Ireland 2019 Lecture 3
- Page ID
- 23973
Hydrogen Bonds
When hydrogen forms a polar covalent bond with an atom of higher electronegativity, the region around the hydrogen will have a fractional positive charge (termed δ+). When this fractional positive charge encounters a partial negative charge (termed δ-) from another electronegative atom to which the hydrogen is NOT bound, AND it is presented to that negative charge in a suitable orientation, a special kind of interaction called a hydrogen bond can form. While chemists are still debating the exact nature of the hydrogen bond, in BIS2A, we like to conceive of it as a weak electrostatic interaction between the δ+ of the hydrogen and the δ- charge on an electronegative atom. We call the molecule that contributes the partially charged hydrogen atom "the hydrogen bond donor" and the atom with the partial negative charge the "hydrogen bond acceptor." You will be asked to start learning to recognize common biological hydrogen bond donors and acceptors and to identify putative hydrogen bonds from models of molecular structures.
Hydrogen bonds are common in biology both within and between all types of biomolecules. Hydrogen bonds are also critical interactions between biomolecules and their solvent, water. It is common, as seen in the figure below, to represent hydrogen bonds in figures with dashed lines.
Figure 1: Two water molecules are depicted forming a hydrogen bond (drawn as a dashed blue line). The water molecule on top "donates" a partially charged hydrogen while the water molecule on the bottom accepts that partial charge by presenting a complementary negatively charged oxygen atom. Attribution: Marc T. Facciotti (original work)
Functional groups
A functional group is a specific group of atoms within a molecule that is responsible for a characteristic of that molecule. Many biologically active molecules contain one or more functional groups. In BIS2A, we will review the major functional groups found in biological molecules. These include the following: hydroxyl, methyl, carbonyl, carboxyl, amino, and phosphate (see Figure 1).

A functional group may participate in a variety of chemical reactions. Some of the important functional groups in biological molecules are shown above: hydroxyl, methyl, carbonyl, carboxyl, amino, phosphate, and sulfhydryl (not shown). These groups play an important role in the formation of molecules like DNA, proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids. Functional groups can sometimes be classified as having polar or nonpolar properties depending on their atomic composition and organization. The term polar describes something that has a property that is not symmetric about it—it can have different poles (more or less of something at different places). In the case of bonds and molecules, the property we care about is usually the distribution of electrons and therefore electric charge between the atoms. In a nonpolar bond or molecule, electrons and charge will be relatively evenly distributed. In a polar bond or molecule, electrons will tend to be more concentrated in some areas than others. An example of a nonpolar group is the methane molecule (see discussion in Bond Types Chapter for more detail). Among the polar functional groups is the carboxyl group found in amino acids, some amino acid side chains, and the fatty acids that form triglycerides and phospholipids.
Nonpolar functional groups
Methyl R-CH3
The methyl group is the only nonpolar functional group in our class list above. The methyl group consists of a carbon atom bound to three hydrogen atoms. In this class, we will treat these C-H bonds as effectively nonpolar covalent bonds (more on this in the Bond Types chapter). This means that methyl groups are unable to form hydrogen bonds and will not interact with polar compounds such as water.
The methyl groups highlighted above are found in a variety of biologically relevant compounds. In some cases, the compound can have a methyl group but still be a polar compound overall due to the presence of other functional groups with polar properties (see the discussion on polar functional groups below).
As we learn more about other functional groups, we will add to the list of nonpolar functional groups. Stay alert!
Polar functional groups
Hydroxyl R-OH
A hydroxyl (alcohol group) is an -OH group covalently bonded another atom. In biological molecules the hydroxyl group is often (but not always) found bound to a carbon atom, as depicted below. The oxygen atom is much more electronegative than either the hydrogen or the carbon, which will cause the electrons in the covalent bonds to spend more time around the oxygen than around the C or H. Therefore, the O-H and O-C bonds in the hydroxyl group will be polar covalent bonds. Figure 3 depicts the partial charges, δ+ and δ-, that are associated with the hydroxyl group.
Hydroxyl groups are very common in biological molecules. Hydroxyl groups appear on carbohydrates (A), on some amino acids (B), and on nucleic acids (C). Can you find any hydroxyl groups in the phospholipid in (D)?
Carboxyl R-COOH
Carboxylic acid is a combination of a carbonyl group and a hydroxyl group attached to the same carbon, resulting in new characteristics. The carboxyl group can ionize, which means it can act as an acid and release the hydrogen atom from the hydroxyl group as a free proton (H+). This results in a delocalized negative charge on the remaining oxygen atoms. Carboxyl groups can switch back and forth between protonated (R-COOH) and deprotonated (R-COO-) states depending on the pH of the solution.
The carboxyl group is very versatile. In its protonated state, it can form hydrogen bonds with other polar compounds. In its deprotonated state, it can form ionic bonds with other positively charged compounds. This will have several biological consequences that will be explored more when we discuss enzymes.
Can you identify all the carboxyl groups on the macromolecules shown above in Figure 5?
Amino R-NH3
The amino group consists of a nitrogen atom attached by single bonds to hydrogen atoms. An organic compound that contains an amino group is called an amine. Like oxygen, nitrogen is also more electronegative than both carbon and hydrogen, which results in the amino group displaying some polar character.
