7.7: Cartilage
- Page ID
- 53608
Cartilage
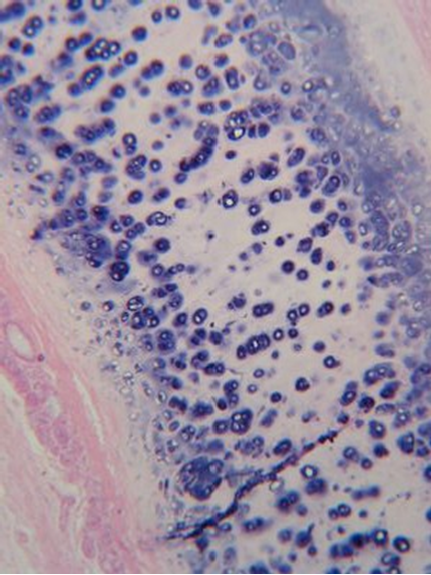
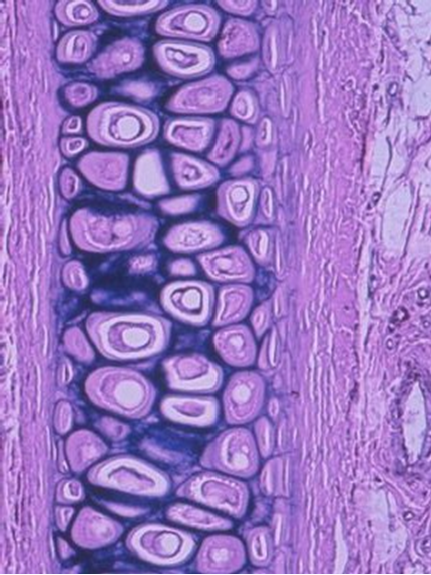
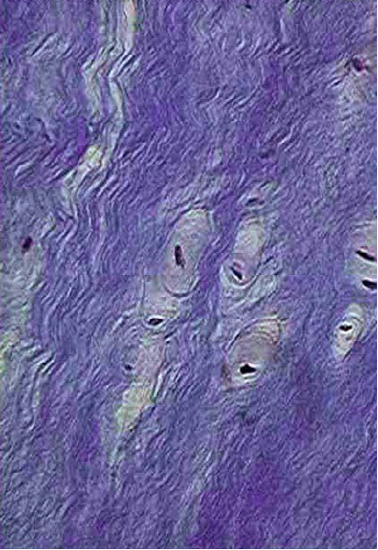
In additional to bone, cartilage is also an important part of the skeletal system creating structure, connecting bones, cushioning joints (articulations), protecting the ends of bones, and providing shock absorption. There are three different types of cartilage in the human body: hyaline cartilage, elastic cartilage, and fibrocartilage (see table below). For example, hyaline cartilage connects the ribs to the sternum