17.6: Circulation Through the Heart
- Page ID
- 53780
Circulation Through the Heart
When the ventricles of the heart contract (ventricular systole), it pumps blood into two different circuits: the pulmonary circuit and the systemic circuit. Pulmonary circulation carries blood from the right side of the heart to the alveoli of the lungs and back to the left side of the heart, while the systemic circulation carries blood from the left side of the heart to all the organs and tissues of the body, before returning to the right side of the heart.
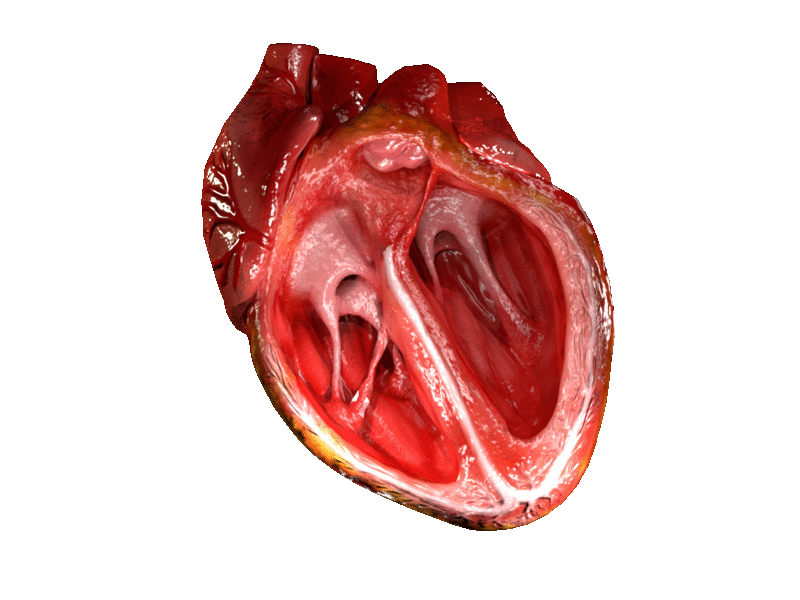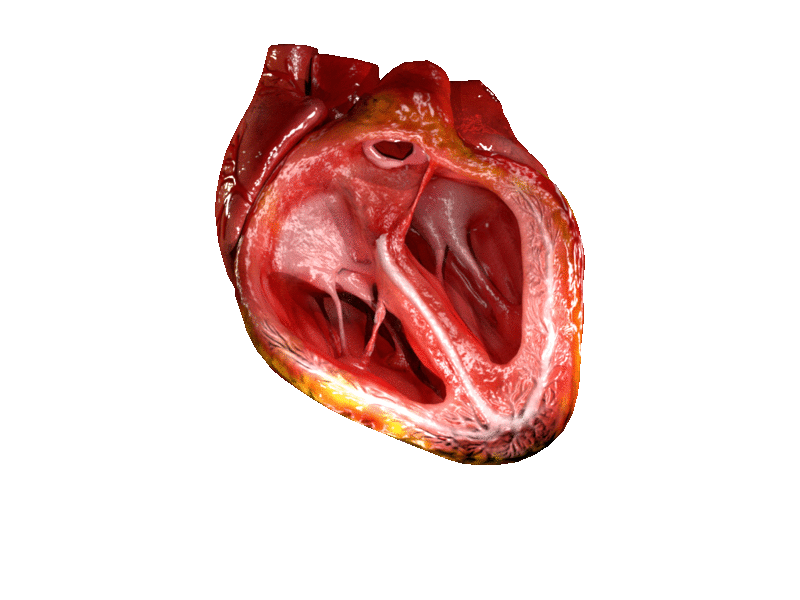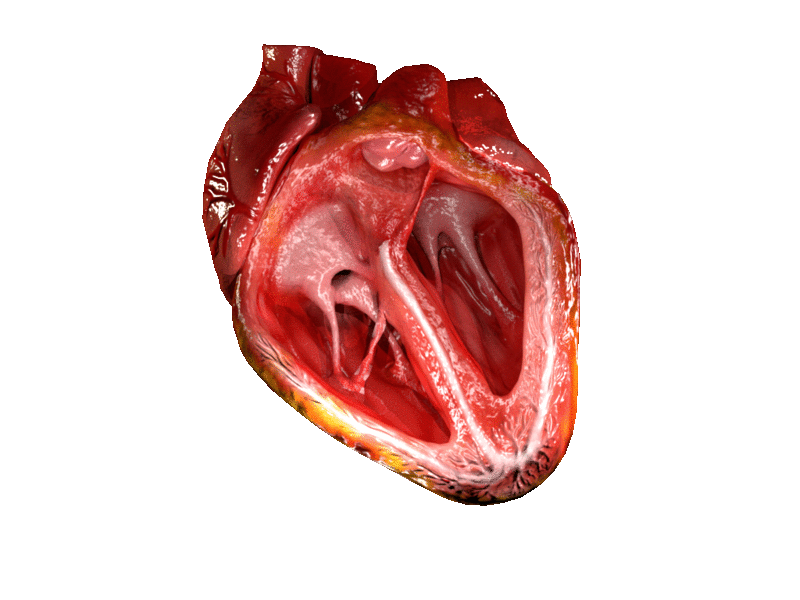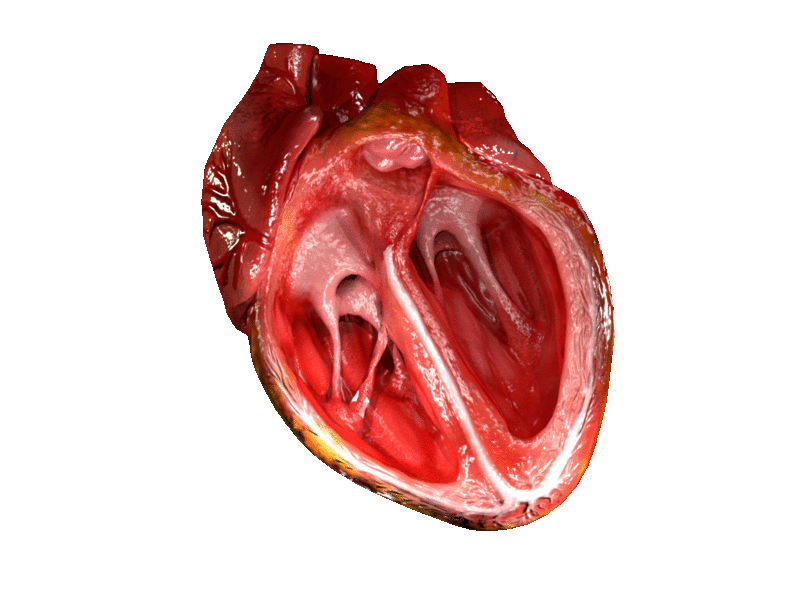
Above: Animated heart pumping with the ventricles shown open.
The Pulmonary Circuit
The function of the pulmonary circuit is to oxygenate (add oxygen to) the blood by transferring low-oxygen blood to the lungs to acquire oxygen. Once oxygenated, blood in the blood vessels of the pulmonary circuit returns to the heart to complete the circuit.
The right side of the heart pumps blood through the systemic circuit. Blood entering the right side of the heart is returning to the heart from the systemic circuit. This blood has had much of its oxygen depleted since oxygen is transferred to the cells of the body in the systemic circuit. Blood enters the right side of the heart through the superior vena cava and the inferior vena cava.
- Blood enters the right atrium by way of the superior vena cava and the inferior vena cava.
- From the right atrium, the blood flows through the tricuspid AV valve into the right ventricle.
- After the ventricle contracts, the blood flows through the pulmonary semilunar valve and into the pulmonary arteries.
- The pulmonary arteries deliver the blood to the lungs where it is enriched with oxygen and exits by way of the pulmonary veins.
- The oxygenated blood is delivered to the left atrium by way of the pulmonary veins.
