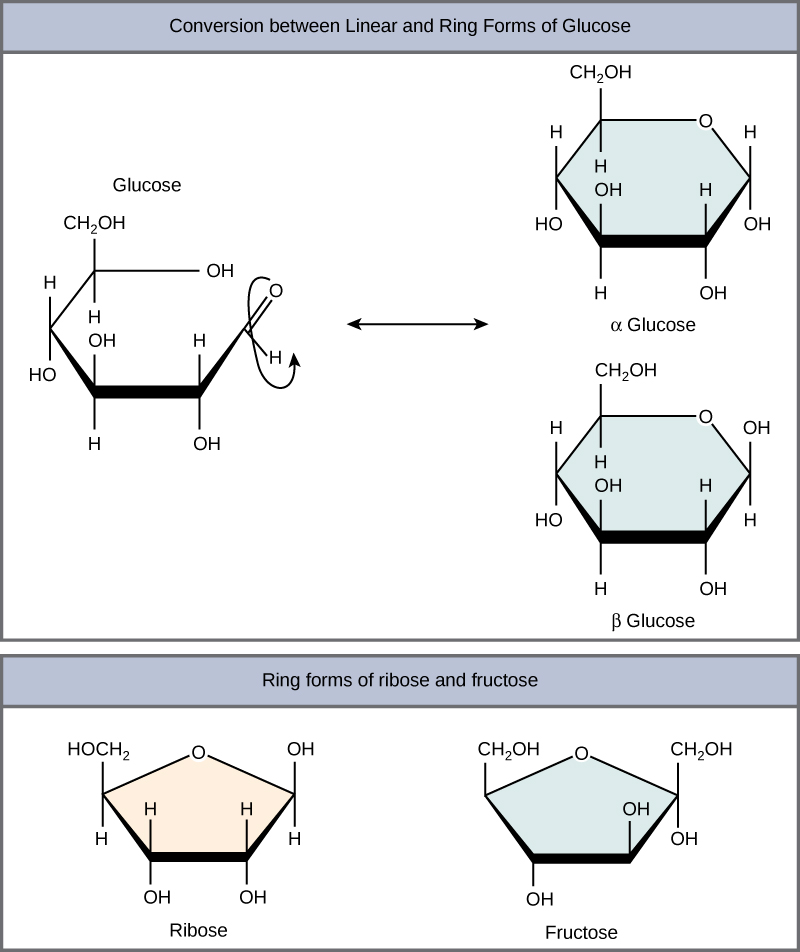
Monosaccharides can exist as a linear chain or as ring-shaped molecules; in aqueous solutions they are usually found in ring forms (Figure \(\PageIndex{3}\)). Glucose in a ring form can have two different arrangements of the hydroxyl group (OH) around the anomeric carbon (carbon 1 that becomes asymmetric in the process of ring formation). If the hydroxyl group is below carbon number 1 in the sugar, it is said to be in the alpha (α) position, and if it is above the plane, it is said to be in the beta (β) position.
Disaccharides
Disaccharides (di- = “two”) form when two monosaccharides undergo a dehydration reaction (also known as a condensation reaction or dehydration synthesis). During this process, the hydroxyl group of one monosaccharide combines with the hydrogen of another monosaccharide, releasing a molecule of water and forming a covalent bond. A covalent bond formed between a carbohydrate molecule and another molecule (in this case, between two monosaccharides) is known as a glycosidic bond (Figure \(\PageIndex{4}\)). Glycosidic bonds (also called glycosidic linkages) can be of the alpha or the beta type.