and is called the costal cartilage (see image/gif animation below). Another example is the fibrocartilage is located between each vertebrae pair making up part of the intervertebral discs, which are crucial for separating the vertebrae, providing shock absorption, and better distributing pressure between the vertebrae (see image/gif animation below).
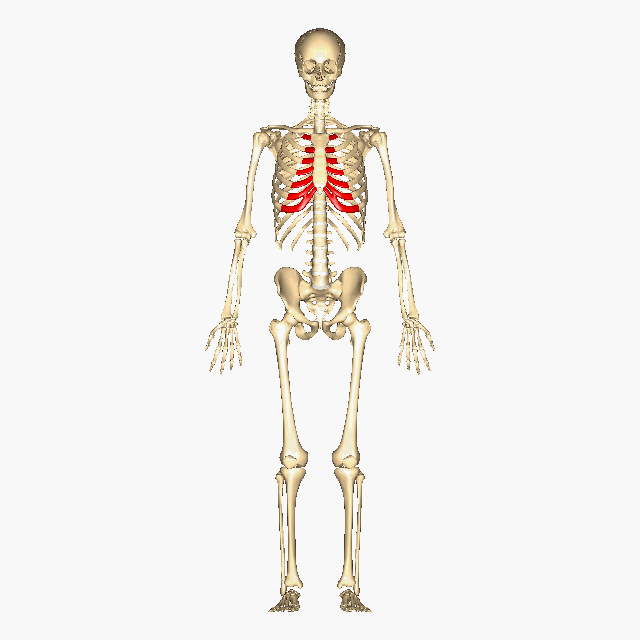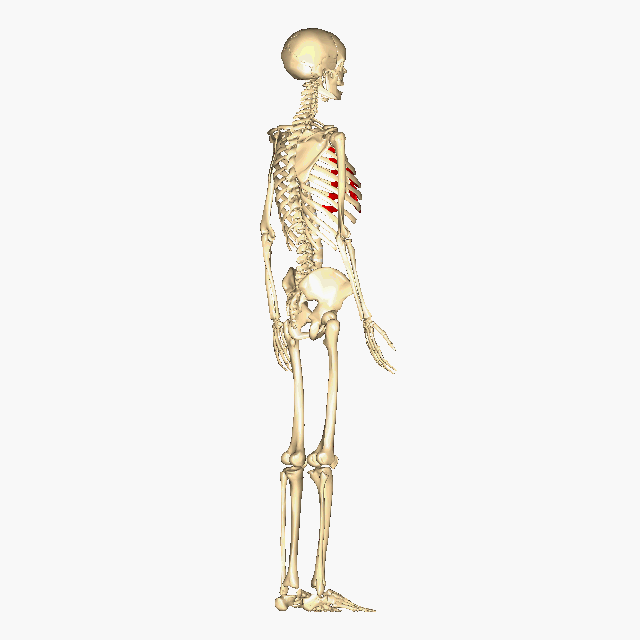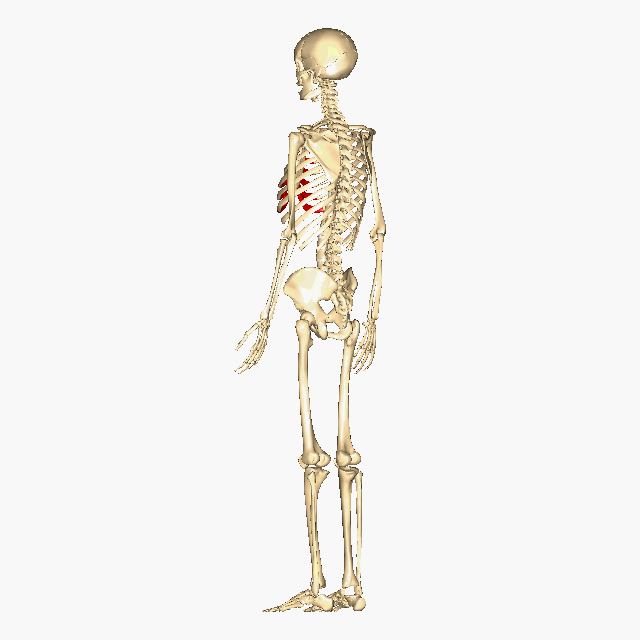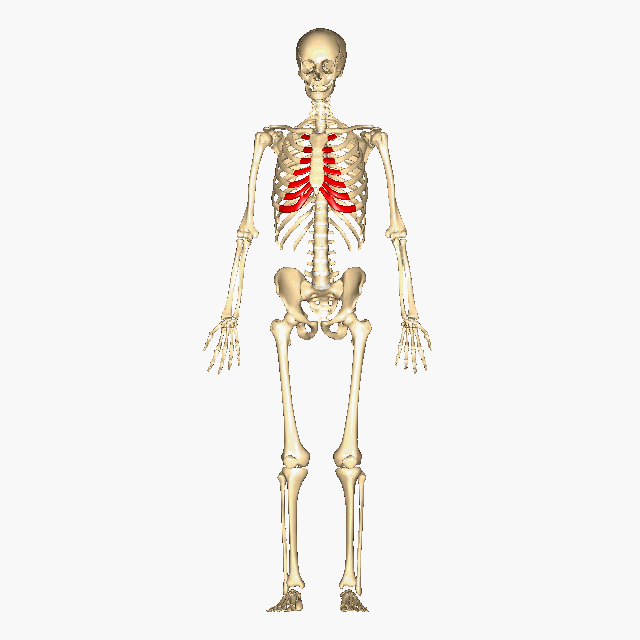
Above: The human skeleton highlighting the costal cartilage in red.
