Microbiology and Protista Lab
- Page ID
- 7675
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\dsum}{\displaystyle\sum\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dint}{\displaystyle\int\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dlim}{\displaystyle\lim\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\(\newcommand{\longvect}{\overrightarrow}\)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)Learning Objectives
After completing this lab, you student should be able to:
- Describe the basic structures of a bacterial cell.
- State the three domains of life
- Name the shape of a given bacteria specimen
- State the domain of cyanobacteria
- Be able to identify the cyanobacteria examples viewed in lab
- State the domain of the protista
- Be able to identify the green algae examples viewed in lab and know if they are colonial or filamentous
- Be able to recognize the protista specimen viewed in lab
- Identify protista as photosynthetic or heterotrophic
Lab 2: Microbiology from Lumen Learning
Download a PDF of the lab to print.
Part 1: Prokaryotes
Procedure
- Access the page “Reading: Prokaryotes.”
- We will not be using any live bacteria specimens. Instead, watch this video about aseptic technique.This technique is important to avoid microorganism contamination.
Questions
- Answer the questions below based on the video.
- What two tools are most commonly used to transfer bacteria?
- With the Bunsen burner, what color is the hottest flame?
- How are the inoculation tools sterilized?
- When transferring bacteria from a liquid culture to a Petri plate, why do you turn the plate while spreading the bacteria?
- When transferring bacteria from a Petri plate to a stab culture, how many times should you stab the needle?
- When transferring bacteria into a liquid tube do you flame the mouth of the tube before inoculation, after inoculation, or both?
- Skip to the end of the lab activity where it says “Prepared slides of typical bacteria” and view the prepared slides of bacterial shapes available in the laboratory.
- Draw a picture of the coccus shaped bacteria.
- Draw a picture of the bacillus shaped bacteria.
- Draw a picture of the spirillum shaped bacteria.
- View the prepared slides of cyanobacteria available in the laboratory. Although they are single celled note how they form colonies and attach to one another
- What is the function of the heterocycst in the Anabaena?
- If the Oscillatoria is moving, describe the movement quality below.
- Which cyanobacteria species form chains? Which cyanobacteria species form clumps?
Part 2: Protista
Procedure
- Access the page “Reading: Protists.”
- Watch this video.
Questions
- View the Euglenozoans specimens available.
- What color is the euglena?
- What structure does the euglena use to move?
- Can you see any internal chloroplasts?
- Can you see the red eyespot? It does not give the organism vision, rather allows it to sense the presence of light.
- Trypanosoma sp. cause African sleeping sickness. (This disease was discussed in the video.)
- What part of the human body does the Trypanosoma invade?
- What structure does the Trypanosoma use to move?
- How does the Trypanosoma avoid being killed by the white blood cells?
- Can African sleeping sickness cause death?
- View the diatom specimens available.
- What material is found in the cell wall of the diatoms?
- Are the organisms single or multi cellular?
- View the brown algae specimens available.
- What pigment does brown algae use for photosynthesis?
- Name and describe the characteristics of one brown algae specimen below.
- View the dinoflagellate specimens available.
- What structure does the dinoflagellate use for movement? How many of these structures does it have?
- Are the organisms single or multi cellular?
- View the ciliate specimens available.
- What structure does Paramecium use to move? Does it have only one or many of these structures?
- Paramecium contains two nucli, a macronucleus (large) and a micronucleus (small). Can you find both of them on your specimen?
- Paramecium also contains contractile vacuoles that help maintain water balance through osmosis. Can you locate any on your specimen?
- View the red algae specimens available.
- What pigment does red algae use for photosynthesis?
- Name and describe the characteristics of one red algae specimen below.
- View the green algae specimens available.
- What pigment does green algae use for photosynthesis?
- Name and describe the characteristics of one green algae specimen below.
- View the Tubulinid specimens available.
- What structure does Amoeba use to move?
- Is the Amoeba single or multi celled?
- The Amoeba contains contractile vacuoles that help maintain water balance through osmosis. Can you locate any on your specimen?
Summary Questions
- Answer the questions below to summarize the lab activity:
- What type of cell is considered more primitive or basic?
- State one difference between a prokaryotic and a eukaryotic cell.
- What two domains contain prokaryotic celled organisms?
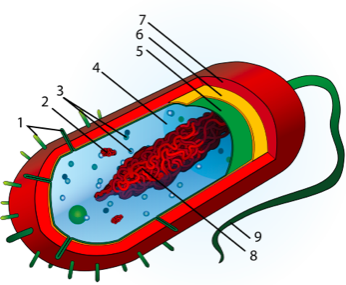
- Identify structures 1, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, and 9 on the generalized prokaryotic cell pictured below
- Are the cyanobacteria autotrophic or heterotrophic?
- Which cyanobacteria species secretes a gelatinous sheath?
- Which protista are most similar to green plants? Why?
- You viewed several protista that exhibited movement. Give an example of a protista that used each of the following movement structures:
- Flagella:
- Cilia:
- Pseudopod:
Give two examples of photosynthetic protista you viewed in lab and state what pigment each uses for photosynthesis.
LICENSES AND ATTRIBUTIONS
CC LICENSED CONTENT, ORIGINAL
- Biology 102 Labs. Authored by: Lynette Hauser. Provided by: Tidewater Community College . Located at: http://www.tcc.edu/. License: CC BY: Attribution
CC LICENSED CONTENT, SHARED PREVIOUSLY
- Prokaryotes Lab (Biology 102). Authored by: Michael J. Gregory, Ph.D.. Located at: https://b51ab7d9e5e1e7063dcb70cee5c33cf7f4b7bad8.googledrive.com/host/0Bx6hk6AUBHxDc2d4TDJZTFIyMGs/default.htm. License: CC BY-NC-SA: Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike