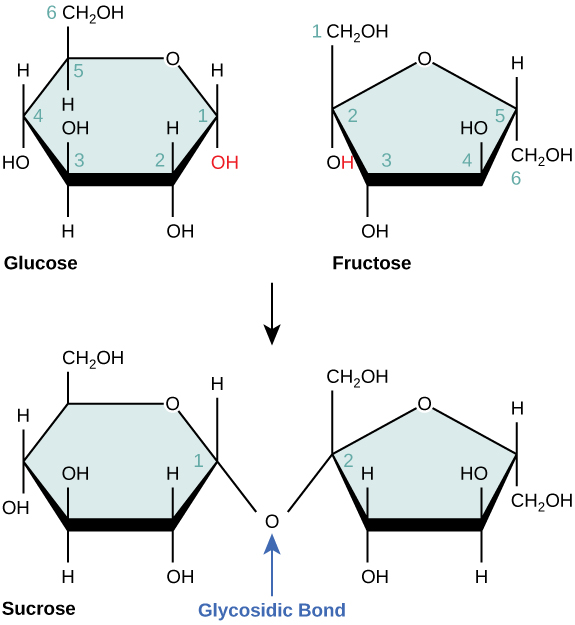
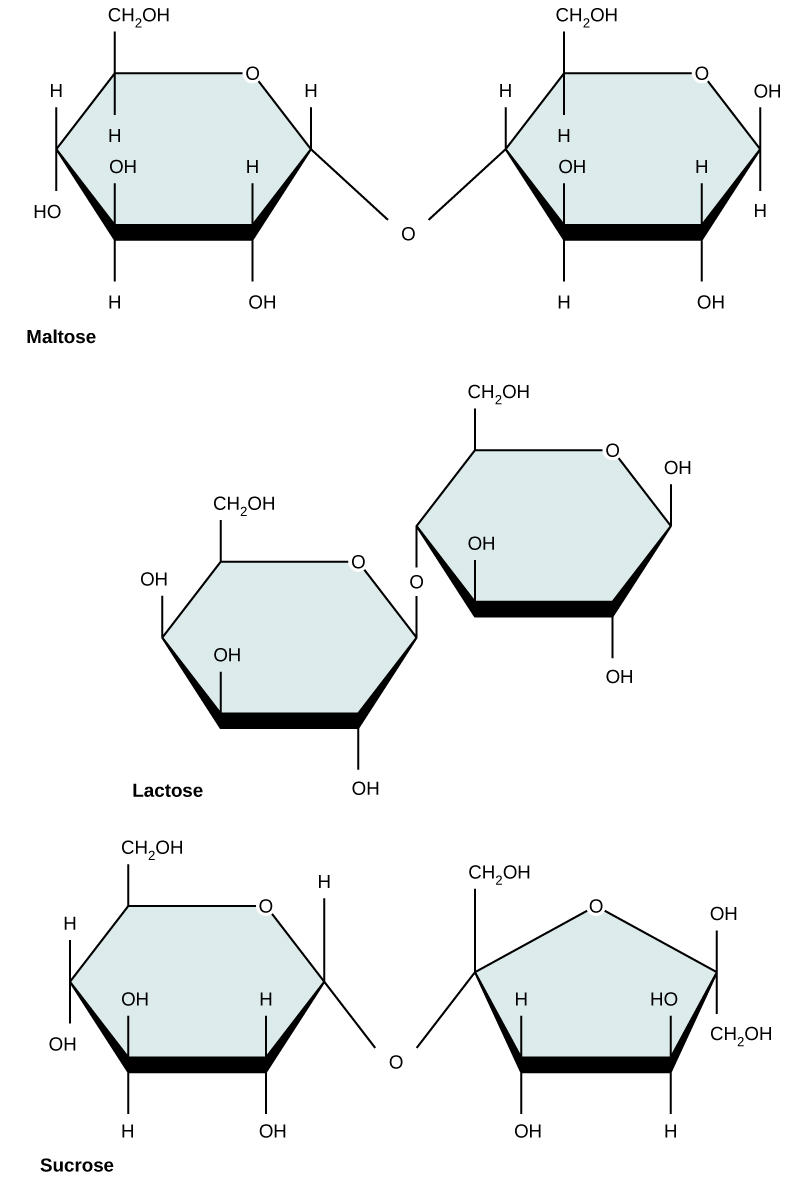
Common disaccharides include lactose, maltose, and sucrose (Figure \(\PageIndex{5}\)). Lactose is a disaccharide consisting of the monomers glucose and galactose. It is found naturally in milk. Maltose, or malt sugar, is a disaccharide formed by a dehydration reaction between two glucose molecules. The most common disaccharide is sucrose, or table sugar, which is composed of the monomers glucose and fructose.
Polysaccharides
A long chain of monosaccharides linked by glycosidic bonds is known as a polysaccharide (poly- = “many”). The chain may be branched or unbranched, and it may contain different types of monosaccharides. The molecular weight may be 100,000 daltons or more depending on the number of monomers joined. Starch, glycogen, cellulose, and chitin are primary examples of polysaccharides.
