4.14: Buffers
- Page ID
- 43521
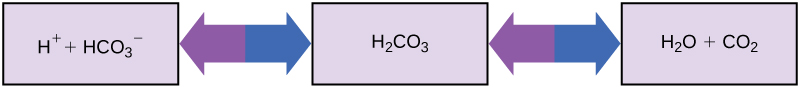
So how can organisms whose bodies require a near-neutral pH ingest acidic and basic substances (a human drinking orange juice, for example) and survive? Buffers are the key. Buffers readily absorb excess H+ or OH–, keeping the pH of the body carefully maintained in the narrow range required for survival. Maintaining a constant blood pH is critical to a person’s well-being. The buffer maintaining the pH of human blood involves carbonic acid (H2CO3), bicarbonate ion (HCO3–), and carbon dioxide (CO2). When bicarbonate ions combine with free hydrogen ions and become carbonic acid, hydrogen ions are removed, moderating pH changes. Similarly, as shown in Figure 1, excess carbonic acid can be converted to carbon dioxide gas and exhaled through the lungs. This prevents too many free hydrogen ions from building up in the blood and dangerously reducing the blood’s pH. Likewise, if too much OH– is introduced into the system, carbonic acid will combine with it to create bicarbonate, lowering the pH. Without this buffer system, the body’s pH would fluctuate enough to put survival in jeopardy.
Other examples of buffers are antacids used to combat excess stomach acid. Many of these over-the-counter medications work in the same way as blood buffers, usually with at least one ion capable of absorbing hydrogen and moderating pH, bringing relief to those that suffer “heartburn” after eating. The unique properties of water that contribute to this capacity to balance pH—as well as water’s other characteristics—are essential to sustaining life on Earth.
In Summary: Buffers
The pH scale is a measure of acidity/alkalinity and provides information about how substances tend to act in aqueous solutions. All living processes occur in an ideal pH range. Buffers act together to keep the pH within a certain range, based off the release or absorption of hydrogen ions.
Contributors and Attributions
- Biology. Provided by: OpenStax CNX. Located at: http://cnx.org/contents/185cbf87-c72e-48f5-b51e-f14f21b5eabd@10.8. License: CC BY: Attribution. License Terms: Download for free at http://cnx.org/contents/185cbf87-c72...f21b5eabd@10.8