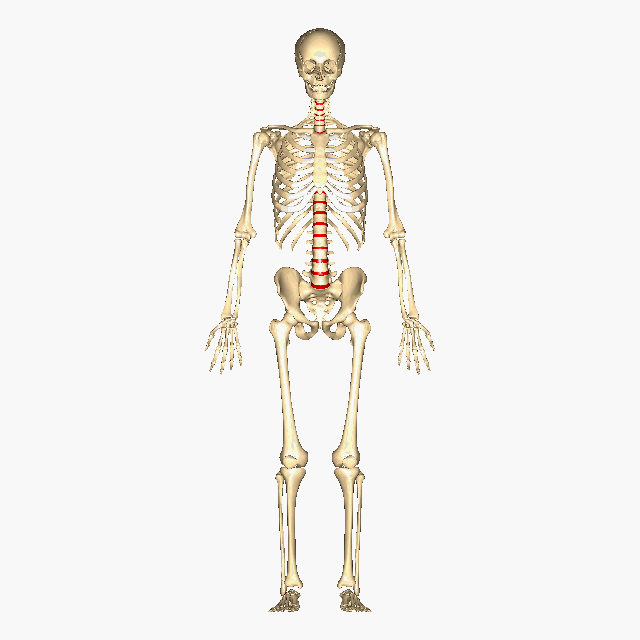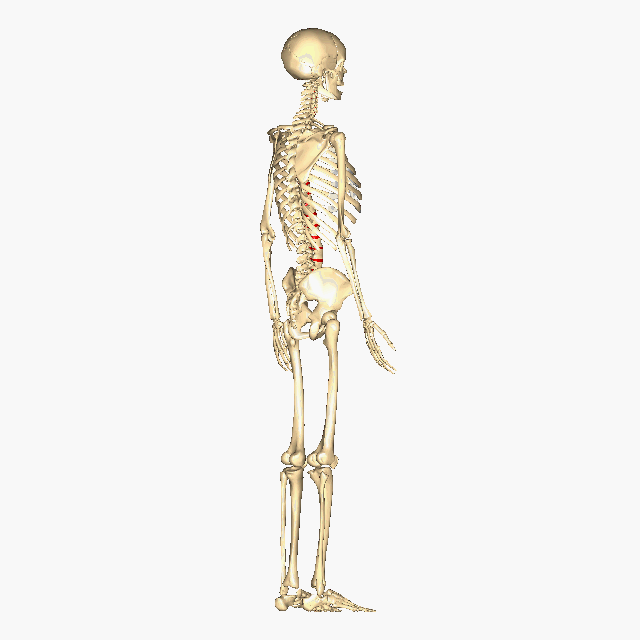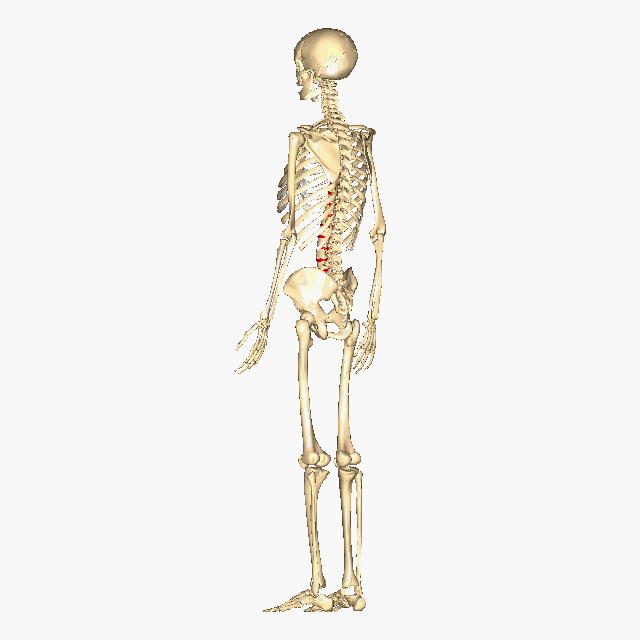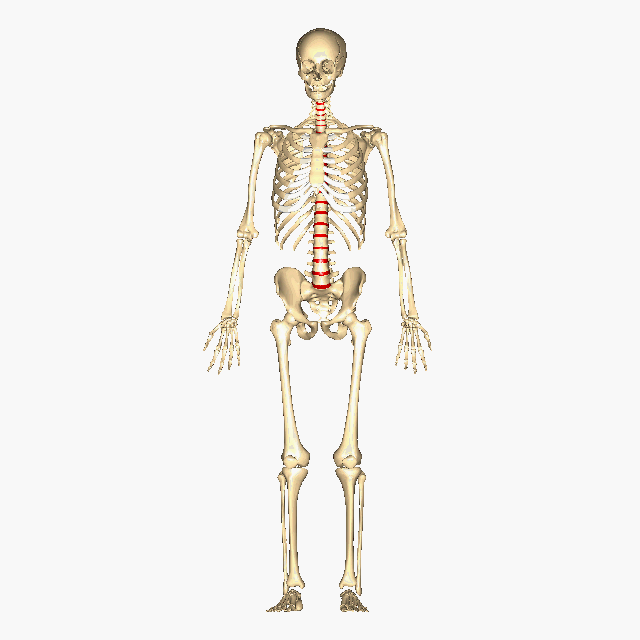
Above: The intervertebral discs containing fibrocartilage are shown in red (located between the vertebrae).
|
hyaline cartilage |
elastic cartilage |
fibrocartilage |
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
Microscopic image of tissue |
|
|
|
|
Characteristics of tissue |
|
|
|
|
Locations of tissue |
|
|
|
Attributions
- "Anatomy and Physiology Lab Reference" by Laird C Sheldahl, OpenOregonEducational Resources, Mt. Hood Community College is licensed under CC BY-SA 4.
- "BodyParts3D/Anatomography" by The Database Center for Life Science is licensed under CC BY-SA 2.1
- "Costal cartilages animation" by Anatomography is licensed under CC BY-SA 2.0
- "Intervertebral discs - close-up - animation" by Anatomography is licensed under CC BY-SA 2.0