Amino groups can also act as bases, which means that the nitrogen atom can bond to a fourth hydrogen atom, as shown in Figure 6. Once this occurs, the nitrogen atom gains a positive charge and can now participate in ionic bonds.
Phosphate R-PO4-
A phosphate group is a phosphorus atom covalently bound to four oxygen atoms and contains one P=O bond and three P-O− bonds. The oxygen atoms are more electronegative than the phosphorous atom, resulting in polar covalent bonds. Therefore, these oxygen atoms are able to form hydrogen bonds with nearby hydrogen atoms that also have a δ+(hydrogen atoms bound to another electronegative atom). Phosphate groups also contain a negative charge and can participate in ionic bonds.
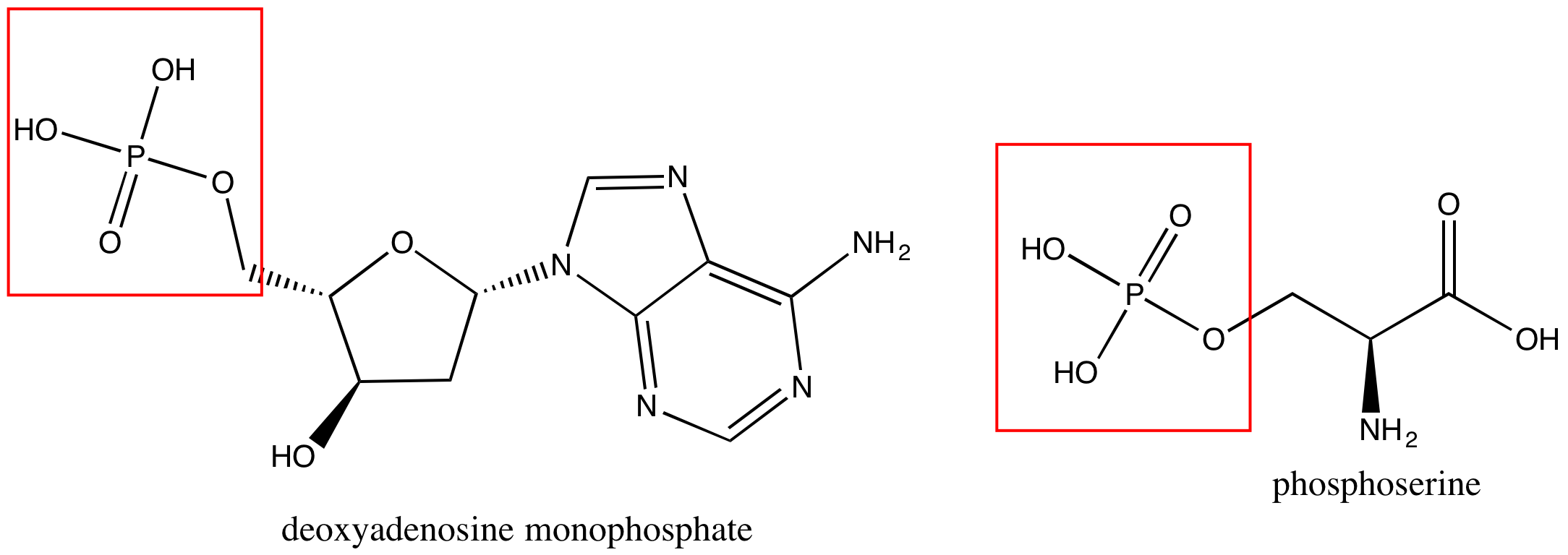
Phosphate groups are common in nucleic acids and on phospholipids (the term "phospho" referring to the phosphate group on the lipid). In Figure 7 are images of a nucleotide, deoxyadenosine monphosphate (left), and a phosphoserine (right).
Figure 7. A nucleotide, deoxyadenosine monphosphate, is on the left, and phosphoserine is on the right. Each has a phosphate group circled in red.
Attribution: created by Marc T. Facciotti (own work)
Water
Water is a unique substance whose special properties are intimately tied to the processes of life. Life originally evolved in a watery environment, and most of an organism’s cellular chemistry and metabolism occur inside the water-solvated contents of the cell. Water solvates or "wets" the cell and the molecules in it, plays a key role as reactant or product in an innumerable number of biochemical reactions, and mediates the interactions between molecules in and out of the cell. Many of water’s important properties derive from the molecule's polar nature, which can be tracked down to the polar molecules whose dipole originates from its polar covalent bonds between hydrogen and oxygen.
In BIS2A, the ubiquitous role of water in nearly all biological processes is easy to overlook by getting caught up in the details of specific processes, proteins, the roles of nucleic acids, and in your excitement for molecular machines (it'll happen). It turns out, however, that water plays key roles in all of those processes and we will need to continuously stay aware of the role that water is playing if we are to develop a more functional understanding. Be on the lookout and also pay attention when your instructor points this out.
In a liquid state, individual water molecule interact with one another through a network of dynamic hydrogen bonds that are being constantly forming and breaking. Water also interacts with other molecules that have charged functional groups and/or functional groups with hydrogen bond donors or acceptors. A substance with sufficient polar or charged character may dissolve or be highly miscible in water is referred to as being hydrophilic (hydro- = “water”; -philic = “loving”). By contrast, molecules with more nonpolar characters such as oils and fats do not interact well with water and separate from it rather than dissolve in it, as we see in salad dressings containing oil and vinegar (an acidic water solution). These nonpolar compounds are called hydrophobic (hydro- = “water”; -phobic = “fearing”). We will consider the some of the energetic components of these types of reactions in other another chapter.
