9.10: Basidiomycota- The Club Fungi
- Page ID
- 43904

The fungi in the Phylum Basidiomycota are easily recognizable under a light microscope by their club-shaped fruiting bodies called basidia (singular, basidium), which are the swollen terminal cell of a hypha. The basidia, which are the reproductive organs of these fungi, are often contained within the familiar mushroom, commonly seen in fields after rain, on the supermarket shelves, and growing on your lawn. The fruiting bodies of a basidiomycete form a ring in a meadow, commonly called “fairy ring” (Figure 1). The best-known fairy ring fungus has the scientific name Marasmius oreades. The body of this fungus, its mycelium, is underground and grows outward in a circle. As it grows, the mycelium depletes the soil of nitrogen, causing the mycelia to grow away from the center and leading to the “fairy ring” of fruiting bodies where there is adequate soil nitrogen.
These mushroom-producing basidiomyces are sometimes referred to as “gill fungi” because of the presence of gill-like structures on the underside of the cap. The “gills” are actually compacted hyphae on which the basidia are borne. This group also includes shelf fungus, which cling to the bark of trees like small shelves. In addition, the basidiomycota includes smuts and rusts, which are important plant pathogens, and toadstools. Most edible fungi belong to the Phylum Basidiomycota; however, some basidiomycetes produce deadly toxins. For example, Cryptococcus neoformans causes severe respiratory illness.
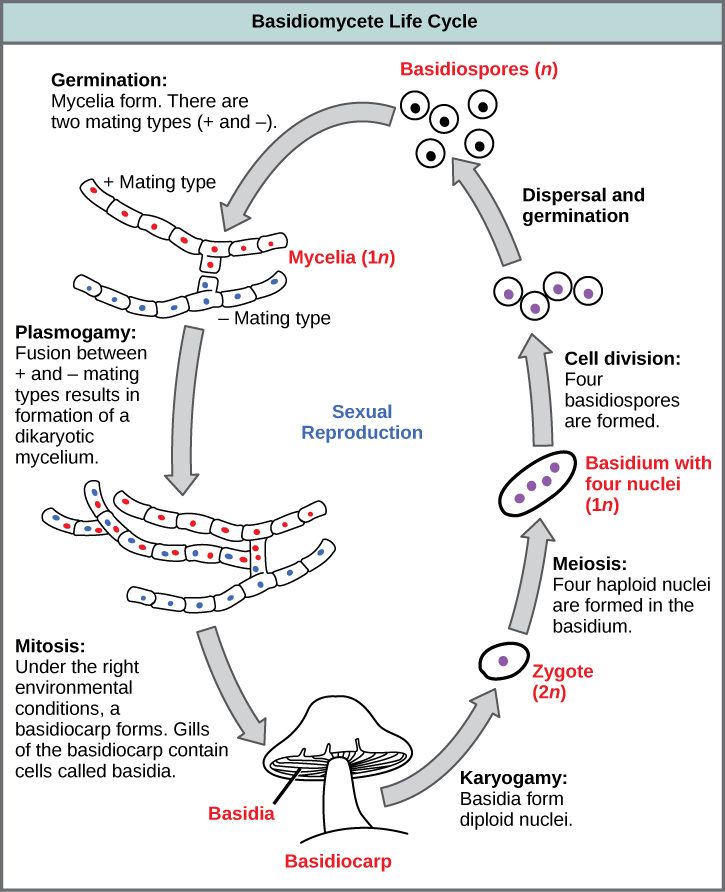
The lifecycle of basidiomycetes includes alternation of generations (Figure 2). Spores are generally produced through sexual reproduction, rather than asexual reproduction. The club-shaped basidium carries spores called basidiospores. In the basidium, nuclei of two different mating strains fuse (karyogamy), giving rise to a diploid zygote that then undergoes meiosis. The haploid nuclei migrate into basidiospores, which germinate and generate monokaryotic hyphae. The mycelium that results is called a primary mycelium. Mycelia of different mating strains can combine and produce a secondary mycelium that contains haploid nuclei of two different mating strains. This is the dikaryotic stage of the basidiomyces lifecyle and and it is the dominant stage. Eventually, the secondary mycelium generates a basidiocarp, which is a fruiting body that protrudes from the ground—this is what we think of as a mushroom. The basidiocarp bears the developing basidia on the gills under its cap.
Practice Question
Which of the following statements is true?
- A basidium is the fruiting body of a mushroom-producing fungus, and it forms four basidiocarps.
- The result of the plasmogamy step is four basidiospores.
- Karyogamy results directly in the formation of mycelia.
- A basidiocarp is the fruiting body of a mushroom-producing fungus.
[reveal-answer q=”197947″]Show Answer[/reveal-answer]
[hidden-answer a=”197947″]Statement d is true.[/hidden-answer]
Contributors and Attributions
- Biology. Provided by: OpenStax CNX. Located at: http://cnx.org/contents/185cbf87-c72e-48f5-b51e-f14f21b5eabd@10.8. License: CC BY: Attribution. License Terms: Download for free at http://cnx.org/contents/185cbf87-c72...f21b5eabd@10.8

