5.6: Laboratory Activities and Assignment
- Page ID
- 53580
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\dsum}{\displaystyle\sum\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dint}{\displaystyle\int\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\dlim}{\displaystyle\lim\limits} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\(\newcommand{\longvect}{\overrightarrow}\)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\(\newcommand{\avec}{\mathbf a}\) \(\newcommand{\bvec}{\mathbf b}\) \(\newcommand{\cvec}{\mathbf c}\) \(\newcommand{\dvec}{\mathbf d}\) \(\newcommand{\dtil}{\widetilde{\mathbf d}}\) \(\newcommand{\evec}{\mathbf e}\) \(\newcommand{\fvec}{\mathbf f}\) \(\newcommand{\nvec}{\mathbf n}\) \(\newcommand{\pvec}{\mathbf p}\) \(\newcommand{\qvec}{\mathbf q}\) \(\newcommand{\svec}{\mathbf s}\) \(\newcommand{\tvec}{\mathbf t}\) \(\newcommand{\uvec}{\mathbf u}\) \(\newcommand{\vvec}{\mathbf v}\) \(\newcommand{\wvec}{\mathbf w}\) \(\newcommand{\xvec}{\mathbf x}\) \(\newcommand{\yvec}{\mathbf y}\) \(\newcommand{\zvec}{\mathbf z}\) \(\newcommand{\rvec}{\mathbf r}\) \(\newcommand{\mvec}{\mathbf m}\) \(\newcommand{\zerovec}{\mathbf 0}\) \(\newcommand{\onevec}{\mathbf 1}\) \(\newcommand{\real}{\mathbb R}\) \(\newcommand{\twovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\ctwovec}[2]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\threevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cthreevec}[3]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfourvec}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\fivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{r}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\cfivevec}[5]{\left[\begin{array}{c}#1 \\ #2 \\ #3 \\ #4 \\ #5 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\mattwo}[4]{\left[\begin{array}{rr}#1 \amp #2 \\ #3 \amp #4 \\ \end{array}\right]}\) \(\newcommand{\laspan}[1]{\text{Span}\{#1\}}\) \(\newcommand{\bcal}{\cal B}\) \(\newcommand{\ccal}{\cal C}\) \(\newcommand{\scal}{\cal S}\) \(\newcommand{\wcal}{\cal W}\) \(\newcommand{\ecal}{\cal E}\) \(\newcommand{\coords}[2]{\left\{#1\right\}_{#2}}\) \(\newcommand{\gray}[1]{\color{gray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\lgray}[1]{\color{lightgray}{#1}}\) \(\newcommand{\rank}{\operatorname{rank}}\) \(\newcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\col}{\text{Col}}\) \(\renewcommand{\row}{\text{Row}}\) \(\newcommand{\nul}{\text{Nul}}\) \(\newcommand{\var}{\text{Var}}\) \(\newcommand{\corr}{\text{corr}}\) \(\newcommand{\len}[1]{\left|#1\right|}\) \(\newcommand{\bbar}{\overline{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bhat}{\widehat{\bvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\bperp}{\bvec^\perp}\) \(\newcommand{\xhat}{\widehat{\xvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\vhat}{\widehat{\vvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\uhat}{\widehat{\uvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\what}{\widehat{\wvec}}\) \(\newcommand{\Sighat}{\widehat{\Sigma}}\) \(\newcommand{\lt}{<}\) \(\newcommand{\gt}{>}\) \(\newcommand{\amp}{&}\) \(\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}\)Laboratory Activities and Assignment