Figure 1. In a liquid state water forms a dynamic network of hydrogen bonds between individual molecules. Shown are one donor-acceptor pair.
Attribution: Marc T. Facciotti (original work)
Water's solvent properties
Since water is a polar molecule with slightly positive and slightly negative charges, ions and polar molecules can readily dissolve in it. Therefore, water is referred to as a solvent, a substance capable of dissolving other polar molecules and ionic compounds. The charges associated with these molecules will form hydrogen bonds with water, surrounding the particle with water molecules. This is referred to as a sphere of hydration, or a hydration shell and serves to keep the particles separated or dispersed in the water.
When ionic compounds are added to water, the individual ions interact with the polar regions of the water molecules, and the ionic bonds are likely disrupted in the process called dissociation. Dissociation occurs when atoms or groups of atoms break off from molecules and form ions. Consider table salt (NaCl, or sodium chloride). A dry block of NaCl is held together by ionic bonds and is difficult to dissociate. When NaCl crystals are added to water, however, the molecules of NaCl dissociate into Na+ and Cl– ions, and spheres of hydration form around the ions. The positively charged sodium ion is surrounded by the partially negative charge of the water molecule’s oxygen. The negatively charged chloride ion is surrounded by the partially positive charge of the hydrogen on the water molecule. One may imagine a model in which the ionic bonds in the crystal are "traded" for many smaller scale ionic bonds with the polar groups on water molecules.
Figure 2. When table salt (NaCl) is mixed in water, spheres of hydration are formed around the ions. This figure depicts a sodium ion (dark blue sphere) and a chloride ion (light blue sphere) solvated in a "sea" of water. Note how the dipoles of the water molecules surrounding the ions are aligned such that complementary charges/partial charges are associating with one another (i.e., the partial positive charges on the water molecules align with the negative chloride ion whereas the partial negative charges on the oxygen of water align with the positively charged sodium ion).
Attribution: Ting Wang - UC Davis (original work modified by Marc T. Facciotti)
Note: possible discussion
Consider the model of water dissolving a salt crystal presented above. Describe in your own words how this model can be used to explain what is happening at the molecular level when enough salt is added to a volume of water that the salt no longer dissolves (the solution reaches saturation). Work together to craft a common picture.
Characteristic Chemical Reactions
Chemical reactions occur when two or more atoms bond together to form molecules or when bonded atoms are broken apart. The substances that "go in" to a chemical reaction are called the reactants (by convention, these are usually listed on the left side of a chemical equation), and the substances found that "come out" of the reaction are known as the products (by convention, these are usually found on the right side of a chemical equation). An arrow linking the reactants and products is typically drawn between them to indicate the direction of the chemical reaction. By convention, for one-way reactions (a.k.a. unidirectional), reactants are listed on the left and products on the right of the single-headed arrow. However, you should be able to identify reactants and products of unidirectional reactions that are written in any orientation (e.g. right-to-left; top-to-bottom, diagonal right-to-left, around a circular arrow, etc.) by using the arrow to orient yourself.
In chemical reactions, the atoms and elements present in the reactant(s) must all also be present in the product(s). Similarly, there can be nothing present in the products that was not present in the reactants. This is because chemical reactions are governed by the law of conservation of mass, which states that matter cannot be created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction. This means that when you examine a chemical reaction, you must try to account for everything that goes in AND make sure that you can find it all in the stuff that comes out!
Just as you can express mathematical calculations in equations such as 2 + 7 = 9, you can use chemical equations to show how reactants become products. By convention, chemical equations are typically read or written from left to right. Reactants on the left are separated from products on the right by a single- or double-headed arrow indicating the direction in which the chemical reaction proceeds. For example, the chemical reaction in which one atom of nitrogen and three atoms of hydrogen produce ammonia would be written as:
N + 3H → NH3.
Correspondingly, the breakdown of ammonia into its components would be written as:
NH3→ N + 3H.
Note that in either direction, you find 1 N and 3 Hs on both sides of the equation.
Reversibility
While all chemical reactions can technically proceed in both directions some reactions tend to favor one direction over the other. Depending on the degree to which a reaction spontaneously proceed in either both or one direction a different name can be given to characterize the reactions reversibility. Some chemical reactions, such as the one shown above, proceed mostly in one direction with the "reverse" direction happening on such long time scales or with such low probability that, for practical purposes, we ignore the "reverse" reaction. These unidirectional reactions are also called irreversible reactions and are depicted with a single-headed (unidirectional) arrow. By contrast, reversible reactions are those that can readily proceed in either direction. Reversible reactions are usually depicted by a chemical equation with a double-headed arrow pointing toward both the reactants and the products. In practice, you will find a continuum of chemical reactions; some proceed mostly in one direction and nearly never reverse, while others change direction easily depending on various factors like the relative concentrations of reactants and products. These terms are just ways of describing reactions with different equilibrium points.
Use of vocabulary
You may have realized that the terms "reactants" and "products" are relative to the direction of the reaction. If you have a reaction that is reversible, though, the products of running the reaction in one direction become the reactants of the reverse. You can label the same compound with two different terms. That can be a bit confusing. So, what is one to do in such cases? The answer is that if you want to use the terms "reactants" and "products", you must be clear about the direction of reaction that you are referring to - even for when discussing reversible reactions. The choice of terms, "reactants" or "products" that you use will communicate to others the directionality of the reaction that you are considering.
