Amino Acids#
- Page ID
- 21257
Amino Acids
Amino acids are the monomers that make up proteins. Each amino acid has the same core structure, which comprises a central carbon atom, also known as the alpha (

Amino acids have a central asymmetric carbon to which an amino group, a carboxyl group, a hydrogen atom, and a side chain (R group)
Attribution:
The Amino Acid Backbone
The name "amino acid" derives from the fact that all amino acids contain both an amino group and carboxyl-acid-group in their backbone. There are 20 common amino acids present in natural proteins and each of these contain the same backbone. The backbone, when ignoring the hydrogen atoms, comprises the pattern:
N-C-C
When looking at a chain of amino acids it is always helpful to first orient yourself by finding this backbone pattern starting from the N terminus (the amino end of the first amino acid) to the C terminus (the carboxylic acid end of the last amino acid).
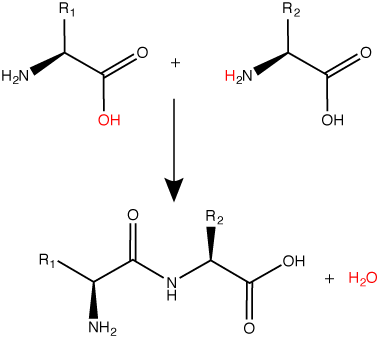
Peptide bond formation is a dehydration synthesis reaction.
Try finding the backbone in the dipeptide formed from this reaction. The pattern you are looking for
Attribution:
The sequence and the number of amino acids ultimately determine the protein's shape, size, and function.
Amino Acid R group
The amino acid R group is a term that refers to the variable group on each amino acid. The amino acid backbone is identical on all amino acids, the R groups are different on all amino acids. For the structure of each amino acid refer to the figure below.

There are 20 common amino acids found in proteins, each with a different R group (variant group) that determines its chemical nature. R-groups
Attribution:
| Glycine | Glutamate | Tryptophan |
Each variable group on an amino acid gives that amino acid specific chemical properties (acidic, basic, polar, or nonpolar). You should be familiar with most of the functional groups in the R groups by now. The chemical properties associated with the whole collection of individual functional groups gives each amino acid R group unique chemical potential.
For example, amino acids such as valine, methionine, and alanine are typically nonpolar or hydrophobic in nature, while amino acids such as serine and threonine are said to have polar character and possess hydrophilic side chains.