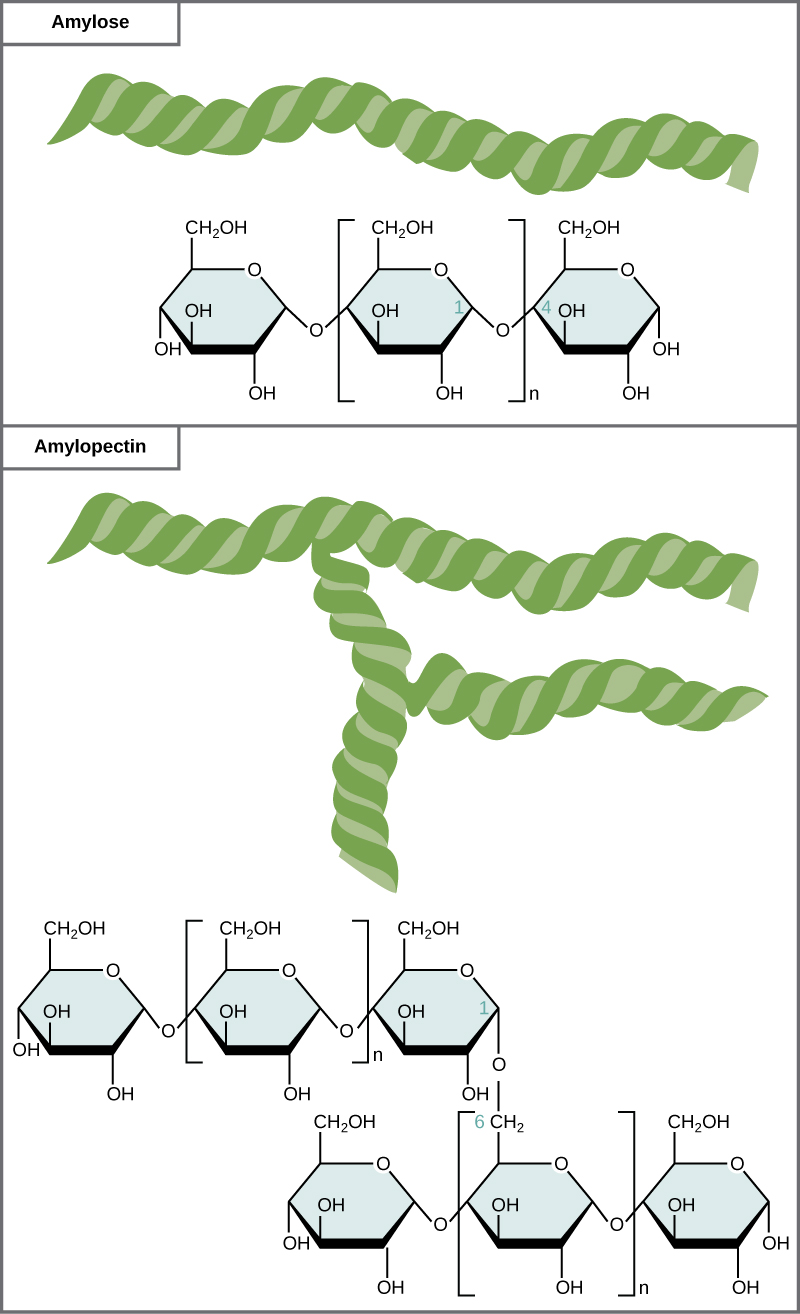
Starch is the stored form of sugars in plants and is made up of a mixture of amylose and amylopectin (both polymers of glucose). Plants are able to synthesize glucose, and the excess glucose, beyond the plant’s immediate energy needs, is stored as starch in different plant parts, including roots and seeds. The starch in the seeds provides food for the embryo as it germinates and can also act as a source of food for humans and animals. The starch that is consumed by humans is broken down by enzymes, such as salivary amylases, into smaller molecules, such as maltose and glucose. The cells can then absorb the glucose.