Part 1: Review of Tissues
Epithelial Tissues
1. Where will you always find epithelial tissues?
2. What functions do simple epithelial tissues have?
3. What functions do stratified epithelial tissues have?
4. Describe how to differentiate each type of epithelial tissue in the table below:
|
Type of epithelial tissue |
Describe how to Differentiate this Tissue Type |
|---|---|
|
simple squamous epithelium |
|
|
simple cuboidal epithelium |
|
|
simple columnar epithelium |
|
|
pseudostratified columnar epithelium |
|
|
stratified squamous epithelium (non-keratinized) |
|
|
stratified squamous epithelium (keratinized) |
|
|
stratified cuboidal epithelium |
|
|
stratified columnar epithelium |
|
|
transitional epithelium |
Connective Tissues
1. List 3 characteristic of connective tissue.
2. List the four categories of connective tissues.
Muscle Tissues
1. List the characteristics of skeletal muscle.
2. List the characteristics of smooth muscle.
3. List the characteristics of cardiac muscle.
Nervous Tissues
1. Name the two main types of cells present in nervous tissue. Describe their functions.
2. Create an illustration of a neuron from the images in Chapter 5. Label the cell body, axon, dendrites, and nucleus.
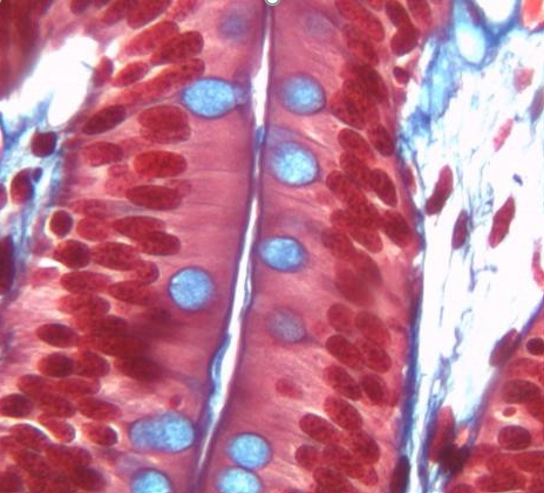
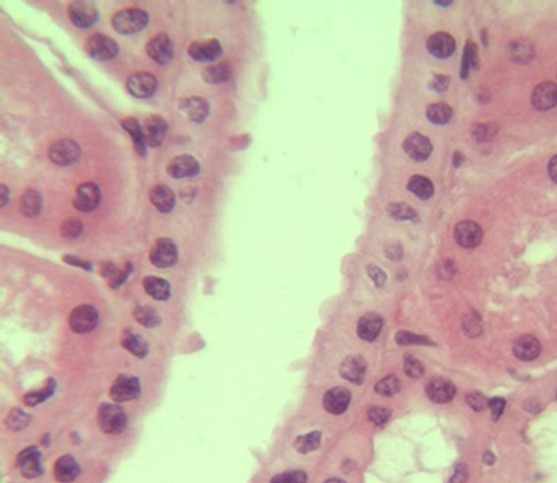
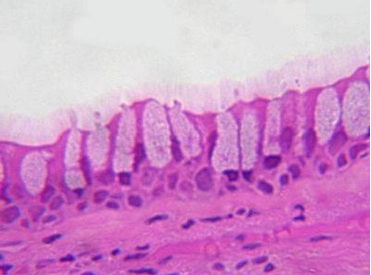
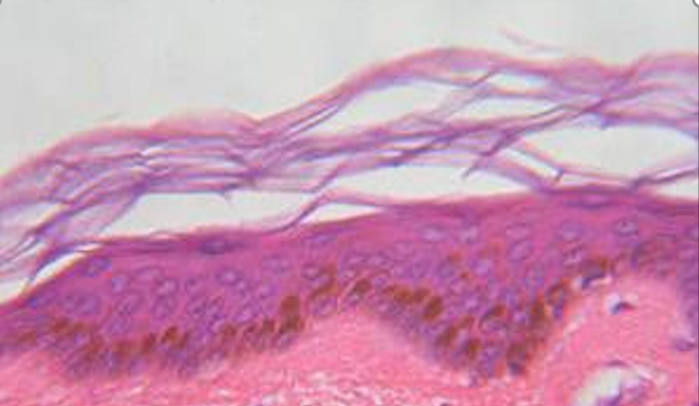
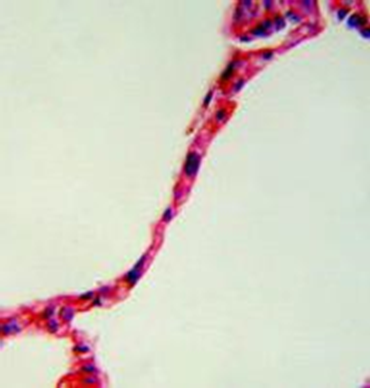
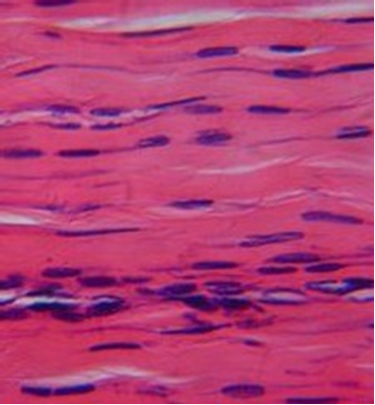
