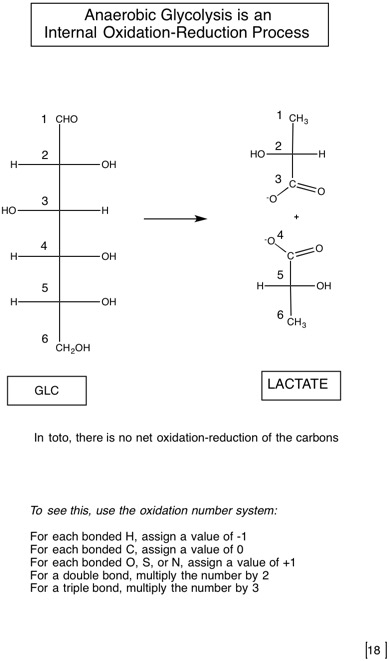
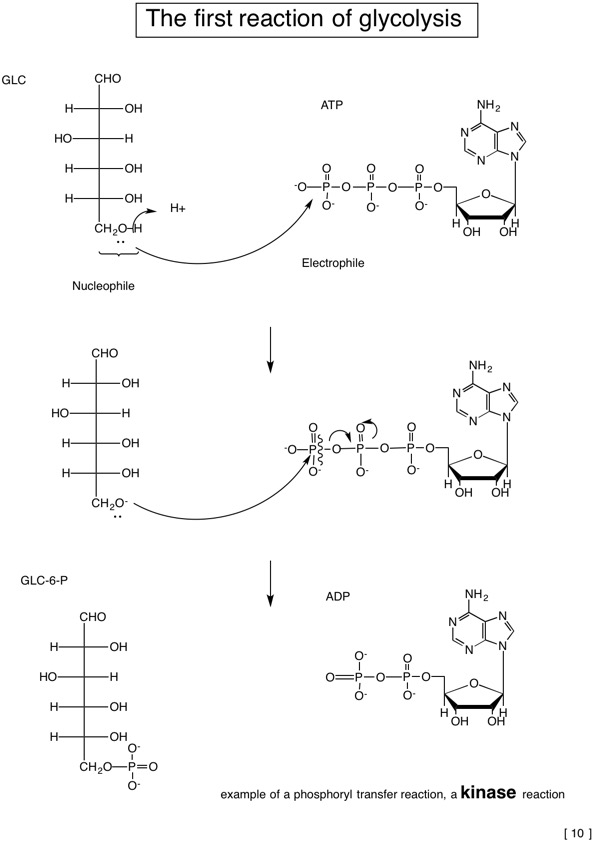
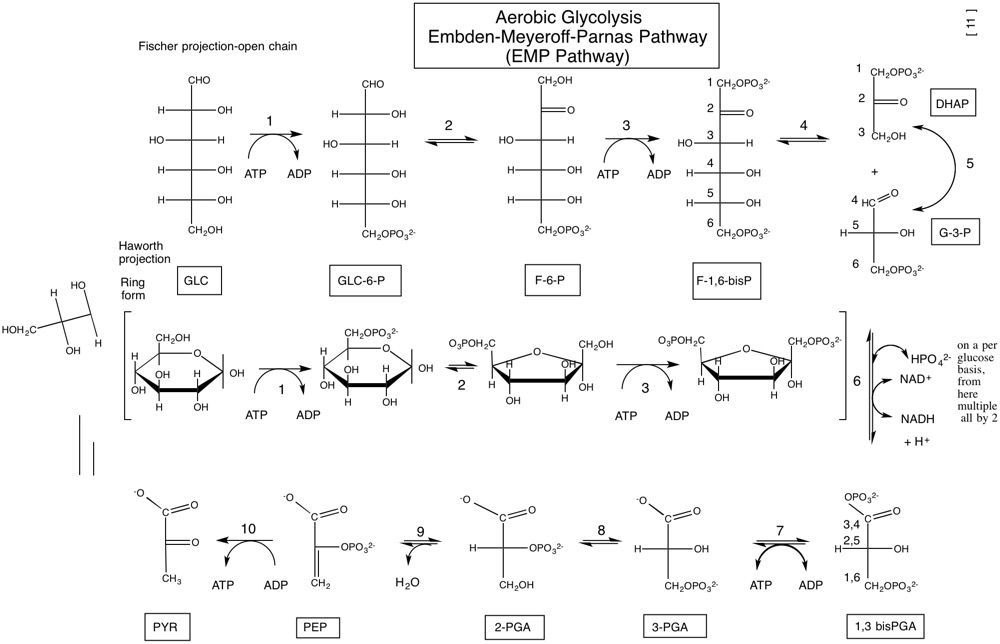
2.2: Catabolism of glucose-glycolysis as the first pathway tells us about some general metabolic principles
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
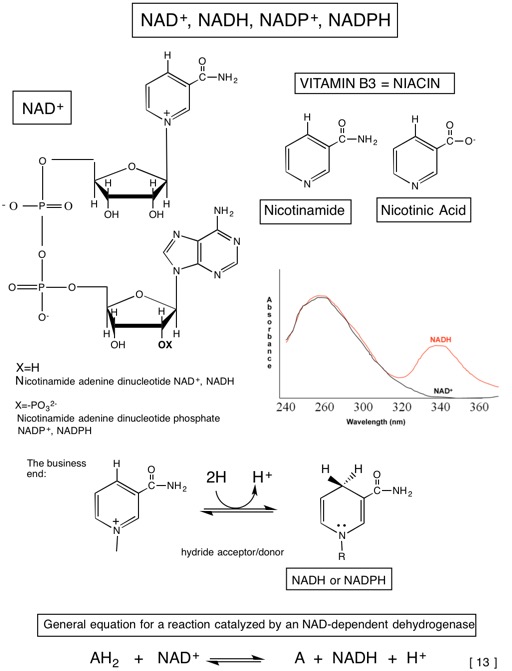
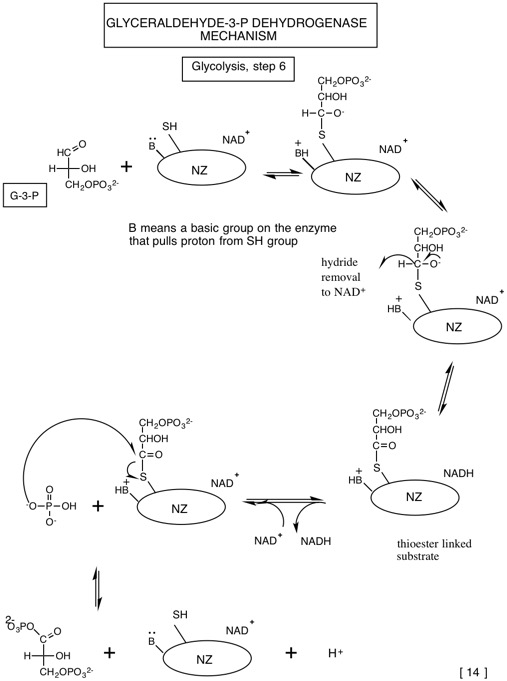
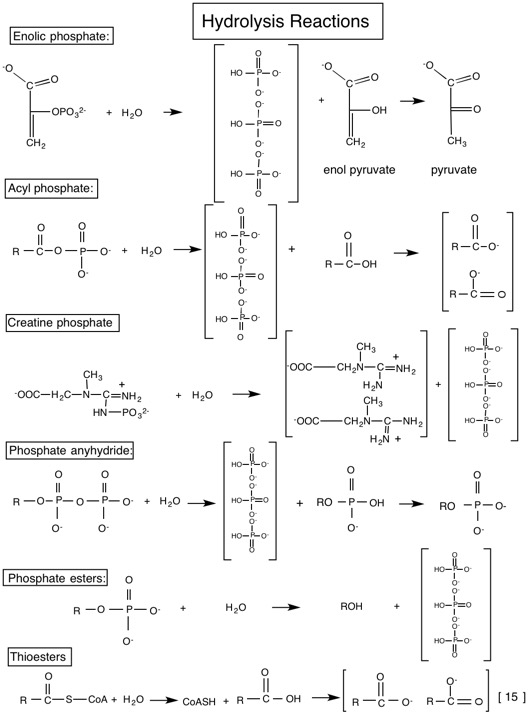
Tables of standard free energies of hydrolysis
Table A. Compounds considered to be "High Energy" Compounds
Pi= inorganic phosphate (doesn’t specify a species) = major species at biological pH is HPO2−4
| Compound (hydrolysis reaction is shown where more than one is possible) | ΔG∘′(kJ/mol) | Transfer Potential=|ΔG∘′| | Compound type | Reason for large ΔG∘′ of hydrolysis S=Substrate P=Product |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PEP | -61.9 | 61.9 | Enolic phosphate | P tatuomerizes (pyruvate) P resonance stability (Pi) |
| 1,3-bisPGA | -49.3 | 49.3 | Acyl phosphate (phosphoric acid + carboxylic acid) | P ionizaiton (PGA) Increased P resonance stability (Pi and PGA) |
| Phosphocreatine | -43.0 | 43.0 | Guanidine phoshpate | P resonance stability |