Starch is made up of glucose monomers that are joined by α 1-4 or α 1-6 glycosidic bonds. The numbers 1-4 and 1-6 refer to the carbon number of the two residues that have joined to form the bond. As illustrated in Figure \(\PageIndex{6}\), amylose is starch formed by unbranched chains of glucose monomers (only α 1-4 linkages), whereas amylopectin is a branched polysaccharide (α 1-6 linkages at the branch points).
Glycogen is the storage form of glucose in humans and other vertebrates and is made up of monomers of glucose. Glycogen is the animal equivalent of starch and is a highly branched molecule usually stored in liver and muscle cells. Whenever blood glucose levels decrease, glycogen is broken down to release glucose in a process known as glycogenolysis.
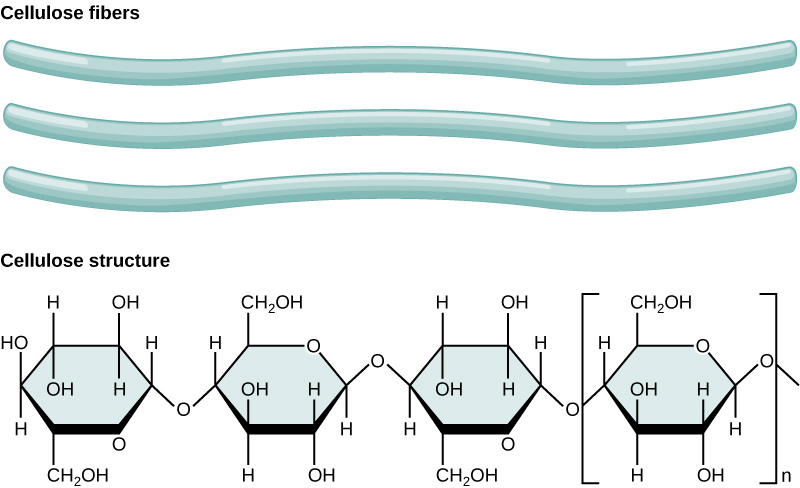
Cellulose is the most abundant natural biopolymer. The cell wall of plants is mostly made of cellulose; this provides structural support to the cell. Wood and paper are mostly cellulosic in nature. Cellulose is made up of glucose monomers that are linked by β 1-4 glycosidic bonds (Figure \(\PageIndex{7}\)).
B. Lipids
Lipids include a diverse group of compounds that are largely nonpolar in nature. This is because they are hydrocarbons that include mostly nonpolar carbon–carbon or carbon–hydrogen bonds. Non-polar molecules are hydrophobic (“water fearing”), or insoluble in water. Lipids perform many different functions in a cell. Cells store energy for long-term use in the form of fats. Lipids also provide insulation from the environment for plants and animals. For example, they help keep aquatic birds and mammals dry when forming a protective layer over fur or feathers because of their water-repellant hydrophobic nature. Lipids are also the building blocks of many hormones and are an important constituent of all cellular membranes. Lipids include fats, oils, waxes, phospholipids, and steroids.
Fats and Oils
A fat molecule consists of two main components—glycerol and fatty acids. Glycerol is an organic compound (alcohol) with three carbons, five hydrogens, and three hydroxyl (OH) groups. Fatty acids have a long chain of hydrocarbons to which a carboxyl group is attached, hence the name “fatty acid.” The number of carbons in the fatty acid may range from 4 to 36; most common are those containing 12–18 carbons. In a fat molecule, the fatty acids are attached to each of the three carbons of the glycerol molecule with an ester bond through an oxygen atom (Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\)).

During this ester bond formation, three water molecules are released. The three fatty acids in the triacylglycerol may be similar or dissimilar. Fats are also called triacylglycerols or triglycerides because of their chemical structure. Some fatty acids have common names that specify their origin. For example, palmitic acid, a saturated fatty acid, is derived from the palm tree. Arachidic acid is derived from Arachis hypogea, the scientific name for groundnuts or peanuts.
Fatty acids may be saturated or unsaturated. In a fatty acid chain, if there are only single bonds between neighboring carbons in the hydrocarbon chain, the fatty acid is said to be saturated. Saturated fatty acids are saturated with hydrogen; in other words, the number of hydrogen atoms attached to the carbon skeleton is maximized. Stearic acid is an example of a saturated fatty acid (Figure \(\PageIndex{3}\))

When the hydrocarbon chain contains a double bond, the fatty acid is said to be unsaturated. Oleic acid is an example of an unsaturated fatty acid (Figure \(\PageIndex{4}\)).