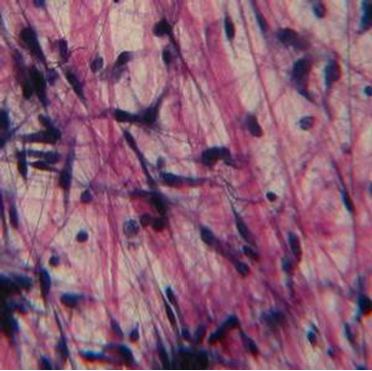
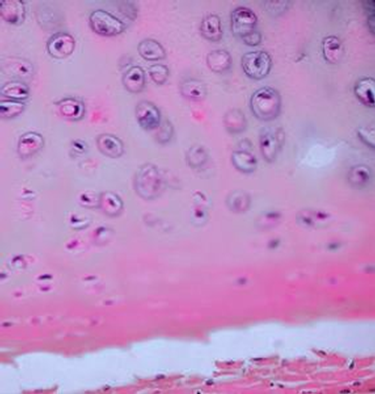
Tissue Identification
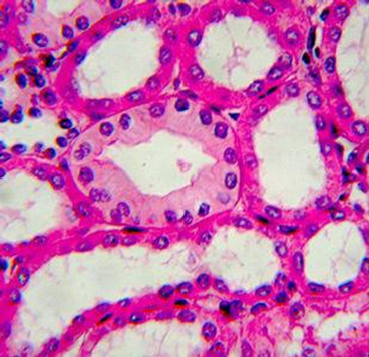
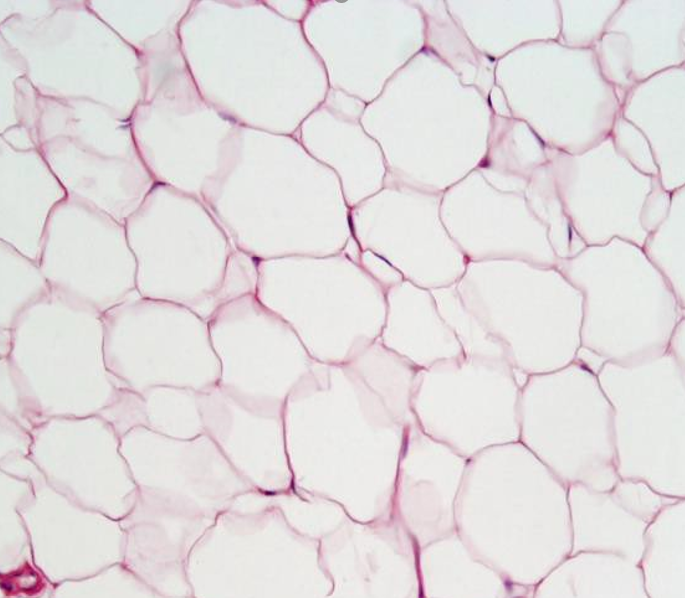
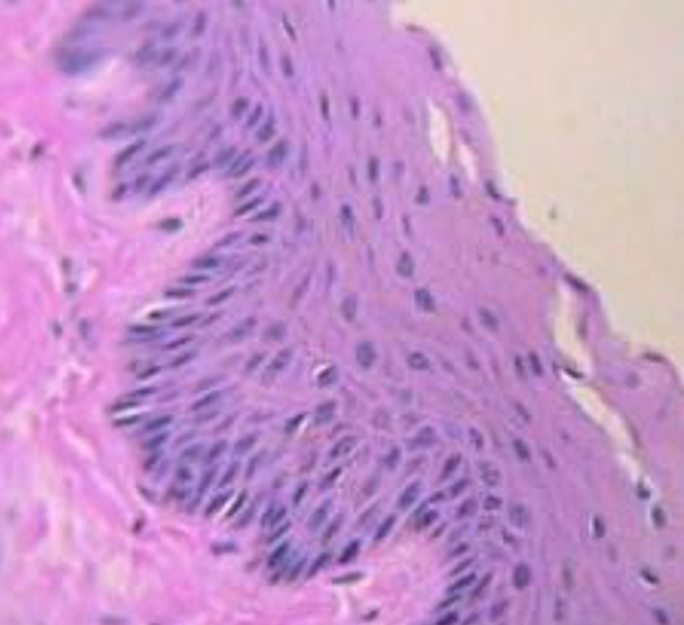
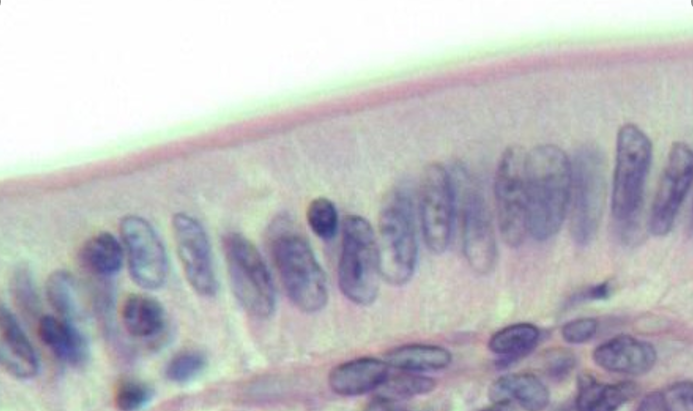
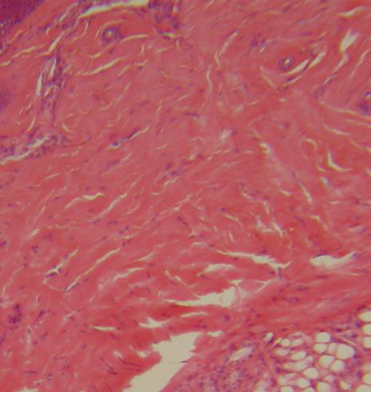
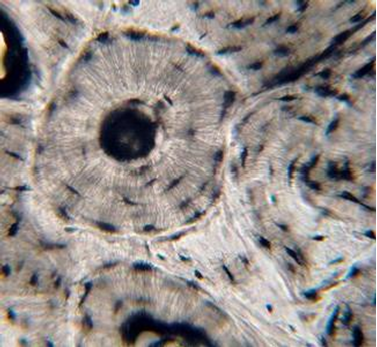
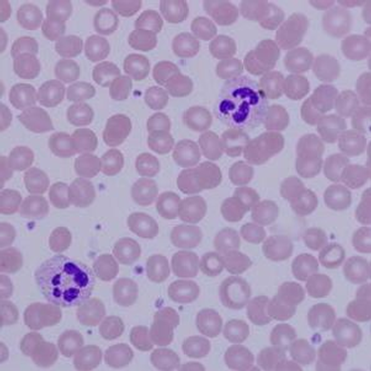
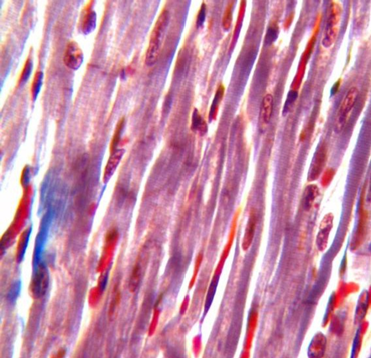
1. For each microscopic tissue image below, give the category of the tissue shown (epithelial, connective, muscle, or nervous) and give the name of the specific tissue shown.
|
Tissue category: Tissue name: |
Tissue category: Tissue name: |
Tissue category: Tissue name: |
|
Tissue category: Tissue name: |
Tissue category: Tissue name: |
Tissue category: Tissue name: |
|
Tissue category: Tissue name: |
Tissue category: Tissue name: |
Tissue category: Tissue name: |
|
Tissue category: Tissue name: |
Tissue category: Tissue name: |
Tissue category: Tissue name: |
|
Tissue category: Tissue name: |
Tissue category: Tissue name: |
Tissue category: Tissue name: |
|
Tissue category: Tissue name: |
Tissue category: Tissue name: |
Tissue category: Tissue name: |
Part 2: Examining, Illustrating, and Labeling Epithelial Tissues
- Obtain the slides listed below that are available for today’s lab.
- Focus on each sample and identify the structures listed for each type of tissue.