| ATP→AMP+PPi | -45.6 | 45.6 | Phosphoric acid anhydride | P resonance stability P ionization S bond strain due to electrostatic repulsion |
| ADP→AMP+Pi | -32.8 | 32.8 | Phosphoric acid anhydirde | Same as for ATP→AMP+P |
| ATP→ADP+Pi | -30.5 | 30.5 | Phosphoric acid anhydride | Same as for ATP→AMP+P |
| UDP-Glucose | -31.9 | 31.9 | Sugar nucleotide | P resonance stability P ionization |
| Acetyl Coenzyme A | -31.4 | 31.4 | Thioester | S no resonance stabilization P ionization P resonance stabilization |
| S-adenosylmethionine | -25.6 | 25.6 | Sulfonium salt | Sulfur more stable in P P less charge repulsion |
Table B. Compounds considered NOT to be "High Energy" Compounds
| Compound | ΔG∘′(kJ/mol) | Transfer Potential | Compound type | Reason for ΔG∘′ of hydrolysis smaller than compounds in Table A. |
| AMP→adenosine+Pi | -14.2 | 14.2 | Phosphate ester | S no destabilizing electrostatic repulsion P (Adenine) doesn't ionize |
| Glc−6−P→Glc+HPO2−4 | -13.8 | 13.8 | Phosphate ester | S no electrostatic repulsion |
"high energy" bonds are those whose hydrolysis proceeds with ΔG∘′ more negative than -25kJ/mol
Most values from Principles of Biochemistry pp. 521.