Let's look at an example of a reversible reaction in biology and discuss an important extension of these core ideas that arises in a biological system. In human blood, excess hydrogen ions (H+) bind to bicarbonate ions (HCO3-), forming an equilibrium state with carbonic acid (H2CO3). This reaction is readily reversible. If carbonic acid were added to this system, some of it would be converted to bicarbonate and hydrogen ions as the chemical system sought out equilibrium.
\[\ce{HCO_3^−+ H^+\rightleftharpoons H_2CO_3}\]
The example above examines and "idealized" chemical systems as it might occur in a test-tube. In biological systems, however, equilibrium for a single reaction is rarely reached as it might be in the test-tube. In biological systems, reactions do not occur in isolation. Rather, the concentrations of the reactants and/or products are constantly changing, often with a product of one reaction being a reactant for another reaction. These linked reactions form what are known as biochemical pathways. The immediate example below illustrates this point. While the reaction between the bicarbonate/proton and carbonic acid is highly reversible, it turns out that, physiologically, this reaction is usually "pulled" toward the formation of carbonic acid. Why? As shown below, carbonic acid becomes a reactant for another biochemical reaction—the conversion of carbonic acid to CO2 and H2O. This conversion reduces the concentration of H2CO3, thus pulling the reaction between bicarbonate and H+ to the right. Moreover, a third, unidirectional reaction, the removal of CO2 and H2O from the system, also pulls the reaction further to the right. These kinds of reactions are important contributors to maintaining the H+ homeostasis of our blood.
\[ \ce{HCO_3^- + H^+ \rightleftharpoons H_2CO_3 \rightleftharpoons CO_2 + H_20 \rightarrow} \text{ waste}\]
The reaction involving the synthesis of carbonic acid is actually linked to its breakdown into \(CO_2\) and \(H_2O\). These products are then removed from the system/body when they are exhaled. Together, the breakdown of carbonic acid and the act of exhaling the products pull the first reaction to the right.
What is the role of Acid/Base Chemistry in Bis2A?
We have learned that the behavior of chemical functional groups depends greatly on the composition, order and properties of their constituent atoms. As we will see, some of the properties of key biological functional groups can be altered depending on the pH (hydrogen ion concentration) of the solution that they are bathed in.
For example, some of the functional groups on the amino acid molecules that make up proteins can exist in different chemical states depending on the pH. We will learn that the chemical state of these functional groups in the context of a protein can have have a profound effect on the shape of protein or its ability to carry out chemical reactions. As we move through the course we will see numerous examples of this type of chemistry in different contexts.
pH is formally defined as:
\[ pH = -\log_{10} [H^+]\]
In the equation above, the square brackets surrounding \(H^+\) indicate concentration. If necessary, try a math review at wiki logarithm or kahn logarithm. Also see: concentration dictionary or wiki concentration.
Hydrogen ions are spontaneously generated in pure water by the dissociation (ionization) of a small percentage of water molecules into equal numbers of hydrogen (H+) ions and hydroxide (OH-) ions. While the hydroxide ions are kept in solution by their hydrogen bonding with other water molecules, the hydrogen ions, consisting of naked protons, are immediately attracted to un-ionized water molecules, forming hydronium ions (H30+).
Still, by convention, scientists refer to hydrogen ions and their concentration as if they were free in this state in liquid water. This is another example of a shortcut that we often take - it's easier to write H+ rather than H3O+. We just need to realize that this shortcut is being taken; otherwise confusion will ensue.
The pH of a solution is a measure of the concentration of hydrogen ions in a solution (or the number of hydronium ions). The number of hydrogen ions is a direct measure of how acidic or how basic a solution is.
The pH scale is logarithmic and ranges from 0 to 14 (Figure 2). We define pH=7.0 as neutral. Anything with a pH below 7.0 is termed acidic and any reported pH above 7.0 is termed alkaline or basic. Extremes in pH in either direction from 7.0 are usually considered inhospitable to life, although examples exist to the contrary. pH levels in the human body usually range between 6.8 and 7.4, except in the stomach where the pH is more acidic, typically between 1 and 2.
Figure 2: The pH scale ranging from acidic to basic with various biological compounds or substances that exist at that particular pH. Attribution: Marc T. Facciotti
For additional information:
Watch this video for an alternative explanation of pH and its logarithmic scale.
Relationship between the hydrogen ion (proton) concentration and pH
There is an inverse relationship the concentration of hydrogen ions (protons) and pH.
- The concentration of hydrogen ions dissociating from pure water is 1 × 10-7 moles H+ ions per liter of water.
- Reminder: One mole (mol) of a substance (which can be atoms, molecules, ions, etc), is defined as being equal to 6.02 x 1023 particles of the substance. Therefore, 1 mole of water is equal to 6.02 x 1023 water molecules.
- The pH is calculated as the negative of the base 10 logarithm of this unit of concentration. The log10 of 1 × 10-7 is -7.0, and the negative of this number yields a pH of 7.0, which is also known as neutral pH.
- Non-neutral pH readings result from dissolving acids or bases in water.
- High concentrations of hydrogen ions yields a low pH number.
- Low levels of hydrogen ions result in a high pH.
