15.1.2.2.1: Streptococcus pneumoniae
- Page ID
- 42658
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \) \( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)\(\newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\) \( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\) \( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \(\newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\) \( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\) \( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)\(\newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
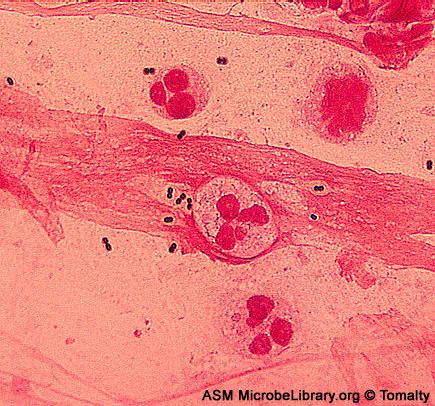
Encapsulated Streptococcus pneumoniae. Encapsulated Streptococcus pneumoniae. © Gloria Delisle and Lewis Tomalty, authors. Licensed for use, ASM MicrobeLibrary.
Organism
- Streptococcus pneumoniae, or the pneumococcus, is a gram-positive coccus usually appearing as a diplococcus, but occasionally appearing singularly or in short chains. Cocci are slightly pointed or "lancet-shaped".
- Encapsulated and non-motile
- Catalase negative
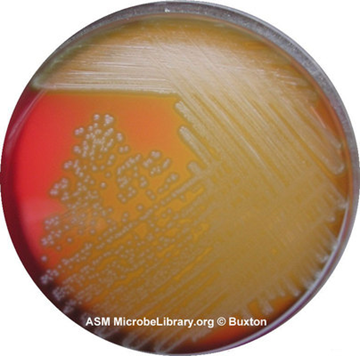
- Alpha-hemolytic (Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\))
- Uses lactic acid fermentation
- Aerotolerant anaerobe (cannot aerobically respire, prefers anaerobic or low-oxygen environment)
- Commonly known as the pneumococcus
Habitat
- Frequently found as normal flora of the nasopharynx of healthy carriers. From 10% to 40% of adults carry the bacterium in the nasopharynx.
Source
- Can be infected by own flora (endogenous infection) or from respiratory droplets of an infected individual (exogenous infection)
Epidemiology
- In the U.S., they are the most common cause of community-acquired pneumonia requiring hospitalization, causing around 500,000 cases per year and usually occurring as a secondary infection in the debilitated or immunocompromised host. The pneumococci also cause over 7,000,000 cases of otitis media per year, are the leading cause of sinusitis in people of all ages, are responsible for 500,000 cases of bacteremia, and 3000 cases of meningitis, being the most common cause of meningitis in adults and children over 4 years of age.
Clinical Disease
- Cause of multiple diseases:
- Pneumonia
- 85% of all cases of pneumonia
- Symptoms: severe shaking chills, fever of 39-41 degrees Celcius, productive cough, slightly bloody sputum, chest pain
- Otitis media (ear infection)
- Sinusitis
- Bacteremia and endocarditis
- Meningitis (one of the three major causes of bacterial meningitis, the others being N. meningitidis and H. influenzae)
- primarily in children
- mortality rate 20 times higher than other forms of meningitis
- Pneumonia
- Can be treated with antibiotics (beta-lactams, erythromycin, chloramphenicol)
- Effective vaccine available (pneumococcal vaccine; purified capsule of 23 most common pathogenic strains)
Primary Virulence Factors
- Polysaccharide capsule: prevents phagocytosis
- Pili: attachment
- Cell wall components are highly inflammatory
- Exotoxin pneumolysin lyses cells of respiratory tract
- Exoenzymes:
- IgA protease: destroys antibodies
- Neuraminidase: breaks down mucus to allow the bacterium access to host tissue
Additional information: http://textbookofbacteriology.net/S.pneumoniae_1.html