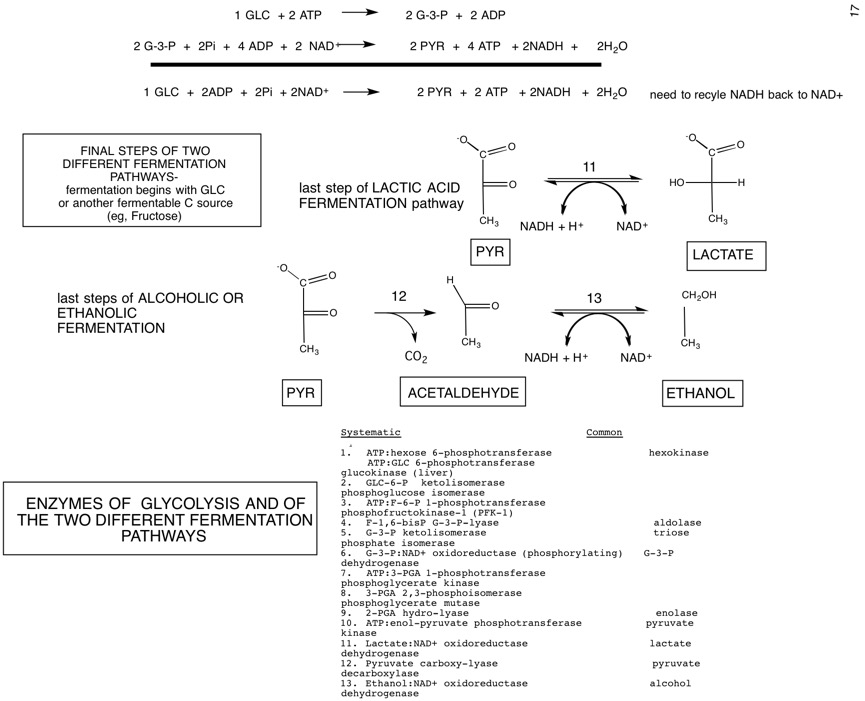
| Systematic | Common |
|---|---|
| ATP:hexose 6-phosphotransferase | Hexokinase |
| ATP:GLC 6-phosphotransferase | Glucokinase (liver) |
| GLC-6-P ketolisomerase | Phosphoglucose isomerase |
| ATP:F-6-P 1-phosphotransferase | Phosphofructokinase-1 (PFK-1) |
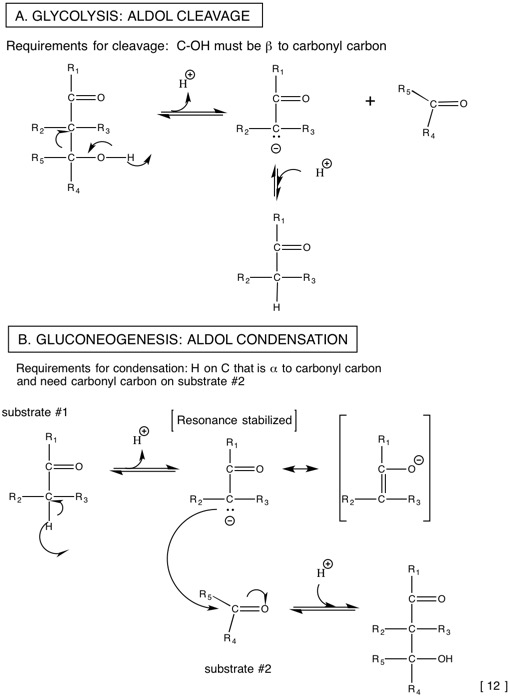
| F-1,6-bisP G-3-P-lyase | aldolase |
| G-3-P ketolisomerase | Triose phosphate isomerase |
| G-3-P:(\mathrm{NAD^{+}}\) oxidoreductase (phosphorylating) | G-3-P dehydrogenase |
| ATP:3-PGA 1-phosphotransferase | Phosphoglycerate kinase |
| 3-PGA 2,3-phosphoisomerase | Phosphoglycerate mutase |
| 2-PGA hydro-lyase | Enolase |
| ATP:enol-pyruvate phosphotransferase | Pyruvate kinase |
| Lactate:NAD+ oxidoreductase | Lactate dehydrogenase |
| Pyruvate carboxy-lyase | Pyruvate decarboxylase |
| Ethanol:NAD+ oxidoreductase | Alcohol dehydrogenase |