This inverse relationship between pH and the concentration of protons confuses many students - take the time to convince yourself that you "get it." Some students find it easier to think about the hydrogen ion concentration and then convert the result to pH; other students find it easier to think about the pH and then convert the result to the hydrogen ion concentration. Either method works as long as you don't get confused.
An acid is a substance that increases the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) in a solution, usually by having one of its hydrogen atoms dissociate. For example, we have learned that the carboxyl functional group is an acid. The hydrogen atom can dissociate from the oxygen atom resulting in a free proton and a negatively charged functional group. A base provides either hydroxide ions (OH–) or other negatively charged ions that combine with hydrogen ions, effectively reducing the H+ concentration in the solution and thereby raising the pH. In cases where the base releases hydroxide ions, these ions bind to free hydrogen ions, generating new water molecules. For example, we have learned that the amine functional group is a base. The nitrogen atom will accept hydrogen ions in solution, thereby reducing the number of hydrogen ions which raises the pH of the solution.
Additional pH resources
Here are some additional links on pH and pKa to help learn the material. Note that there is an additional module devoted to pKa.
ChemLibreText Links
Khan Academy Links
Simulations
pKa
NOTE: This section will be your first exposure to pKa in BIS2A. If you are struggling with the concept of pH, you should reread the section of pH to make sure you understand the inverse relationship between the pH and the hydrogen ion concentration before proceeding.
pKa is defined as the negative log10 of the dissociation constant of an acid, its Ka. Therefore, the pKa is a quantitative measure of how easily or how readily the acid gives up its proton [H+] in solution and thus a measure of the "strength" of the acid. Strong acids have a small pKa; weak acids have a larger pKa. This inverse relationship between pKa and the dissociation constant of an acid confuses many students - take the time to convince yourself that you "get it."
The most common acid we will talk about in BIS2A is the carboxylic acid functional group. These acids are typically weak acids, meaning that they only partially dissociate (into H+ cations and RCOO- anions) in neutral solution. HCl (hydrogen chloride) is a common strong acid, meaning that it will fully dissociate into H+ and Cl-.
Note that the key difference in the figure below between a strong acid or base and a weak acid or base is the single arrow (strong) versus a double arrow (weak). In the case of the single arrow you can interpret that by imagining that nearly all reactants have been converted into products. Moreover, it is difficult for the reaction to reverse backwards to a state where the protons are again associated with the molecule there were associated with before. In the case of a weak acid or base, the double-sided arrow can be interpreted by picturing a reaction in which:
- both forms of the conjugate acid or base (that is what we call the molecule that "holds" the proton - i.e. CH3OOH and CH3OO-, respectively in the figure) are present at the same time and
- the ratio of those two quantities can change easily by moving the reaction in either direction.
Figure 1. An example of strong acids and strong bases in their protonation and deprotonation states. The value of their pKa is shown on the left. Attribution: Marc T. Facciotti
Electronegativity plays a role in the strength of an acid. If we consider the hydroxyl group as an example, the greater electronegativity of the atom or atoms (indicated R) attached to the hydroxyl group in the acid R-O-H results in a weaker H-O bond, which is thus more readily ionized. This means that the pull on the electrons away from the hydrogen atom gets greater when the oxygen atom attached to the hydrogen atom is also attached to another electronegative atom. An example of this is HOCL. The electronegative Cl polarizes the H-O bond, weakening it and facilitating the ionization of the hydrogen. If we compare this to a weak acid where the oxygen is bound to a carbon atom (as in carboxylic acids) the oxygen is bound to the hydrogen and carbon atom. In this case, the oxygen is not bound to another electronegative atom. Thus the H-O bond is not further destabilized and the acid is considered a weak acid (it does not give up the proton as easily as a strong acid).
Figure 2. The strength of the acid can be determined by the electronegativity of the atom the oxygen is bound to. For example, the weak acid Acetic Acid, the oxygen is bound to carbon, an atom with low electronegativity. In the strong acid, Hypochlorous acid, the oxygen atom is bound to an even more electronegative Chloride atom.
Attribution: Erin Easlon
In Bis2A you are going to be asked to relate pH and pKa to each other when discussing the protonation state of an acid or base, for example, in amino acids. How can we use the information given in this module to answer the question: Will the functional groups on the amino acid Glutamate be protonated or deprotonated at a pH of 2, at a pH of 8, at a pH of 11?
In order to start answering this question we need to create a relationship between pH and pKa. The relationship between pKa and pH is mathematically represented by Henderson-Hasselbach equation shown below, where [A-] represents the deprotonated form of the acid and [HA] represents the protonated form of the acid.
Figure 3. The Henderson-Hasselbach equation
A solution to this equation is obtained by setting pH = pKa. In this case, log([A-] / [HA]) = 0, and [A-] / [HA] = 1. This means that when the pH is equal to the pKa there are equal amounts of protonated and deprotonated forms of the acid. For example, if the pKa of the acid is 4.75, at a pH of 4.75 that acid will exist as 50% protonated and 50% deprotonated. This also means that as the pH rises, more of the acid will be converted into the deprotonated state and at some point the pH will be so high that the majority of the acid will exist in the deprotonated state.