- Indicate the total magnification you make each illustration at in the space provided.
- Illustrate each tissue you observe with the microscope at the magnification you listed.
- Label each illustration with the structures listed for each.
Simple Squamous Epithelium (Slide: Lung or Kidney)
Label the tissue with: squamous cell, nucleus of squamous cell, simple squamous epithelium, basement membrane, connective tissue
Stratified Squamous Epithelium (Slide: Skin or Stratified Squamous Epithelium
Label the tissue with: squamous cell, nucleus of squamous cell, stratified squamous epithelium, basement membrane, connective tissue
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium (Slide: Simple Cuboidal Epithelium or Kidney Tubules)
Label the tissue with: cuboidal cell, nucleus of cuboidal cell, simple cuboidal epithelium, basement membrane, connective tissue
Simple Columnar Epithelium (Slide: Simple Columnar Epithelium or Small Intestine)
Label the tissue with: columnar cell, nucleus of columnar cell, simple columnar epithelium, basement membrane, goblet cell, connective tissue
Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium (Slide: Pseudostratified Ciliated Columnar Epithelium)
Label the tissue with: columnar cell, nucleus of columnar cell, pseudostratified columnar epithelium, cilia, basement membrane, connective tissue
Part 3: Examining, Illustrating, and Labeling Connective Tissues
- Obtain the slides listed below that are available for today’s lab.