Most unsaturated fats are liquid at room temperature and are called oils. If there is one double bond in the molecule, then it is known as a monounsaturated fat (e.g., olive oil), and if there is more than one double bond, then it is known as a polyunsaturated fat (e.g., canola oil).
When a fatty acid has no double bonds, it is known as a saturated fatty acid because no more hydrogen may be added to the carbon atoms of the chain. A fat may contain similar or different fatty acids attached to glycerol. Long straight fatty acids with single bonds tend to get packed tightly and are solid at room temperature. Animal fats with stearic acid and palmitic acid (common in meat) and the fat with butyric acid (common in butter) are examples of saturated fats. Mammals store fats in specialized cells called adipocytes, where globules of fat occupy most of the cell’s volume. In plants, fat or oil is stored in many seeds and is used as a source of energy during seedling development. Unsaturated fats or oils are usually of plant origin and contain cis unsaturated fatty acids. Cis and trans indicate the configuration of the molecule around the double bond. If hydrogens are present in the same plane, it is referred to as a cis fat; if the hydrogen atoms are on two different planes, it is referred to as a trans fat. The cis double bond causes a bend or a “kink” that prevents the fatty acids from packing tightly, keeping them liquid at room temperature (Figure \(\PageIndex{5}\)). Olive oil, corn oil, canola oil, and cod liver oil are examples of unsaturated fats. Unsaturated fats help to lower blood cholesterol levels whereas saturated fats contribute to plaque formation in the arteries.

Trans Fats
In the food industry, oils are artificially hydrogenated to make them semi-solid and of a consistency desirable for many processed food products. Simply speaking, hydrogen gas is bubbled through oils to solidify them. During this hydrogenation process, double bonds of the cis- conformation in the hydrocarbon chain may be converted to double bonds in the trans- conformation.
Margarine, some types of peanut butter, and shortening are examples of artificially hydrogenated trans fats. Recent studies have shown that an increase in trans fats in the human diet may lead to an increase in levels of low-density lipoproteins (LDL), or “bad” cholesterol, which in turn may lead to plaque deposition in the arteries, resulting in heart disease. Many fast food restaurants have recently banned the use of trans fats, and food labels are required to display the trans fat content.
C. Proteins
Proteins are one of the most abundant organic molecules in living systems and have the most diverse range of functions of all macromolecules. Proteins may be structural, regulatory, contractile, or protective; they may serve in transport, storage, or membranes; or they may be toxins or enzymes. Each cell in a living system may contain thousands of proteins, each with a unique function. Their structures, like their functions, vary greatly. They are all, however, polymers of amino acids, arranged in a linear sequence.
Amino Acids
All proteins are made up of different arrangements of the same 20 types of amino acids. Amino acids are the monomers that make up proteins. Each amino acid has the same fundamental structure, which consists of a central carbon atom, also known as the alpha (α) carbon, bonded to an amino group (NH2), a carboxyl group (COOH), and to a hydrogen atom. Every amino acid also has another atom or group of atoms bonded to the central atom known as the R group (Figure \(\PageIndex{11}\)).
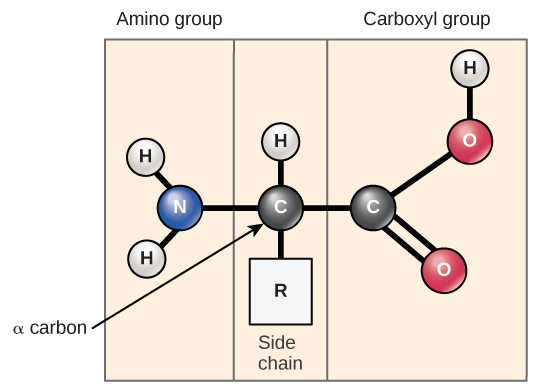
The name "amino acid" is derived from the fact that they contain both amino group and carboxyl-acid-group in their basic structure. As mentioned, there are 20 amino acids present in proteins. Ten of these are considered essential amino acids in humans because the human body cannot produce them and they are obtained from the diet. For each amino acid, the R group (or side chain) is different (Figure \(\PageIndex{12}\)).