Figure 4. This graph depicts the protonation state of acetic acid as the pH changes. At a pH below the pKa, the acid is protonated. At a pH above the pKa the acid is deprotonated. If the pH equals the pKa, the acid is 50% protonated and 50% deprotonated. Attribution: Ivy Jose
Biomolecules: Proteins are composed of amino acids
Amino acids are the monomers that make up proteins. Each amino acid has the same core structure, which consists of a central carbon atom, also known as the alpha (α) carbon, bonded to an amino group (NH2), a carboxyl group (COOH), and a hydrogen atom. Every amino acid also has another atom or group of atoms bonded to the alpha carbon known alternately as the R group, the variable group or the side-chain.

Amino acids have a central asymmetric carbon to which an amino group, a carboxyl group, a hydrogen atom, and a side chain (R group) are attached.
Attribution: Marc T. Facciotti (own work)
Note: Possible discussion
Recall that one of the learning goals for this class is that you (a) be able to recognize, in a molecular diagram, the backbone of an amino acid and its side chain (R-group) and (b) that you be able to draw a generic amino acid. Make sure that you practice both. You should be able to recreate something like the figure above from memory (a good use of your sketchbook is to practice drawing this structure until you can do it with the crutch of a book or the internet).
Amino Acid R group
The amino acid R group is a term that refers to the variable group on each amino acid. The amino acid backbone is identical on all amino acids, the R groups are different on all amino acids. For the structure of each amino acid refer to the figure below.

There are 20 common amino acids found in proteins, each with a different R group (variant group) that determines its chemical nature. R-groups are circled in teal. Charges are assigned assuming pH ~6.0. The full name, three letter abbreviation and single letter abbreviations are all shown.
Attribution: Marc T. Facciotti (own work)
The amino acids are drawn at pH 6.0. Note that the carboxyl group (CO2-) and the amino groups (NH3+) have charges due to pKa of these functional groups at pH 6.0. You should also note that the R-groups of some of the amino acids carry a positive charge, some carry a negative charge, and some have no charge. The properties of the R groups give an amino acid specific chemical properties (acidic, basic, polar, or nonpolar). You should be familiar with most of the functional groups in the R groups by now.
The chemical properties associated with the whole collection of individual functional groups gives each amino acid R group unique chemical potential. For example, amino acids such as valine, methionine, and alanine are typically nonpolar or hydrophobic in nature, while amino acids such as serine and threonine are said to have polar character and possess hydrophilic side chains.
Note: Possible Discussion
Let's think about the relevance of having 20 different amino acids. If you were using biology to build proteins from scratch, how might it be useful if you had 10 more different amino acids at your disposal? By the way, this is actually happening in a variety of research labs - why would this be potentially useful?
Note: Practice
Using your knowledge of functional groups, try classifying each amino acid in the figure above as either having the tendency to be polar or nonpolar. Try to find other classification schemes and think make lists for yourself of the amino acids you would put into each group. You can also search the internet for amino acid classification schemes - you will notice that there are different ways of grouping these chemicals based on chemical properties. You may even find that there are contradictory schemes. Try to think about why this might be and apply your chemical logic to figuring out why certain classification schemes were adopted and why specific amino acids were placed in certain groups.
Amino Acids and pKa
In BIS2A, we will be looking at the protonation state and deprotonation state of amino acids. Amino acids contain multiple functional groups that can be acids or bases. Therefore their protonation/deprotonation status can be more complicated. Below is the relationship between the pH and pKa of the amino acid Glutamic Acid.
In this graph we can ask the question we posed earlier: Will the functional groups on the amino acid Glutamate be protonated or deprotonated at a pH of 2, at a pH of 8, at a pH of 11?
Figure 5. This graph depicts the protonation state of glutamate as the pH changes. At a pH below the pKa for each functional group on the amino acid, the functional group is protonated. At a pH above the pKa for the functional group it is deprotonated. If the pH equals the pKa, the functional group is 50% protonated and 50% deprotonated.
Attribution: Ivy Jose
Note: Possible discussion
- What is the overall charge of free Glutamate at a pH of 5?
- What is the overall charge of free Glutamate at a pH of 10?
Common reactions to make or break macromolecules
Synthesis reactions
Many macromolecules are made from smaller subunits, or building blocks, called monomers. Monomers covalently link to form larger molecules known as polymers. Often, the synthesis of polymers from monomers will also produce water molecules as products of the reaction. This type of reaction is known as dehydration synthesis or condensation reaction.
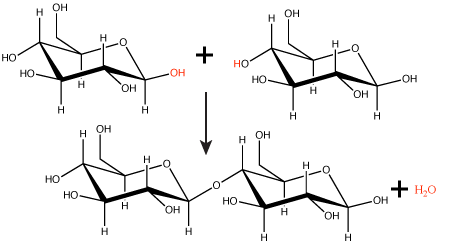
Figure 1. In the dehydration synthesis reaction depicted above, two molecules of glucose are linked together to form the disaccharide maltose. In the process, a water molecule is formed. Attribution: Marc T. Facciotti (original work)
In a dehydration synthesis reaction (Figure 1), the hydrogen of one monomer combines with the hydroxyl group of another monomer, releasing a molecule of water. At the same time, the monomers share electrons and form covalent bonds. As additional monomers join, this chain of repeating monomers forms a polymer. Different types of monomers can combine in many configurations, giving rise to a diverse group of macromolecules. Even one kind of monomer can combine in a variety of ways to form several different polymers; for example, glucose monomers are the constituents of starch, glycogen, and cellulose.