- Focus on each sample and identify the structures listed for each type of tissue.
- Indicate the total magnification you make each illustration at in the space provided.
- Illustrate each tissue you observe with the microscope at the magnification you listed.
- Label each illustration with the structures listed for each.
Connective Tissue Proper - Loose - Areolar Tissue (Slide: Areolar Tissue)
Label the tissue with: nucleus of fibroblast (cell type), collagen fibers, elastic fibers, ground substance
Connective Tissue Proper - Loose - Adipose Tissue (Slide: Adipose Tissue)
Label the tissue with: adipocyte, nucleus of adipocyte, fat-containing vacuole
Connective Tissue Proper - Loose - Reticular Tissue (Slide: Reticular Tissue)
Label the tissue with: lymphocytes, reticular fibers
Connective Tissue Proper - Dense - Regular (Slide: Tendon)
Label the tissue with: nucleus of fibroblast (cell), collagen fibers
Connective Tissue Proper - Dense - Irregular (Slide: Skin)
Label the tissue with: cell nucleus, collagen fibers
Cartilage - Hyaline Cartilage (Slide: Hyaline Cartilage)
Label the tissue with: chondrocyte, lacuna, matrix
Cartilage - Elastic Cartilage (Slide: Elastic Cartilage)
Label the tissue with: chondrocyte, lacuna, elastic fibers, matrix
Cartilage - Fibrocartilage (Slide: Fibrocartilage)
Label the tissue with: chondrocyte, lacuna, collagen fibers
Compact Bone Tissue (Slide: Dry Bone Ground)
Label the tissue with: osteon, lamella, osteocyte in lacuna, central canal, canaliculi
Fluid Tissue - Blood (Slide: Human Blood)
Label the tissue with: erythrocyte, plasma, leukocyte
Part 4: Examining, Illustrating, and Labeling Muscle Tissues
- Obtain the slides listed below that are available for today’s lab.
- Focus on each sample and identify the structures listed for each type of tissue.
- Indicate the total magnification you make each illustration at in the space provided.
- Illustrate each tissue you observe with the microscope at the magnification you listed.
- Label each illustration with the structures listed for each.
Skeletal Muscle (Slide: Skeletal Muscle)
Label the tissue with: muscle fiber, nucleus, striations
Cardiac Muscle (Slide: Cardiac Muscle)
Label the tissue with: striations, cell nucleus, intercalated disc, branch
Smooth Muscle (Slide: Smooth Muscle)
Label the tissue with: smooth muscle cell, cell nucleus
Part 5: Examining, Illustrating, and Labeling Nervous Tissue
- Obtain the slide listed below that is available for today’s lab.
- Focus on the sample and identify the structures listed for this type of tissue.
- Indicate the total magnification you make the illustration at in the space provided.
- Illustrate the tissue you observe with the microscope at the magnification you listed.
- Label the illustration with the structures listed.
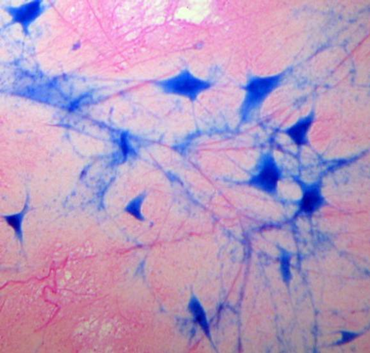
Nervous Tissue (Slide: Giant Multipolar Neuron Smear)
Label the tissue with: neuron, cell body of neuron, dendrites, axon, nucleus of neuron, nuclei of neuroglia
Attributions
Part 1: Review of Tissues
- "Anatomy and Physiology I Lab" by Victoria Vidal is licensed under CC BY 4.0
- "Anatomy and Physiology Lab Homework" by Laird C Sheldahl is licensed under CC BY-SA 4.0
Part 2: Examining, Illustrating, and Labeling Epithelial Tissues
- "BIOL 250 Human Anatomy Lab Manual SU 19" by Yancy Aquino, Skyline College is licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0
Part 3: Examining, Illustrating, and Labeling Connective Tissues
- "BIOL 250 Human Anatomy Lab Manual SU 19" by Yancy Aquino, Skyline College is licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0
Part 4: Examining, Illustrating, and Labeling Muscle Tissues
- "BIOL 250 Human Anatomy Lab Manual SU 19" by Yancy Aquino, Skyline College is licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0
Part 5: Examining, Illustrating, and Labeling Nervous Tissue
- "BIOL 250 Human Anatomy Lab Manual SU 19" by Yancy Aquino, Skyline College is licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0
Updated 2025.