Art Connection
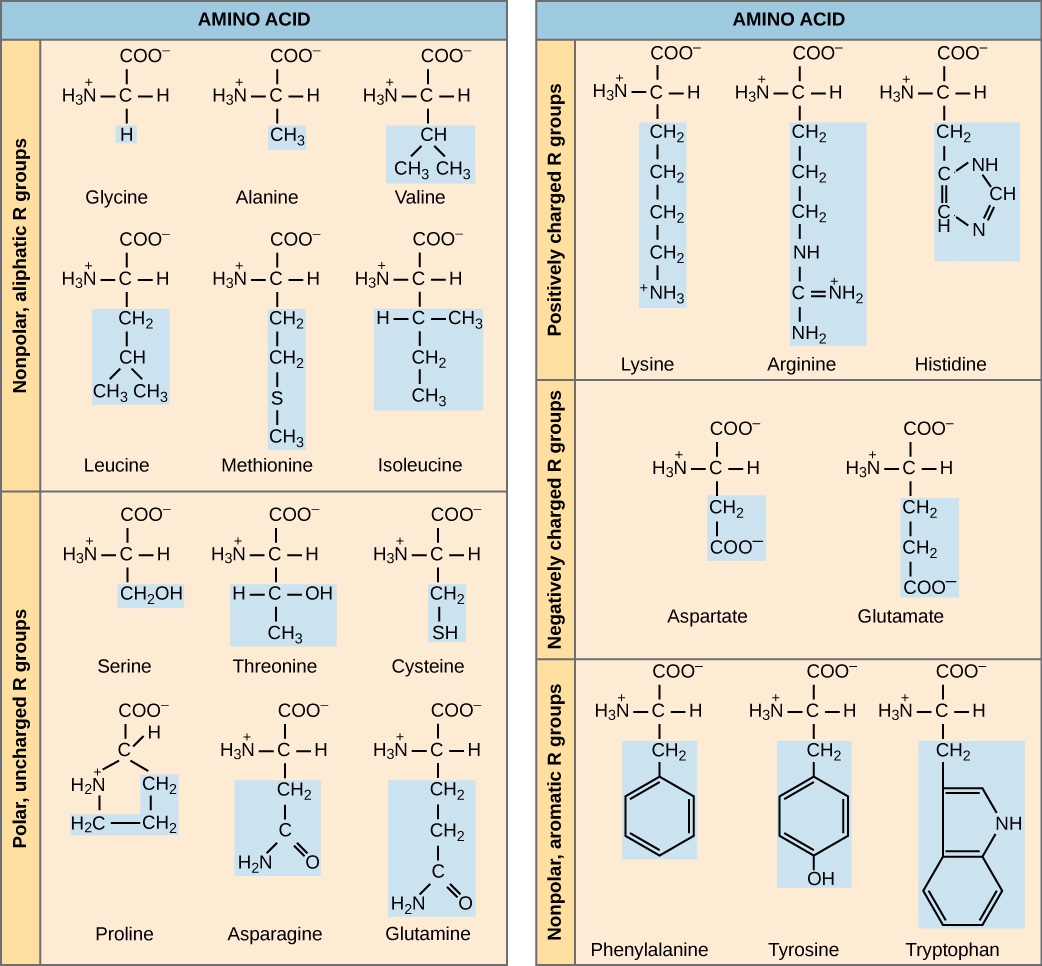
Which categories of amino acid would you expect to find on the surface of a soluble protein, and which would you expect to find in the interior? What distribution of amino acids would you expect to find in a protein embedded in a lipid bilayer?
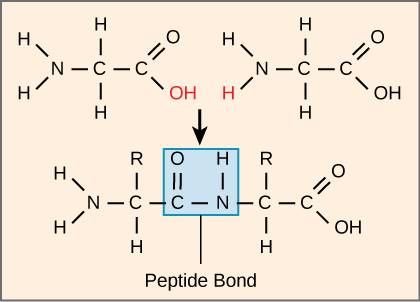
The sequence and the number of amino acids ultimately determine the protein's shape, size, and function. Each amino acid is attached to another amino acid by a covalent bond, known as a peptide bond, which is formed by a dehydration reaction. The carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amino group of the incoming amino acid combine, releasing a molecule of water. The resulting bond is the peptide bond (Figure \(\PageIndex{13}\)).