In the carbohydrate monomer example above, the polymer is formed by a dehydration reaction; this type of reaction is also used to add amino acids to a growing peptide chain and nucleotides to the growing DNA or RNA polymer. Visit the modules on Amino Acids, Lipids, and Nucleic Acids to see if you can identify the water molecules that are removed when a monomer is added to the growing polymer.
![]()
Figure 2. This depicts, using words, (decorated with functional groups colored in red) a generic dehydration synthesis/condensation reaction. Attribution: Marc T. Facciotti (original work)
Hydrolysis reactions
Polymers are broken down into monomers in a reaction known as hydrolysis. A hydrolysis reaction includes a water molecule as a reactant (Figure 3). During these reactions, a polymer can be broken into two components: one product carries a hydrogen ion (H+) from the water, while the second product carries the water's remaining hydroxide (OH–).
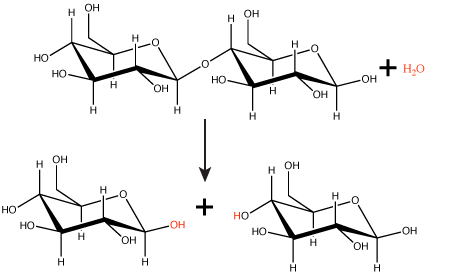
Figure 3. In the hydrolysis reaction shown here, the disaccharide maltose is broken down to form two glucose monomers with the addition of a water molecule. Note that this reaction is the reverse of the synthesis reaction shown in Figure 1 above. Attribution: Marc T. Facciotti (original work)
![]()
Figure 4. This depicts using words (decorated with functional groups colored in red) a generic hydrolysis reaction. Attribution: Marc T. Facciotti (original work)
Dehydration synthesis and hydrolysis reactions are catalyzed, or “sped up,” by specific enzymes. Note that both dehydration synthesis and hydrolysis reactions involve the making and breaking of bonds between the reactants—a reorganization of the bonds between the atoms in the reactants. In biological systems (our bodies included), food in the form of molecular polymers is hydrolyzed into smaller molecules by water via enzyme-catalyzed reactions in the digestive system. This allows for the smaller nutrients to be absorbed and reused for a variety of purposes. In the cell, monomers derived from food may then be reassembled into larger polymers that serve new functions.
Helpful links:
Visit this site to see visual representations of dehydration synthesis and hydrolysis.
Example of Hydrolysis with Enzyme Action is shown in this 3 minute video entitled: Hydrolysis of Sucrose by Sucrase.
Exchange/transfer reactions
We will also encounter reactions termed exchange reactions. In these types of reactions, "parts" of molecules are transferred between one another—bonds are broken to release a part of a molecule and bonds are formed between the released part and another molecule. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions are usually reasonably complex multi-step chemical processes.

Figure 5. An exchange reaction in which both synthesis and hydrolysis can occur, chemical bonds are both formed and broken, is depicted using a word analogy.
Amino Acids are used to make proteins
The name "amino acid" is derived from the fact that all amino acids contain both an amino group and carboxyl-acid-group in their backbone. There are 20 common amino acids present in natural proteins and each of these contain the same backbone. The backbone, when ignoring the hydrogen atoms, consists of the pattern:
N-C-C
When looking at a chain of amino acids it is always helpful to first orient yourself by finding this backbone pattern starting from the N terminus (the amino end of the first amino acid) to the C terminus (the carboxylic acid end of the last amino acid).

Peptide bond formation is a dehydration synthesis reaction. The carboxyl group of the first amino acid is linked to the amino group of the second incoming amino acid. In the process, a molecule of water is released and a peptide bond is formed.
Try finding the backbone in the dipeptide formed from this reaction. The pattern you are looking for is: N-C-C-N-C-C
Attribution: Marc T. Facciotti (own work)
The sequence and the number of amino acids ultimately determine the protein's shape, size, and function. Each amino acid is attached to another amino acid by a covalent bond, known as a peptide bond, which is formed by a dehydration synthesis (condensation) reaction. The carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amino group of the incoming amino acid combine, releasing a molecule of water and creating the peptide bond.
Proteins
Proteins are class of biomolecules that perform a wide array of functions in biological systems. Some proteins serve as catalysts for specific biochemical reactions. Other proteins act as signaling molecules that allow cells to "talk" with one another. Proteins, like the keratin in fingernails, can also act in a structural capacity. While the variety of possible functions for proteins is remarkably diverse, all of these functions are encoded by a linear assembly of amino acids, each connected to their neighbor via a peptide bond. The unique composition (types of amino acids and the number of each) and the order in which they are linked together determine the final three dimensional form that the protein will adopt and therefore, also the protein's biological "function". Many proteins can, in a cellular environment, spontaneously and often rapidly take on their final form in a process called protein folding. To watch a short (four minutes) introduction video on protein structure click here.
Protein structure
Protein structures can be described by four different levels of structural organization called primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structures. These are briefly introduced in the sections that follow.
Primary structure
The unique sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain is its primary structure (Figure 1). The amino acids in this chain are linked to one another other via a series of peptide bonds. The chain of amino acids is often referred to as a polypeptide (multiple peptides).
