8.4: Auditory Ossicles
- Page ID
- 53622
Auditory Ossicles
Within the external acoustic meatus of the temporal bone is the external auditory canal that carries sound into the middle ear. The tympanic membrane (ear drum) vibrates as it receives auditory information and transfers those vibrations to three small bones in the tympanic cavity of the middle ear: malleus, incus, and stapes, often known as the auditory ossicles.
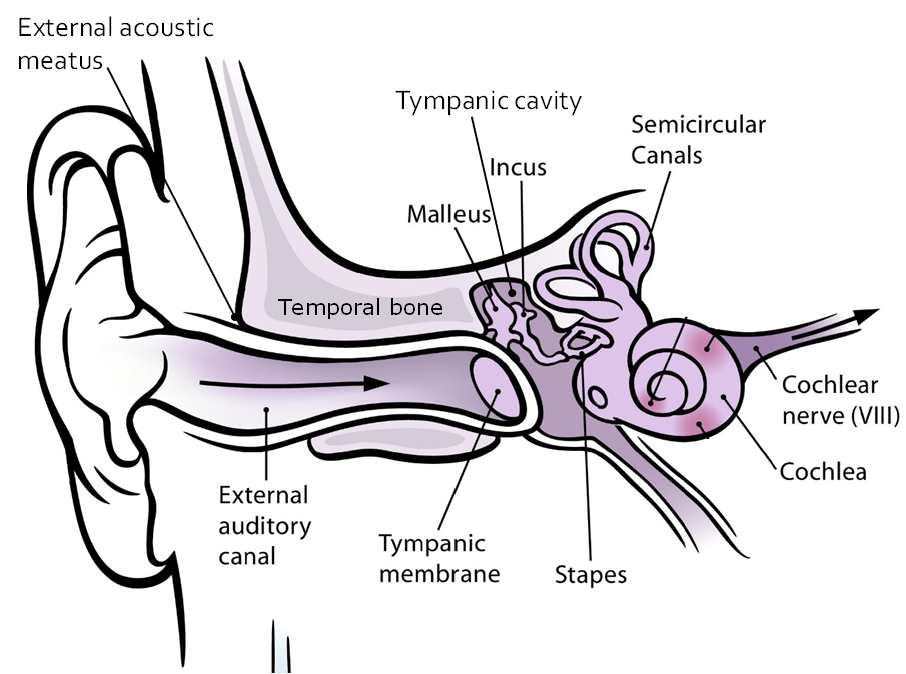
Above: External, middle, and inner ear including the auditory ossicles.
Malleus, also known as the hammer, articulates with incus (the anvil), which articulates with stapes (the stirrup). The aptly named stapes looks very much like a stirrup. The three ossicles are unique to mammals, and each plays a role in hearing. The malleus attaches at three points to the interior surface of the tympanic membrane. The incus attaches the malleus to the stapes. In humans, the stapes is not long enough to reach the tympanum. If we did not have the malleus and the incus, then the vibrations of the tympanum would never reach the inner ear. These bones also function to collect force and amplify sounds. These bones transfer the vibrations collected by the tympanic membrane to the cochlea, the specialized auditory sense organ. Auditory information in the cochlear is transferred to the cochlear nerve, part of C.N. VIII vestibulocochlear nerve, that carries auditory information to the brain.
There are two sets of auditory ossicles in the human body, one set in the right middle ear and one set in the left middle ear.
Attributions
- "Biology 2e" by Mary Ann Clark, Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, OpenStax is licensed under CC BY-NC 4.0
- "Frequency mapping in human ear and brain - 10.1371 journal.pbio.0030137.g001-L.jpg" by Chittka L. and Brockmann A. is licensed under CC BY 2.