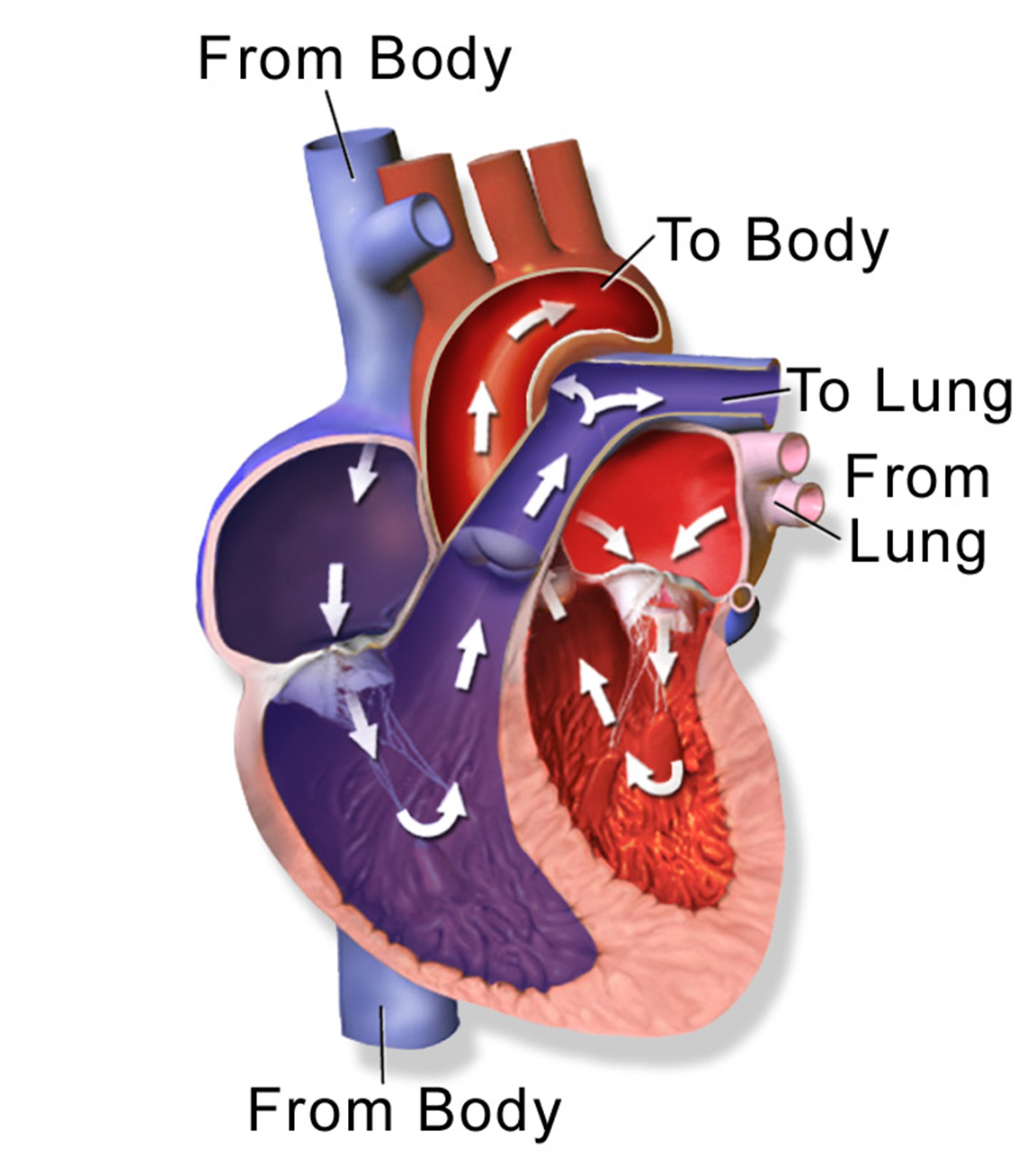
Above: Diagram showing the movement of blood into, out of, and through the heart.
The Systemic Circuit
The function of the systemic circuit is to carry oxygen-rich blood to the organs and tissues throughout the body. Blood returning to the heart from the pulmonary circuit enters the systemic circuit in the left atrium. Blood transfers from the left atrium to the left ventricle, and then exits the left ventricle when pressure forces blood into the aorta. The aorta branches to all the other arteries of the systemic circuit traveling to the head, thorax, upper limbs, abdominopelvic region, and lower limbs. After oxygen is transferred from the blood in the smallest blood vessels of the systemic circuit (capillaries), veins return low-oxygen blood back to the heart through the superior vena cava and inferior vena cava to enter the pulmonary circuit.
- The oxygenated blood is delivered to the left atrium by way of the pulmonary veins.
- Blood moves through the bicuspid (or mitral) AV valve into the left ventricle.
- From here the blood is pushed through the systemic semilunar valve (aortic valve) into the aorta and then out into the body.
- Oxygen-depleted blood returns to the right atrium by way of the superior vena cava and the inferior vena cava.
Attributions
- "CG Heart.gif" by DrJanaOfficial is licensed under CC BY-SA 4.0
- "Heart Anatomy" by Dongho Kim is licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0
- "Medical gallery of Blausen Medical 2014" by Blausen.com staff is licensed under CC BY 3.0
- "Human Anatomy Lab Manual" by Malgosia Wilk-Blaszczak, Mavs Open Press, University of Texas at Arlington is licensed under CC BY 4.0