Due to the common backbone structure of amino acids, the resulting backbone of the protein has a repeating -N-Cα-C-N-Cα-C- pattern that can be readily identified in atomic resolution models of protein structures (Figure 2). Be aware that one of the learning goals for this class is for you to be able to examine a model like the one below and to identify the backbone from the side chain atoms (e.g. create the purple trace and blue shading if there aren't any). This can be done by finding the -N-Cα-C-N-Cα-C- pattern. Moreover, another learning goal for this class is that you are able to create drawings that model the structure of a typical protein backbone and its side chains (aka. variable group, R group). This task can be greatly simplified if you remember to start your model by first creating the -N-Cα-C-N-Cα-C- pattern and then filling in the variable groups.

Secondary structure
Due to the specific chemistry of the peptide bond the backbone between adjacent alpha-carbon atoms forms a highly planar structure (Figure 3). This means that all of the atoms linked by the pink quadrilateral lie on the same plane. The polypeptide is therefore structurally constrained since very little rotation can happen around the peptide bond itself. Rather, rotations occur around the two bonds extending away from the alpha carbons. These structural constraints lead to two commonly observed patterns of structure that are associated with the organization of the backbone itself.
We call these patterns of backbone structure the secondary structure of the protein. The most common secondary structure patterns occurring via rotations of the bonds around each alpha-carbon, are the α-helix, β-sheet and loop structures. As the name suggests, the α-helix is characterized by a helical structure made by twisting the backbone. The β-sheet is actually the association between two or more structures called β-strands. If the orientation (N-terminus to C-terminus direction) of two associating β-strands are oriented in the same/parallel direction, the resulting β-sheet is called a parallel β-sheet. Meanwhile, if two associating β-strands are oriented in opposite/anti-parallel directions, the resulting β-sheet is called an anti-parallel β-sheet. The α-helix and β-sheet are both stabilized by hydrogen bonds that form between backbones atoms of amino acids in close proximity to one another. More specifically, the oxygen atom in the carbonyl group from one amino acid can form a hydrogen bond with a hydrogen atom bound to the nitrogen in the amino group of another amino acid. Loop structures by contrast refer to all secondary structure (e.g. backbone structure) that can not be identified as either α-helix or β-sheet.
Tertiary structure
The backbone and secondary structure elements will further fold into a unique and relatively stable three-dimensional structure called the tertiary structure of the protein. The tertiary structure is what we typically associate with the "functional" form of a protein. In Figure 6 two examples of tertiary structure are shown. In both structures, the protein is abstracted into a "cartoon" that depicts the polypeptide chain as a single continuous line or ribbon tracing the path between alpha carbons of amino acids linked to one another by peptide bonds - the ribbon traces the backbone of the protein (Figure 5).

The ribbon created by joining alpha-carbons can be drawn as a simple continuous line or it can be enhanced by uniquely representing secondary structural elements. For instance, when an α-helix is identified, the helix is usually highlighted by accentuating/broadening the ribbon to make the helical structure stand out. When a β-strand is present, the ribbon is usually broadened and an arrow is typically added to the C-terminal end of each β-strand - the arrow helps to identify the orientation of the polypeptide and whether β-sheets are parallel or anti-parallel. The thin ribbon connecting α-helix and β-strand elements is used to represent the loops. Loops in proteins can be highly structured and play an important role in the protein's function. They should not be treated lightly or dismissed as unimportant because their name lacks a Greek letter.

Attribution: Marc T. Facciotti (own work)
The tertiary structure is the product of many different types of chemical interactions among amino acid R groups, backbone atoms, ions in solution and water. These bonds include ionic, covalent, and hydrogen bonds and Van der Waals interactions. For example, ionic bonds may form between various ionizable side chains. It may, for instance, be energetically favorable for a negatively charged R group (e.g. an Aspartate) to interact with a positively charged R group (e.g. an Arginine). The resulting ionic interaction may then become part of the network of interactions that helps to stabilize the three dimensional fold of the protein. By contrast, R groups with like charges will likely be repelled by each other and be therefore unlikely to form a stable association thereby disfavoring a structure that would include that association. Likewise, hydrogen bonds may form between various R groups or between R groups and backbone atoms. These hydrogen bonds may also contribute to stabilizing the tertiary structure of the protein. In some cases covalent bonds may also form between amino acids. The most commonly observed covalent linkage between amino acids involves two cysteines and is termed a disulfide bond or disulfide linkage.
Finally, the association of the protein's functional groups with water also helps to drive chemical associations that help to stabilize the final protein structure. The interactions with water can, of course, include the formation of hydrogen bonds between polar functional groups on the protein and water molecules. Perhaps more importantly, however, is the drive for the protein to avoid placing too many hydrophobic functional groups in contact with water. The result of this desire to avoid interactions between water and hydrophobic functional groups means that the less polar side chains will often associate with one another away from water resulting in some energetically favorable Van der Waals interactions and the avoidance of energetic penalties associated with exposing the non-polar side chains to water. Indeed, the energetic penalty is so high for "exposing" the non-polar side chains to water that burying these groups away from water is thought to be one of the primary energetic drivers of protein folding and stabilizing forces holding the protein together in its tertiary structure.
Quaternary structure
In nature, the functional forms of some proteins are formed by the close association of several polypeptides. In such cases the individual polypeptides are also known as subunits. When the functional form of a protein requires the assembly of two or more subunits we call this level of structural organization the protein's quaternary structure. Yet again, combinations of ionic, hydrogen, and covalent bonds together with Van der Waals associations that occur through the "burial" of hydrophobic group at the interfaces between subunits help to stabilize the quaternary structures of proteins.
Tags recommended by the template: article:topic